STAAR Review, Friday, Jan 20
... b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. c. New cells are produced only from existing cells. Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells A. Both have a. Cell membranes b. Cytoplasm c. Contain ribosomes d. DNA B. Major differences a. Eukaryotes are more complex and larger in size ...
... b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. c. New cells are produced only from existing cells. Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells A. Both have a. Cell membranes b. Cytoplasm c. Contain ribosomes d. DNA B. Major differences a. Eukaryotes are more complex and larger in size ...
Cell Review Cell Theory Levels of Organization Organelle
... 9. Mitochondria – Eats protein to make energy (ATP) for the cell. (Powerhouse) 1. Nucleus – Command center of the cell. (Receives and sends messages) 6. Cell Membrane – Barrier of protection for the cell (Allows nutrients in and waste out) 8. Vacuole – Stores water and waste. 4. Chloroplasts – Makes ...
... 9. Mitochondria – Eats protein to make energy (ATP) for the cell. (Powerhouse) 1. Nucleus – Command center of the cell. (Receives and sends messages) 6. Cell Membrane – Barrier of protection for the cell (Allows nutrients in and waste out) 8. Vacuole – Stores water and waste. 4. Chloroplasts – Makes ...
The Cell Theory
... __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 2. Why didn’t anyone know about cells before the late 17th century? __________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
... __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 2. Why didn’t anyone know about cells before the late 17th century? __________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 5
... A special protein that transports Na+ ions and K+ up their concentration gradients ...
... A special protein that transports Na+ ions and K+ up their concentration gradients ...
sample exam Bio106 - KSU Faculty Member websites
... 2. Put (√) in front of true sentences and (X) in front of false ones: (5 marks) 1. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes on its surface ...
... 2. Put (√) in front of true sentences and (X) in front of false ones: (5 marks) 1. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes on its surface ...
Bill Nye Reviews Cells
... Part 1 What are cells? What does Bill say? Click on the link to find out! ...
... Part 1 What are cells? What does Bill say? Click on the link to find out! ...
1. Cells PPT
... 2. Proteins (may attach cell membrane to other structures, recognize invaders, speed up chemical reactions, bind & transport certain substances) 3. Cholesterol (↑ stability of cell membrane) ...
... 2. Proteins (may attach cell membrane to other structures, recognize invaders, speed up chemical reactions, bind & transport certain substances) 3. Cholesterol (↑ stability of cell membrane) ...
Carbohydrate: an organic molecule that provides energy for the cell
... Hypertonic: this occurs when the solute concentration is more outside than inside of the cell. Diffusion: the movement of “anything” from high to low concentrations. Osmosis: the movement of water molecules from high to low concentrations. Concentration Gradient: the difference between concentration ...
... Hypertonic: this occurs when the solute concentration is more outside than inside of the cell. Diffusion: the movement of “anything” from high to low concentrations. Osmosis: the movement of water molecules from high to low concentrations. Concentration Gradient: the difference between concentration ...
Document
... Cellular Structure: the unit of life, one or many Metabolism: photosynthesis, respiration, fermentation, digestion, gas exchange, secretion, excretion, circulation--processing materials and energy Growth: cell enlargement, cell number Movement: intracellular, movement, locomotion ...
... Cellular Structure: the unit of life, one or many Metabolism: photosynthesis, respiration, fermentation, digestion, gas exchange, secretion, excretion, circulation--processing materials and energy Growth: cell enlargement, cell number Movement: intracellular, movement, locomotion ...
Microbiology Slides - Welcome to Cherokee High School
... • Small size ( 0.5 to 2um) • Large surface area to volume ratio • A variety of shapes • Outer cell wall- very thick made of specialized molecules • Cell membranes may have a different constituency of molecules from eukaryote cells • Ribosomes smaller ...
... • Small size ( 0.5 to 2um) • Large surface area to volume ratio • A variety of shapes • Outer cell wall- very thick made of specialized molecules • Cell membranes may have a different constituency of molecules from eukaryote cells • Ribosomes smaller ...
Biology Notes 3-2
... 1. All living things are made of 1 or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit(s) of life’s function and structure. 3. All cells arise from existing cells. Most Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye: they are 5µm-20 µm (micrometers in diameter) Cells must have a high Surface Area-to-Volume ratio (S ...
... 1. All living things are made of 1 or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit(s) of life’s function and structure. 3. All cells arise from existing cells. Most Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye: they are 5µm-20 µm (micrometers in diameter) Cells must have a high Surface Area-to-Volume ratio (S ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Surface area represents the “access” available to and from a cell for supplies. • Volume represents how much has to be supplied. • The more “access” you have to supply each unit of volume, the more efficient the cell is. ...
... • Surface area represents the “access” available to and from a cell for supplies. • Volume represents how much has to be supplied. • The more “access” you have to supply each unit of volume, the more efficient the cell is. ...
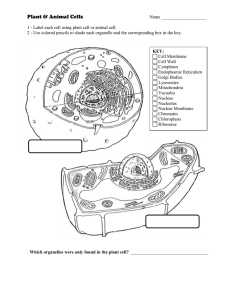
Name Date The Structure and Function of Cells Cell Part Structure
... 2. Name two cell parts that are found in plant cells and are not found in animal cells. ...
... 2. Name two cell parts that are found in plant cells and are not found in animal cells. ...
Cell Organelle Organelle Function City Part Cell Membrane
... Cell Organelle Cell Membrane Nucleus ...
... Cell Organelle Cell Membrane Nucleus ...
Cell Review
... Cell Membrane- controls what enters and leaves the cell Lysosome- contains enzymes that break down worn out cell parts Golgi Body- pack and carry proteins Endoplasmic Reticulum- series of channels that move things around the cells Ribosome- manufacture proteins- site of protein synthesis Vacuole- st ...
... Cell Membrane- controls what enters and leaves the cell Lysosome- contains enzymes that break down worn out cell parts Golgi Body- pack and carry proteins Endoplasmic Reticulum- series of channels that move things around the cells Ribosome- manufacture proteins- site of protein synthesis Vacuole- st ...
http://en
... CELLS Visit this web page: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_%28biology%29 and answer the questions. ...
... CELLS Visit this web page: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_%28biology%29 and answer the questions. ...
l2 biology: topics covered on the midterm exam and what to study
... Are a type of protein How do they function/are used in living organisms How do they work in a chemical reaction? Understand substrate, reactants, products. Effects of temperature, pH on enzyme action Cell Membrane and Cellular Transport: diffusion and osmosis: passive vs. active transport ...
... Are a type of protein How do they function/are used in living organisms How do they work in a chemical reaction? Understand substrate, reactants, products. Effects of temperature, pH on enzyme action Cell Membrane and Cellular Transport: diffusion and osmosis: passive vs. active transport ...
Cells
... The CELL THEORY: – All living things are made of cells. – Cells come from pre-existing cells. – Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in all living organisms. ...
... The CELL THEORY: – All living things are made of cells. – Cells come from pre-existing cells. – Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in all living organisms. ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.