water
... About Cell Membranes (continued) Cell membranes have pores (holes) in it a.Selectively permeable: Allows some molecules in and keeps other molecules out b.The structure helps it be selective! ...
... About Cell Membranes (continued) Cell membranes have pores (holes) in it a.Selectively permeable: Allows some molecules in and keeps other molecules out b.The structure helps it be selective! ...
Eukaryotic organelles - Sonoma Valley High School
... • Vacuoles store water, salt, proteins and carbohydrates • Vacuoles also serve as support structures in plants • The cytoplasm is the fluid that fills the cell in which all the other organelles float. Left side: What would represent the cytoplasm be in your analogy? ...
... • Vacuoles store water, salt, proteins and carbohydrates • Vacuoles also serve as support structures in plants • The cytoplasm is the fluid that fills the cell in which all the other organelles float. Left side: What would represent the cytoplasm be in your analogy? ...
Document
... The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Functions: Protein synthesis (about half the cell’s proteins are made here). Protein movement (trafficking) Protein “proofreading” ...
... The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Functions: Protein synthesis (about half the cell’s proteins are made here). Protein movement (trafficking) Protein “proofreading” ...
Summary: Function and Structure of Cell Parts
... • these organelles make proteins • they can be free in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum • free ribosomes make proteins that are used in the cytoplasm, for example, for the cytoskeleton • ribosomes that are attached to the ER make proteins which must be kept separate from ...
... • these organelles make proteins • they can be free in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum • free ribosomes make proteins that are used in the cytoplasm, for example, for the cytoskeleton • ribosomes that are attached to the ER make proteins which must be kept separate from ...
Study Guide for Chapter 4 - Cells: Basic Unit of Life
... NOTE: Please understand that these are only general questions. Any information you read, took notes on, saw in a movie, practiced in an activity, answered on a worksheet, etc. could be found on the test, including questions, topics, and vocabulary we used in class that is not listed here. 1) What is ...
... NOTE: Please understand that these are only general questions. Any information you read, took notes on, saw in a movie, practiced in an activity, answered on a worksheet, etc. could be found on the test, including questions, topics, and vocabulary we used in class that is not listed here. 1) What is ...
C8-Cellular Transport
... Cancer: Mistake in Cell Cycle Cancerous cells form masses of tissues called tumors. Later cancer cells enter the bloodstream and metastasize to other parts of the body. A healthy lifestyle can reduce the incidence of cancer. Low-fat high-fiber ...
... Cancer: Mistake in Cell Cycle Cancerous cells form masses of tissues called tumors. Later cancer cells enter the bloodstream and metastasize to other parts of the body. A healthy lifestyle can reduce the incidence of cancer. Low-fat high-fiber ...
Flyer
... vitro models of neurodegenerative diseases” In normal central nervous system, neurons and astrocytes, the most abundant cells, express pannexins and connexins, which form gap-junctional channels and hemichannels. It seems that in mammals, native pannexins form only hemichannels whereas connexins for ...
... vitro models of neurodegenerative diseases” In normal central nervous system, neurons and astrocytes, the most abundant cells, express pannexins and connexins, which form gap-junctional channels and hemichannels. It seems that in mammals, native pannexins form only hemichannels whereas connexins for ...
Cells
... – Cells are the fundamental units of life. – All organisms are composed of cells. – All cells come from preexisting cells. • each cell possesses the different molecules necessary for sustaining life & specializations ...
... – Cells are the fundamental units of life. – All organisms are composed of cells. – All cells come from preexisting cells. • each cell possesses the different molecules necessary for sustaining life & specializations ...
Cell Organelle Review Game
... It is your job as the teacher to set up the main objective of the game before it is played. This game can be modified to fit your needs. You want to highlight what you feel that the students need the most help in. For example, if you are just covering the basic cell organelles and their roles in pla ...
... It is your job as the teacher to set up the main objective of the game before it is played. This game can be modified to fit your needs. You want to highlight what you feel that the students need the most help in. For example, if you are just covering the basic cell organelles and their roles in pla ...
Review Session: Name: ______ Use your Unit 3 Notes to complete
... 16. What organelles do plant cells have that animal cells do not? Cell wall, chloroplast, and the vacuoles are large rather than small. 17. Both animal and plant cells contain vacuoles, why do plant cells have a single large vacuole while animal cells do not? Plants use their vacuole to add stabilit ...
... 16. What organelles do plant cells have that animal cells do not? Cell wall, chloroplast, and the vacuoles are large rather than small. 17. Both animal and plant cells contain vacuoles, why do plant cells have a single large vacuole while animal cells do not? Plants use their vacuole to add stabilit ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Compare the inside water concentration with the outside water concentration: • Isotonic: inside and outside same concentration of solute (and water) • Hypertonic: solution with higher solute concentration (lower water) • Hypotonic: solution with lower solute concentration (higher water) ...
... • Compare the inside water concentration with the outside water concentration: • Isotonic: inside and outside same concentration of solute (and water) • Hypertonic: solution with higher solute concentration (lower water) • Hypotonic: solution with lower solute concentration (higher water) ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER THREE
... 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of all living things 3. All cells come from existing cells 8. Explain the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. -Prokaryotic Cells: an organism that consists of a single cell that does not have a nucl ...
... 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of all living things 3. All cells come from existing cells 8. Explain the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. -Prokaryotic Cells: an organism that consists of a single cell that does not have a nucl ...
Unit 2 Practice Questions
... 3. The carbohydrates attached to some proteins and lipids of the plasma membrane are added as the membrane is made and refined in the ER and Golgi apparatus. The new membrane then forms transport vesicles that travel to the cell surface. On which side of the vesicle membrane are the carbohydrates? 4 ...
... 3. The carbohydrates attached to some proteins and lipids of the plasma membrane are added as the membrane is made and refined in the ER and Golgi apparatus. The new membrane then forms transport vesicles that travel to the cell surface. On which side of the vesicle membrane are the carbohydrates? 4 ...
CELLS -> TISSUES -> ORGANS
... 1) The smallest unit of life is known as the __________________. An individual unit of life. 2) Cells with similar structures and functions form ____________________ and these groups work together for a common purpose form _______________ ...
... 1) The smallest unit of life is known as the __________________. An individual unit of life. 2) Cells with similar structures and functions form ____________________ and these groups work together for a common purpose form _______________ ...
The Cell - delongscience
... • Lysosomes are types of vesicles, or small, membrane-bound sacs that transport substances in cells ...
... • Lysosomes are types of vesicles, or small, membrane-bound sacs that transport substances in cells ...
Cell Analogy Project - Warren Hills Regional School District
... Mitochondrion DNA Cell wall cell membrane nuclear membrane Chloroplast ribosomes cytoplasm ...
... Mitochondrion DNA Cell wall cell membrane nuclear membrane Chloroplast ribosomes cytoplasm ...
# Unit 4 LT1
... Create a model to illustrate how prokaryotic DNA is divided for cell reproduction. What is this process called? How are the two cells related to each other genetically? ...
... Create a model to illustrate how prokaryotic DNA is divided for cell reproduction. What is this process called? How are the two cells related to each other genetically? ...
A Cell in a Bag Project
... A cell is really like a plastic bag with some interesting “stuff” inside of it. The “stuff” in the bag also works like the inside of a car to be sure that the cell is able survive. This project will help you to visualize the cell as a 3D structure with the machinery necessary to sustain life. Proced ...
... A cell is really like a plastic bag with some interesting “stuff” inside of it. The “stuff” in the bag also works like the inside of a car to be sure that the cell is able survive. This project will help you to visualize the cell as a 3D structure with the machinery necessary to sustain life. Proced ...
lo*-t-{
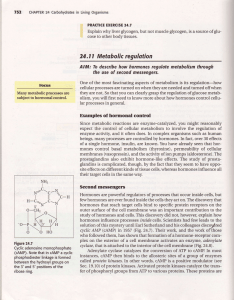
... the presence of cAMP starts some cellular processesand stops others. CyclicAMP a-lsomay play roles other than that of activating protein kinases. In at least one instance, cAMP activates an en4rrne by releasing it from an en4rme-inhibitor complex (Fig. 24.9). Hormone action is often compared with a ...
... the presence of cAMP starts some cellular processesand stops others. CyclicAMP a-lsomay play roles other than that of activating protein kinases. In at least one instance, cAMP activates an en4rrne by releasing it from an en4rme-inhibitor complex (Fig. 24.9). Hormone action is often compared with a ...
cells - Humble ISD
... • Eukaryotic = “true nucleus” • Eukaryotic cells contain a true nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. • Eukaryotic organisms may be single celled or multicellular. In multicellular organisms cells become specialized. ...
... • Eukaryotic = “true nucleus” • Eukaryotic cells contain a true nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. • Eukaryotic organisms may be single celled or multicellular. In multicellular organisms cells become specialized. ...
Basic Cell Structure
... • Movement of molecules, especially gases and liquids from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration ...
... • Movement of molecules, especially gases and liquids from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration ...
Types of Transport Across Cell Membranes
... • They bond and drag molecules through the lipid bilayer and release them on the opposite side. ...
... • They bond and drag molecules through the lipid bilayer and release them on the opposite side. ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.