THE CELL MEMBRANE - Mrs. Guida's AP Biology Class
... • Diffusion rate depends on the amount of available receptors • Can reach saturation • Specific to certain molecules or ions • Found in RBCs (glucose and Chloride HCO3) ...
... • Diffusion rate depends on the amount of available receptors • Can reach saturation • Specific to certain molecules or ions • Found in RBCs (glucose and Chloride HCO3) ...
Structure and Function of the Cell
... What are the seven basic characteristics of living organisms?(pg 6-9) ...
... What are the seven basic characteristics of living organisms?(pg 6-9) ...
Assessment Test
... 2) All of the following are true concerning enzymes, except that they A. affect only the rate of a chemical reaction B. lower the activation energy required for a reaction C. function as biological catalysts D. are proteins E. are consumed during the reaction 3) During ionization, water molecules di ...
... 2) All of the following are true concerning enzymes, except that they A. affect only the rate of a chemical reaction B. lower the activation energy required for a reaction C. function as biological catalysts D. are proteins E. are consumed during the reaction 3) During ionization, water molecules di ...
Lecture #3 Date
... Nucleoid: DNA concentration No organelles with membranes Ribosomes: protein synthesis Plasma membrane (all cells); semi-permeable Cytoplasm/cytosol (all cells) ...
... Nucleoid: DNA concentration No organelles with membranes Ribosomes: protein synthesis Plasma membrane (all cells); semi-permeable Cytoplasm/cytosol (all cells) ...
Plasma Membrane
... • Thin, flexible boundary between a cell and its environment. Allows nutrients in and allows waste to leave cell • Plasma membranes have Selective permeability: allows some substances to pass through while keeping others out. • A cell membrane is called a fluid mosaic because it behaves more like a ...
... • Thin, flexible boundary between a cell and its environment. Allows nutrients in and allows waste to leave cell • Plasma membranes have Selective permeability: allows some substances to pass through while keeping others out. • A cell membrane is called a fluid mosaic because it behaves more like a ...
Plant Cell
... Rough ER is important in the synthesis of other proteins. At the ribosomes on the rough ER, the messenger RNA is translated into proteins Smooth ER is important in the synthesis of lipids and membrane proteins ...
... Rough ER is important in the synthesis of other proteins. At the ribosomes on the rough ER, the messenger RNA is translated into proteins Smooth ER is important in the synthesis of lipids and membrane proteins ...
Document
... cytoplasm is the term for all material located between the cell membrane and nucleus. Potassium ion concentration is higher in cytoplasm than in cytosol. Cytosol and cytoplasm refer to the same substance. ...
... cytoplasm is the term for all material located between the cell membrane and nucleus. Potassium ion concentration is higher in cytoplasm than in cytosol. Cytosol and cytoplasm refer to the same substance. ...
Chapter 3 - FacultyWeb
... cytoplasm is the term for all material located between the cell membrane and nucleus. Potassium ion concentration is higher in cytoplasm than in cytosol. Cytosol and cytoplasm refer to the same substance. ...
... cytoplasm is the term for all material located between the cell membrane and nucleus. Potassium ion concentration is higher in cytoplasm than in cytosol. Cytosol and cytoplasm refer to the same substance. ...
Keyword/concepts: Definition: Darwin Charles Darwin theorised
... Interior of the cell. The cytosol and organelles of eukaryotic cells, excluding the nucleus. ...
... Interior of the cell. The cytosol and organelles of eukaryotic cells, excluding the nucleus. ...
Cells and Microscope Test Study Guide
... Use your notes and handouts to help you study! Know different parts of cell and function of each part (what it does) Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Vacuole Mitochondria Chloroplast Cell wall Understand that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things Know what make ...
... Use your notes and handouts to help you study! Know different parts of cell and function of each part (what it does) Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Vacuole Mitochondria Chloroplast Cell wall Understand that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things Know what make ...
cell_structure_tt
... Chemicals made in endocrine glands that are carried in the blood to target cells/tissues/organs. They act as chemical messengers and are associated with developmental changes of the organism. Most are polypeptides but some are ...
... Chemicals made in endocrine glands that are carried in the blood to target cells/tissues/organs. They act as chemical messengers and are associated with developmental changes of the organism. Most are polypeptides but some are ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... Makes proteins by combining amino acids through condensation reactions ...
... Makes proteins by combining amino acids through condensation reactions ...
Microsoft PowerPoint 97-2004 presentation
... What is the difference between resolution and magnification? ...
... What is the difference between resolution and magnification? ...
S3O1 Curr Map
... Plant cells have a cell membrane and a cell wall. They have green chloroplasts. They are regular in shape, boxlike. Animals cells vary in shape because they do not have cell walls. The flexible cell membrane holds them together. They lack chloroplasts. Diffusion is the movement of atoms and molecule ...
... Plant cells have a cell membrane and a cell wall. They have green chloroplasts. They are regular in shape, boxlike. Animals cells vary in shape because they do not have cell walls. The flexible cell membrane holds them together. They lack chloroplasts. Diffusion is the movement of atoms and molecule ...
Biology First Semester Final Exam REVIEW #2 Name: Pd:_____
... 19. First to view living pond animals which he called “animalcules.” __________________________________ 20. Concluded that all animals are made of cells: _________________________________ 21. Concluded that all plants are made of cells:__________________________________ 22. The smallest part of life ...
... 19. First to view living pond animals which he called “animalcules.” __________________________________ 20. Concluded that all animals are made of cells: _________________________________ 21. Concluded that all plants are made of cells:__________________________________ 22. The smallest part of life ...
TRANSPORT
... State of matter (gas-fast, liquid-slow) Concentration gradient (steep-fast, gentleslow) – Distance involved (short-fast, long-slow) – Surface Area involved (large-fast, smallslow) ...
... State of matter (gas-fast, liquid-slow) Concentration gradient (steep-fast, gentleslow) – Distance involved (short-fast, long-slow) – Surface Area involved (large-fast, smallslow) ...
Organelles Cheat Sheet
... - Composes 25% of cell's mass - Stationary type: embedded in rough endoplasmic reticulum - Mobile type: injects proteins directly into cytoplasm ...
... - Composes 25% of cell's mass - Stationary type: embedded in rough endoplasmic reticulum - Mobile type: injects proteins directly into cytoplasm ...
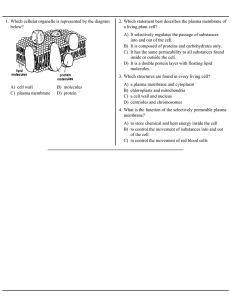
A) cell wall B) molecules C) plasma membrane D) protein 1. Which
... 1. Which cellular organelle is represented by the diagram below? ...
... 1. Which cellular organelle is represented by the diagram below? ...
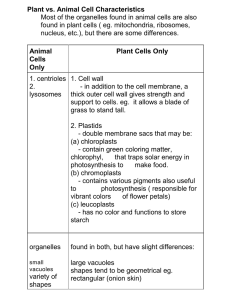
Plant vs. Animal Cell Characteristics Most of the organelles found in
... Plant vs. Animal Cell Characteristics Most of the organelles found in animal cells are also found in plant cells ( eg. mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus, etc.), but there are some differences. Animal Cells Only ...
... Plant vs. Animal Cell Characteristics Most of the organelles found in animal cells are also found in plant cells ( eg. mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus, etc.), but there are some differences. Animal Cells Only ...
The Magic Universe of Cells Directions
... draw, label, and define the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. You need to include at least: nucleus, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, vacuoles, centrioles, lysosomes, nuclear envelope, and chromatin. If there is ...
... draw, label, and define the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. You need to include at least: nucleus, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, vacuoles, centrioles, lysosomes, nuclear envelope, and chromatin. If there is ...
Unit 2 Cells Test Study Guide
... cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, vacuole, nucleus, nuclear membrane, chromosomes, chloroplasts, mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, and ribosomes. b. What are the differences between an animal cell and a plant cell? List not only the parts of the cells that are differen ...
... cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, vacuole, nucleus, nuclear membrane, chromosomes, chloroplasts, mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, and ribosomes. b. What are the differences between an animal cell and a plant cell? List not only the parts of the cells that are differen ...
Centrioles are self-replicating organelles made up
... proteins and fats built in the endoplasmic reticulum and prepares them for export to the outside of the cell. Lysosomes - The main function of these microbodies is digestion. Lysosomes break down cellular waste products and debris from outside the cell into simple compounds, which are transferred to ...
... proteins and fats built in the endoplasmic reticulum and prepares them for export to the outside of the cell. Lysosomes - The main function of these microbodies is digestion. Lysosomes break down cellular waste products and debris from outside the cell into simple compounds, which are transferred to ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.