cell theory
... Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of structure All living things are composed of cells Unicellular and multi cellular all cells come from pre-existing cell Important organs in a cell Nuclease: contains the cells DNA brain of the cell Mitochondria: site of respiring provides the energy for the c ...
... Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of structure All living things are composed of cells Unicellular and multi cellular all cells come from pre-existing cell Important organs in a cell Nuclease: contains the cells DNA brain of the cell Mitochondria: site of respiring provides the energy for the c ...
Lab 8: Atomic force microscopy imaging of cells PI: Lab Instructor: Summary
... In this laboratory, you will use the atomic force microscope to image the structure and stiffness of living and chemically fixed human microvascular endothelial cells. The pN- to nN-scale mechanical force used to create these images allows you to observe both the micrometer-scale height of these cel ...
... In this laboratory, you will use the atomic force microscope to image the structure and stiffness of living and chemically fixed human microvascular endothelial cells. The pN- to nN-scale mechanical force used to create these images allows you to observe both the micrometer-scale height of these cel ...
plant transport cd
... sucrose is transported. It has very little cytoplasm, no nucleus, and non-thickened cellulose cell walls, with the end walls perforated to form sieve plates through which the cell sap passes from element to element. ...
... sucrose is transported. It has very little cytoplasm, no nucleus, and non-thickened cellulose cell walls, with the end walls perforated to form sieve plates through which the cell sap passes from element to element. ...
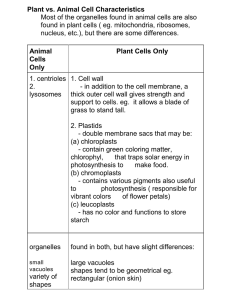
Plant vs. Animal Cell Characteristics Most of the organelles found in
... found in plant cells ( eg. mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus, etc.), but there are some differences. Animal Cells Only ...
... found in plant cells ( eg. mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus, etc.), but there are some differences. Animal Cells Only ...
Cellular Crossword
... 13. organelle that packages and exports materials out of the cell 17. describes an organism that is made of many cells 20. the smallest unit of structure and function in an organism 23. the scientist who first described cells 24. food-making organelle in plant cells 25. made up of organ systems work ...
... 13. organelle that packages and exports materials out of the cell 17. describes an organism that is made of many cells 20. the smallest unit of structure and function in an organism 23. the scientist who first described cells 24. food-making organelle in plant cells 25. made up of organ systems work ...
P006 Could Stem Cells be a source for primary cells in HTS scenario?
... than the stable cell lines currently used. The adult stem cells could be the key as they can expand to high number of cells and differentiate into any adult specialized cell type. At the same time, the use of adult stem cells overcomes any ethical consideration. But because the telomeres shortening ...
... than the stable cell lines currently used. The adult stem cells could be the key as they can expand to high number of cells and differentiate into any adult specialized cell type. At the same time, the use of adult stem cells overcomes any ethical consideration. But because the telomeres shortening ...
Biology Packet 5: Cell Growth and Division
... Star Review Book pages 98-104 and 113-115 Prentice Hall Review Book pages 53-58 At the end of this unit, the students will be able to: ...
... Star Review Book pages 98-104 and 113-115 Prentice Hall Review Book pages 53-58 At the end of this unit, the students will be able to: ...
cells_can_you
... Describe and draw the structure of an epithelial cell from the small intestine, and a palisade mesophyll cell from a plant, as seen with a light microscope. Recall that eukaryotic cells have organelles, including the cell wall, the cell membrane, the nucleus, the mitochondrion, the chloroplast, roug ...
... Describe and draw the structure of an epithelial cell from the small intestine, and a palisade mesophyll cell from a plant, as seen with a light microscope. Recall that eukaryotic cells have organelles, including the cell wall, the cell membrane, the nucleus, the mitochondrion, the chloroplast, roug ...
Synthetic Biology: From Parts to Modules to Therapeutic Systems
... abstraction, standardization, modularity, and computer aided design. But we also spend considerable effort towards understanding what makes synthetic biology different from all other existing engineering disciplines and discovering new design and construction rules that are effective for this unique ...
... abstraction, standardization, modularity, and computer aided design. But we also spend considerable effort towards understanding what makes synthetic biology different from all other existing engineering disciplines and discovering new design and construction rules that are effective for this unique ...
In 1839
... medicine and chemistry in Berlin at the Prussian Military Academy 1839-1843 on a scholarship of dinner. Virchow's most widely known scientific contribution is his cell theory, which built on the work of Theodor Schwann. He is cited as the first to recognize leukemia cells. ...
... medicine and chemistry in Berlin at the Prussian Military Academy 1839-1843 on a scholarship of dinner. Virchow's most widely known scientific contribution is his cell theory, which built on the work of Theodor Schwann. He is cited as the first to recognize leukemia cells. ...
Slide 1
... – To learn characteristics of all cells – To identify cell parts – To compare and contrast various cell types• Plant and animal cells ...
... – To learn characteristics of all cells – To identify cell parts – To compare and contrast various cell types• Plant and animal cells ...
11-14-02
... Robert Hooke , Looked at cork Saw little boxes that reminded him of cells in a monastery; Coined the word cell Anton von Leeuwenhoek observed the first living cell ...
... Robert Hooke , Looked at cork Saw little boxes that reminded him of cells in a monastery; Coined the word cell Anton von Leeuwenhoek observed the first living cell ...
Basal phyla - Robert D. Podolsky
... Phylogeny of basal animal groups Note: On an exam you would not be given the labels, only the phylogeny. Use this exercise to organize your understanding of when major features evolved. ...
... Phylogeny of basal animal groups Note: On an exam you would not be given the labels, only the phylogeny. Use this exercise to organize your understanding of when major features evolved. ...
Document
... Epitheliums and their regional differentiation (tegument, respiratory tract, intestine). Glands and their secretion functions (exocrine glands: salivary glands, liver, pancreas). 2. Connective tissues: description of the extracellular matrix components and of the cellular microenvironment. Different ...
... Epitheliums and their regional differentiation (tegument, respiratory tract, intestine). Glands and their secretion functions (exocrine glands: salivary glands, liver, pancreas). 2. Connective tissues: description of the extracellular matrix components and of the cellular microenvironment. Different ...
Document
... Supplemental Methods Stimulation of Cell Lines The same concentrations of TLR agonists were used to stimulate reactivation of the J-Lat 10.6, ACH-2 and U1 HIV-1 latently cell lines, and in order to induce expression of IL-8 cytokine in THP-1 cells. Cells were maintained in culture medium made of RPM ...
... Supplemental Methods Stimulation of Cell Lines The same concentrations of TLR agonists were used to stimulate reactivation of the J-Lat 10.6, ACH-2 and U1 HIV-1 latently cell lines, and in order to induce expression of IL-8 cytokine in THP-1 cells. Cells were maintained in culture medium made of RPM ...
CELLS AND TISSUES WORKSHEET ANATOMY AND
... 1. Forms the lining of the small intestine______________________________ 2. A single layer of flattened cells___________________________________3. Lines the esophagus__________________________ 4. A single layer of hexagonal cells_________________________ 5. A single layer of square-like cells_______ ...
... 1. Forms the lining of the small intestine______________________________ 2. A single layer of flattened cells___________________________________3. Lines the esophagus__________________________ 4. A single layer of hexagonal cells_________________________ 5. A single layer of square-like cells_______ ...
Cell Structure and Function: Review
... when looking under a microscope. Describe the rule you would tell them: ...
... when looking under a microscope. Describe the rule you would tell them: ...
I1-3 Cell organelle notes
... 10. Nuclear membrane 11. Nucleolus Plant Cells A. Have many of the same organelles, but also include: 1. Cell wall – (look up definition in text) 2. Vacuoles a. Can occupy 90% of plant cell’s volume b. Filled with fluid c. Store water, enzymes and waste products 3. Plastids a. Store starch or fats b ...
... 10. Nuclear membrane 11. Nucleolus Plant Cells A. Have many of the same organelles, but also include: 1. Cell wall – (look up definition in text) 2. Vacuoles a. Can occupy 90% of plant cell’s volume b. Filled with fluid c. Store water, enzymes and waste products 3. Plastids a. Store starch or fats b ...
Cell theory and levels of organization quiz
... Only animals have cells Plant cells have larger vacuoles Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things ...
... Only animals have cells Plant cells have larger vacuoles Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things ...
Cells Test Review
... 7. Give 3 examples of things that are not made up of cells. 8. What are cells? 9. What are tissues? 10. What are organs? 11. What is an organ system? 12. Define organism. 13. What are the levels of organization of organisms from simple to complex? ...
... 7. Give 3 examples of things that are not made up of cells. 8. What are cells? 9. What are tissues? 10. What are organs? 11. What is an organ system? 12. Define organism. 13. What are the levels of organization of organisms from simple to complex? ...
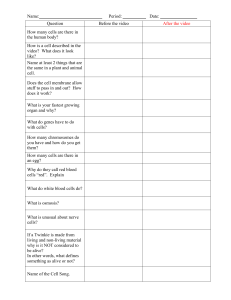
Question Before the video After the video How many cells are there
... stuff to pass in and out? How does it work? What is your fastest growing organ and why? What do genes have to do with cells? How many chromosomes do you have and how do you get them? How many cells are there in an egg? Why do they call red blood cells “red”. Explain What do white blood cells do? Wha ...
... stuff to pass in and out? How does it work? What is your fastest growing organ and why? What do genes have to do with cells? How many chromosomes do you have and how do you get them? How many cells are there in an egg? Why do they call red blood cells “red”. Explain What do white blood cells do? Wha ...
Tissue engineering

Tissue engineering is the use of a combination of cells, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to improve or replace biological functions. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field in its own right.While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e., bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. The term has also been applied to efforts to perform specific biochemical functions using cells within an artificially-created support system (e.g. an artificial pancreas, or a bio artificial liver). The term regenerative medicine is often used synonymously with tissue engineering, although those involved in regenerative medicine place more emphasis on the use of stem cells or progenitor cells to produce tissues.