Organelles - Granbury ISD
... packaging proteins for the cell. Once the proteins are produced by the rough ER, they pass into the sack like cisternae that are the main part of the Golgi body. ...
... packaging proteins for the cell. Once the proteins are produced by the rough ER, they pass into the sack like cisternae that are the main part of the Golgi body. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... 12. A pupil prepared a microscope slide of onion cells using water. Diagram A shows how the cells looked when first seen with the microscope. Diagram B shows their appearance after the addition of another liquid. ...
... 12. A pupil prepared a microscope slide of onion cells using water. Diagram A shows how the cells looked when first seen with the microscope. Diagram B shows their appearance after the addition of another liquid. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Cells can increase in number- hyperplasia • Cells have the ability to change into another type of cell- metaplasia – A protective response to a stimulus such as ...
... • Cells can increase in number- hyperplasia • Cells have the ability to change into another type of cell- metaplasia – A protective response to a stimulus such as ...
Title: Surface Area to Volume Ratio Questions: Why can`t cells
... Title: Surface Area to Volume Ratio Questions: Why can’t cells continue to grow larger and larger to become giant cells, like the blob? Why are most cells like those in an elephant or an earthworm, microscopic in size? What happens when a cell grows larger? What causes cells to remain small? Procedu ...
... Title: Surface Area to Volume Ratio Questions: Why can’t cells continue to grow larger and larger to become giant cells, like the blob? Why are most cells like those in an elephant or an earthworm, microscopic in size? What happens when a cell grows larger? What causes cells to remain small? Procedu ...
Chapter 3 The Cell
... procaryotic, algae, plants, fungi and many protozoans. Animal cells do not contain a cell wall. II. Cytoplasm ...
... procaryotic, algae, plants, fungi and many protozoans. Animal cells do not contain a cell wall. II. Cytoplasm ...
BIO.A.1 – Basic Biological Principles
... • Some eukaryotes are single celled (amoeba) and some are multicellular (us) ...
... • Some eukaryotes are single celled (amoeba) and some are multicellular (us) ...
Notes 1 Introduction to Chapter 5
... Cells use the cell membrane to regulate what comes in and out of the cell to keep steady levels of nutrients, water and other substances. ...
... Cells use the cell membrane to regulate what comes in and out of the cell to keep steady levels of nutrients, water and other substances. ...
File
... ● Passive Transport - movement of substances across the plasma membrane without the use of the cell’s energy (with the concentration gradient). ● Osmosis - diffusion of water across the plasma membrane from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration. ● Diffusion - movement of substa ...
... ● Passive Transport - movement of substances across the plasma membrane without the use of the cell’s energy (with the concentration gradient). ● Osmosis - diffusion of water across the plasma membrane from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration. ● Diffusion - movement of substa ...
Plant Cell “Penny Pitch” game
... • Yarn (three colors- one for the cell membrane, ore for the endoplasmic reticulum, one for the vacuole) • Green fabric, felt or paper than can be cut into chloroplasts • Other colors of fabric (or paper) scraps with which to make other organelles • Objects to pitch—such as pennies or bean bags, dep ...
... • Yarn (three colors- one for the cell membrane, ore for the endoplasmic reticulum, one for the vacuole) • Green fabric, felt or paper than can be cut into chloroplasts • Other colors of fabric (or paper) scraps with which to make other organelles • Objects to pitch—such as pennies or bean bags, dep ...
INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY
... • Cells have evolved into two fundamentally different types, eukaryotes and prokaryotes. which can be distinguished on the basis of their structure and the complexity of their organization. • Fungi and the protozoa are eukaryotic where as bacteria are prokaryotic ...
... • Cells have evolved into two fundamentally different types, eukaryotes and prokaryotes. which can be distinguished on the basis of their structure and the complexity of their organization. • Fungi and the protozoa are eukaryotic where as bacteria are prokaryotic ...
4_ Cells and cell di..
... It contains enzymes and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newly-made proteins and lipids to the Golgi body, lysosomes, and membranes Vacuole - fluid-filled, membrane-surrounded cavities inside a cell. The vacuole fills with food be ...
... It contains enzymes and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newly-made proteins and lipids to the Golgi body, lysosomes, and membranes Vacuole - fluid-filled, membrane-surrounded cavities inside a cell. The vacuole fills with food be ...
CELLS
... What does it do? Acts like a post office by packaging proteins in vesicles and delivering them to other parts of the cell. Vesicles containing proteins exit the Golgi body and are sent to parts of the cell that need them. ...
... What does it do? Acts like a post office by packaging proteins in vesicles and delivering them to other parts of the cell. Vesicles containing proteins exit the Golgi body and are sent to parts of the cell that need them. ...
Biology Unit Test Review Sheet
... Different types of cells are structured differently (specialized) because they have different functions o Example: sperm cells have flagella so they are able to move towards an egg cell ...
... Different types of cells are structured differently (specialized) because they have different functions o Example: sperm cells have flagella so they are able to move towards an egg cell ...
What is a Cell Analogy?
... 1. The project can be done individually or as a group of two or three (no more). 2. The project requires a poster (no tri-fold poster board). a. On the poster should be a picture of the cell next to a picture of the object (if doing this one). If you’re doing an organization, you need a picture of t ...
... 1. The project can be done individually or as a group of two or three (no more). 2. The project requires a poster (no tri-fold poster board). a. On the poster should be a picture of the cell next to a picture of the object (if doing this one). If you’re doing an organization, you need a picture of t ...
Cell Analogy Worksheet
... In a faraway city called Grant City, the main export and production product is the steel widget. Everyone in the town has something to do with steel widget making and the entire town is designed to build and export widgets. The town hall has the instructions for widget making, widgets come in all sh ...
... In a faraway city called Grant City, the main export and production product is the steel widget. Everyone in the town has something to do with steel widget making and the entire town is designed to build and export widgets. The town hall has the instructions for widget making, widgets come in all sh ...
Use prefixes, suffixes, and roots to define the
... membrane • Processes – Pinocytosis. The cell takes tiny droplets from its surroundings into tiny vesicles. – Phagocytosis. The vesicle engulfs food particles that are digested by lysosomes. ...
... membrane • Processes – Pinocytosis. The cell takes tiny droplets from its surroundings into tiny vesicles. – Phagocytosis. The vesicle engulfs food particles that are digested by lysosomes. ...
Cells
... • Cholesterol Gives membrane shape; rigidity • Receptor Proteins bind hormones & other substances coming in from outside the cell • Recognition Proteins proteins on membrane that are used for recognition by extra-cellular substances • Adhesion Proteins help cells of a certain type stick toge ...
... • Cholesterol Gives membrane shape; rigidity • Receptor Proteins bind hormones & other substances coming in from outside the cell • Recognition Proteins proteins on membrane that are used for recognition by extra-cellular substances • Adhesion Proteins help cells of a certain type stick toge ...
cell division cs
... member of each pair from the male parent and the other member from the female parent. (Can also be used to refer to structures that have different functions but have a common evolutionary origin, such as human arm and a bird wing.) ...
... member of each pair from the male parent and the other member from the female parent. (Can also be used to refer to structures that have different functions but have a common evolutionary origin, such as human arm and a bird wing.) ...
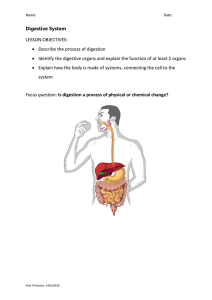
Digestive System
... The movement of molecules from high to low concentration until they are evenly distributed Osmosis: The movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane from high to low concentration Metabolism: All the physical and chemical processes in an organism that create energy and maintain growth, from d ...
... The movement of molecules from high to low concentration until they are evenly distributed Osmosis: The movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane from high to low concentration Metabolism: All the physical and chemical processes in an organism that create energy and maintain growth, from d ...
Cell - OnCourse
... is a system of membranous tubules and sacs in eukaryotic cells that functions as a path along which molecules move from one part of the cell to another. Can be Smooth or Rough largest and most visible organelle in a eukaryotic cell. stores the DNA that contains information that tells the cell how to ...
... is a system of membranous tubules and sacs in eukaryotic cells that functions as a path along which molecules move from one part of the cell to another. Can be Smooth or Rough largest and most visible organelle in a eukaryotic cell. stores the DNA that contains information that tells the cell how to ...
10 - Origin of Life
... somehow restrained in the area of that RNA. If some form of compartment evolved to enclose the protein, it would prevent free diffusion. ...
... somehow restrained in the area of that RNA. If some form of compartment evolved to enclose the protein, it would prevent free diffusion. ...
TITLE: ELODEA CELLS 05
... 8. Apply a small drop of stain to the leaf and let it soak in for about two minutes, then blot off the stain with a paper towel. 9. Add a drop of water to the stained leaf and apply a coverslip. 10. Examine the slide again at low and then high power. TRY to locate a cell with a nucleus and ADD this ...
... 8. Apply a small drop of stain to the leaf and let it soak in for about two minutes, then blot off the stain with a paper towel. 9. Add a drop of water to the stained leaf and apply a coverslip. 10. Examine the slide again at low and then high power. TRY to locate a cell with a nucleus and ADD this ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.