cell
... A) Cells are the basic units of life. Every cell has got a cell membrane, organelles and cytoplasm. ...
... A) Cells are the basic units of life. Every cell has got a cell membrane, organelles and cytoplasm. ...
cell wall - HCC Learning Web
... • Each chromosome is composed of a single DNA molecule associated with proteins • The DNA and proteins of chromosomes are together called chromatin • Chromatin condenses to form discrete chromosomes as a cell prepares to divide • The nucleolus is located within the nucleus and is the site of ribosom ...
... • Each chromosome is composed of a single DNA molecule associated with proteins • The DNA and proteins of chromosomes are together called chromatin • Chromatin condenses to form discrete chromosomes as a cell prepares to divide • The nucleolus is located within the nucleus and is the site of ribosom ...
Cell Theory
... 1. All living things are made of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in ...
... 1. All living things are made of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in ...
Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote Worksheet
... Protein-making bodies called ribosomes also form part of the cytoplasm. Like all cells, prokaryotes have a cell membrane. All prokaryotes also have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane. The cell wall helps provide support and protection for the cell. Some prokaryotes are enclosed by an addition ...
... Protein-making bodies called ribosomes also form part of the cytoplasm. Like all cells, prokaryotes have a cell membrane. All prokaryotes also have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane. The cell wall helps provide support and protection for the cell. Some prokaryotes are enclosed by an addition ...
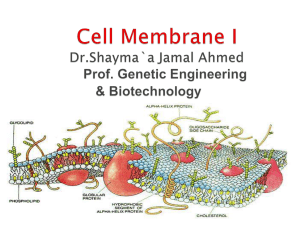
Plasma membrane Dr.Shayma`a Jamal Ahmed
... A. Mosaic: an object comprised of bits and pieces embedded in a supporting structure 1. membrane lipids form the supporting structure 2. membrane proteins provide the bits and pieces 3. both lipids and proteins may be mobile or 'fluid' B. Membrane lipids: the supporting structure ...
... A. Mosaic: an object comprised of bits and pieces embedded in a supporting structure 1. membrane lipids form the supporting structure 2. membrane proteins provide the bits and pieces 3. both lipids and proteins may be mobile or 'fluid' B. Membrane lipids: the supporting structure ...
File - JAdams Teaches
... Protein-making bodies called ribosomes also form part of the cytoplasm. Like all cells, prokaryotes have a cell membrane. All prokaryotes also have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane. The cell wall helps provide support and protection for the cell. Some prokaryotes are enclosed by an addition ...
... Protein-making bodies called ribosomes also form part of the cytoplasm. Like all cells, prokaryotes have a cell membrane. All prokaryotes also have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane. The cell wall helps provide support and protection for the cell. Some prokaryotes are enclosed by an addition ...
prokaryote vs eukaryote worksheet
... cytoplasm. Protein-making bodies called ribosomes also form part of the cytoplasm. Like all cells, prokaryotes have a cell membrane. All prokaryotes also have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane. The cell wall helps provide support and protection for the cell. Some prokaryotes are enclosed by ...
... cytoplasm. Protein-making bodies called ribosomes also form part of the cytoplasm. Like all cells, prokaryotes have a cell membrane. All prokaryotes also have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane. The cell wall helps provide support and protection for the cell. Some prokaryotes are enclosed by ...
Goal Two
... They can be both species and cell specific High pH and high temperatures can denature (kill or make unusable) Induce Fit theory The cell membrane has specific receptor for specific enzymes. Only the triangle enzyme will fit into the triangle active site. Once the enzyme and the active site (called ...
... They can be both species and cell specific High pH and high temperatures can denature (kill or make unusable) Induce Fit theory The cell membrane has specific receptor for specific enzymes. Only the triangle enzyme will fit into the triangle active site. Once the enzyme and the active site (called ...
Cell Structure, Function and Transport
... it allows some molecules to pass through while keeping others out of the cell (small, uncharged particles) by passive transport b) Water constantly moves in and out of the cell c) Other charged particles (calcium and sodium ions) and large molecules can only be allowed in at certain times through di ...
... it allows some molecules to pass through while keeping others out of the cell (small, uncharged particles) by passive transport b) Water constantly moves in and out of the cell c) Other charged particles (calcium and sodium ions) and large molecules can only be allowed in at certain times through di ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Transmembrane proteins form pores that allow small molecules to pass from cell to cell. • For spread of ions between cardiac or smooth muscle cells. ...
... • Transmembrane proteins form pores that allow small molecules to pass from cell to cell. • For spread of ions between cardiac or smooth muscle cells. ...
Name: Date: Period: _____ Unit 2 Notes, Part 3 – The Origin and
... -Oparin hypothesized that the molecules found in early Earth’s atmosphere + lightning and UV radiation organic compounds such as amino acids -Miller and Urey tested Oparin’s hypothesis with the apparatus shown to the right and were able to synthesize amino acids from these conditions 7. Steps invo ...
... -Oparin hypothesized that the molecules found in early Earth’s atmosphere + lightning and UV radiation organic compounds such as amino acids -Miller and Urey tested Oparin’s hypothesis with the apparatus shown to the right and were able to synthesize amino acids from these conditions 7. Steps invo ...
Chapter 7 III. Cell Boundaries
... – Bursting not so much a problem in larger organisms….tend to be in isotonic environments • Osmotic pressure may not allow a plant or bacterial cell to burst , but could weaken the cell wall hypertonic ...
... – Bursting not so much a problem in larger organisms….tend to be in isotonic environments • Osmotic pressure may not allow a plant or bacterial cell to burst , but could weaken the cell wall hypertonic ...
Section 1 Chemistry of Life A. Everything around you is
... 1. Producers—organisms that make their own food; consumers—organisms that can’t make their own food 2. Chlorophyll and other pigments are used in photosynthesis to capture light energy which is used to produce sugar and oxygen. C. Respiration—the process in which chemical reactions break down food m ...
... 1. Producers—organisms that make their own food; consumers—organisms that can’t make their own food 2. Chlorophyll and other pigments are used in photosynthesis to capture light energy which is used to produce sugar and oxygen. C. Respiration—the process in which chemical reactions break down food m ...
lecture notes-microbiology-3-Eucaryotes
... eukaryote cell, where respiration takes place. It reduces oxygen and store energy in ATP (Adenosine triphosphate). Shape: Mitochondria have cylindrical shape with 1 µm in diameter and 2-3 µm in length. ...
... eukaryote cell, where respiration takes place. It reduces oxygen and store energy in ATP (Adenosine triphosphate). Shape: Mitochondria have cylindrical shape with 1 µm in diameter and 2-3 µm in length. ...
Test 60 Ques. Review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 2. Property of molecules that means it is attracted to water. 3. All cells live in this type of environment. 4. Particles that are soluble in this can pass easily across the cell membrane. 5. These molecules help to stabilize the plasma membrane. 6. Property of molecules that means it is “water repe ...
... 2. Property of molecules that means it is attracted to water. 3. All cells live in this type of environment. 4. Particles that are soluble in this can pass easily across the cell membrane. 5. These molecules help to stabilize the plasma membrane. 6. Property of molecules that means it is “water repe ...
TCAP review(#2)
... A. carbon dioxide and nitrogen B. carbon dioxide and oxygen C. oxygen and nitrogen D. oxygen and hydrogen ...
... A. carbon dioxide and nitrogen B. carbon dioxide and oxygen C. oxygen and nitrogen D. oxygen and hydrogen ...
Cell Unit Study Guide
... You should be able to do the following: 1. Identify and provide examples of the traits of living things. 2. List and describe the levels of organization from smallest to largest. 3. Identify the three parts of cell theory. 4. Determine if a cell is a eukaryote or prokaryote given limited information ...
... You should be able to do the following: 1. Identify and provide examples of the traits of living things. 2. List and describe the levels of organization from smallest to largest. 3. Identify the three parts of cell theory. 4. Determine if a cell is a eukaryote or prokaryote given limited information ...
90464 Describe cell structure and function
... Cells will include: plant cells, animal cells, and unicellular organisms. ...
... Cells will include: plant cells, animal cells, and unicellular organisms. ...
travel_bro. student instructions
... Students are required to produce a travel brochure that describes a plant or animal cell as if it were a large exhibit, amusement park, or roadside attraction. Students must describe the function of the organelles accurately and compare it to a part of the attraction. For example, the mitochondr ...
... Students are required to produce a travel brochure that describes a plant or animal cell as if it were a large exhibit, amusement park, or roadside attraction. Students must describe the function of the organelles accurately and compare it to a part of the attraction. For example, the mitochondr ...
Selectively Permeable Membranes Reading and Pics
... energy. Many waste materials exit the cell through diffusion because that is their natural direction of movement as they build up within the cell. • Osmosis: Osmosis is simply the diffusion of water; it has its own name because water is so important to life. Solutions with higher amounts of dissolve ...
... energy. Many waste materials exit the cell through diffusion because that is their natural direction of movement as they build up within the cell. • Osmosis: Osmosis is simply the diffusion of water; it has its own name because water is so important to life. Solutions with higher amounts of dissolve ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.