DR 4-2 Active Transport
... than the concentration of sodium ions outside the cell. 6. The concentration of potassium ions inside the cell is usually ...
... than the concentration of sodium ions outside the cell. 6. The concentration of potassium ions inside the cell is usually ...
Cell Test Review
... Cells work together to form a __________________. Tissue What organelles are used to store water, food, or waste materials? Vacuoles What threadlike structures contain information about the organism? Chromosomes What is the jelly-like substance between the cell membrane and the nucleus? Cytoplasm Wh ...
... Cells work together to form a __________________. Tissue What organelles are used to store water, food, or waste materials? Vacuoles What threadlike structures contain information about the organism? Chromosomes What is the jelly-like substance between the cell membrane and the nucleus? Cytoplasm Wh ...
Lesson 1
... solution is hypotonic. b. The cell would swell because the water solution is hypertonic. c. The cell would shrivel because the water solution is hypertonic. d. The cell would shrivel because the water solution is hypotonic. ...
... solution is hypotonic. b. The cell would swell because the water solution is hypertonic. c. The cell would shrivel because the water solution is hypertonic. d. The cell would shrivel because the water solution is hypotonic. ...
Biology Chapter 7
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
Cells
... single chromosome no streaming in the cytoplasm cell division without mitosis simple flagella smaller ribosomes simple cytoskeleton no cellulose in cell walls no histone proteins ...
... single chromosome no streaming in the cytoplasm cell division without mitosis simple flagella smaller ribosomes simple cytoskeleton no cellulose in cell walls no histone proteins ...
Study Guide: Cell Test
... 28. Which would most likely cause the liquid in Tube A to rise? A Starch concentrations being equal on each side of the membrane B Water passing from a region of lower starch concentration to one of higher starch concentration C Water and starch volumes being the same D Solute in the tubes changing ...
... 28. Which would most likely cause the liquid in Tube A to rise? A Starch concentrations being equal on each side of the membrane B Water passing from a region of lower starch concentration to one of higher starch concentration C Water and starch volumes being the same D Solute in the tubes changing ...
A Head - School
... © Pearson Education Ltd 2011. Copying permitted for purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. ...
... © Pearson Education Ltd 2011. Copying permitted for purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. ...
Across 1. an organelle within the nucleus that produces ribosomes 3
... 2. a series of highly folded membranes involved in the production and storage of lipids 4. flattened tubular membranes that packs proteins 6. a membrane that separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell 8. an organelle that contains digestive enzymes and breaks down foreign particles and wastes 9 ...
... 2. a series of highly folded membranes involved in the production and storage of lipids 4. flattened tubular membranes that packs proteins 6. a membrane that separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell 8. an organelle that contains digestive enzymes and breaks down foreign particles and wastes 9 ...
HB Unit 3 Homeostasis and Cell Transport
... • Cells ingest materials by enfolding them into a pouch. • Pouch pinches off and becomes a membrane-bound ...
... • Cells ingest materials by enfolding them into a pouch. • Pouch pinches off and becomes a membrane-bound ...
AP BIOLOGY-EXAM REVIEW The Cell
... The organelles that contain their own DNA are all enclosed in double membranes. Relate this observation to the endosymbiotic theory. ...
... The organelles that contain their own DNA are all enclosed in double membranes. Relate this observation to the endosymbiotic theory. ...
Aim: How can we apply our knowledge of cells?
... 2. Write a description of each phase of mitosis. 3. Identify the part of the cell cycle being discussed. a. b. c. d. ...
... 2. Write a description of each phase of mitosis. 3. Identify the part of the cell cycle being discussed. a. b. c. d. ...
Basic features of all cells
... high concentration to low concentration and doesn’t require energy. Active transport: molecules move through the membrane from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration with the help of energy. It uses energy to move solutes against their gradients. ...
... high concentration to low concentration and doesn’t require energy. Active transport: molecules move through the membrane from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration with the help of energy. It uses energy to move solutes against their gradients. ...
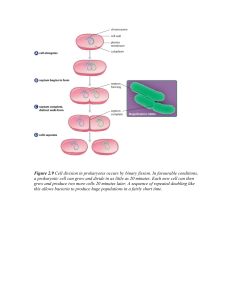
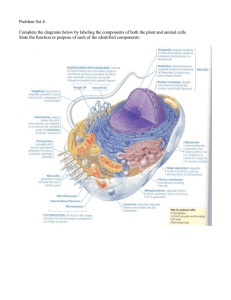
Problem Set 4:
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
Diffusion/Osmosis
... Know cells are enclosed within semipermeable membranes that regulate their interaction with their surroundings. ...
... Know cells are enclosed within semipermeable membranes that regulate their interaction with their surroundings. ...
Chapter 4
... 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know cells are enclosed within semi-permeable membranes that regulate their interaction wi ...
... 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know cells are enclosed within semi-permeable membranes that regulate their interaction wi ...
A Tour of the Cell - Ursuline High School
... modify proteins and lipids into vesicles (small, spherical shaped sacs that bud form the Golgi apparatus). The vesicles often merge and merge with the plasma membrane to release contents to the outside of the cell. ...
... modify proteins and lipids into vesicles (small, spherical shaped sacs that bud form the Golgi apparatus). The vesicles often merge and merge with the plasma membrane to release contents to the outside of the cell. ...
Cells - Wsfcs
... The liquid environment of the cell. The cytoplasm contains the organelles of ...
... The liquid environment of the cell. The cytoplasm contains the organelles of ...
Matching Cell Parts WS File
... ____3. Also called the plasma membrane ____4. Bags of enzymes used to digest particles/bacteria; “garbage men” of the cell; work with vacuoles. ____5. Control center of the cell; contains nucleolus and DNA ____6. External surface is studded with ribosomes ____7. Formed from a piece of cell membrane ...
... ____3. Also called the plasma membrane ____4. Bags of enzymes used to digest particles/bacteria; “garbage men” of the cell; work with vacuoles. ____5. Control center of the cell; contains nucleolus and DNA ____6. External surface is studded with ribosomes ____7. Formed from a piece of cell membrane ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.