Homeostasis Nucleus Decomposers Producers Consumer Abiotic
... Decomposers Producers Consumer Abiotic Biotic Asexual Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Chloroplasts Vacuole Echinoderm Bivalve Protozoa Flagella Pseudopod Mycelium Arthropod Turn over for more → ...
... Decomposers Producers Consumer Abiotic Biotic Asexual Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Chloroplasts Vacuole Echinoderm Bivalve Protozoa Flagella Pseudopod Mycelium Arthropod Turn over for more → ...
Cells and Homeostasis - Mrs. Blevins` Science
... – Over watering a plant cell may cause it to blow up and burst. – An animal cell without enough food may die. – The temperature needs to be regulated or the cell could freeze or over heat. ...
... – Over watering a plant cell may cause it to blow up and burst. – An animal cell without enough food may die. – The temperature needs to be regulated or the cell could freeze or over heat. ...
Host Defence
... » also a mechanism by with cells respond to external stimuli (“mechanical transducers”) ...
... » also a mechanism by with cells respond to external stimuli (“mechanical transducers”) ...
1. dia
... Cells are the basic units of life. All living organisms are made up of cells. Only living cells can produce new cells. ...
... Cells are the basic units of life. All living organisms are made up of cells. Only living cells can produce new cells. ...
Ch. 7 Rd Assign.
... You will be quizzed over the information in this assignment. Use your books and notes Reading Assignment: Pages 169-173 1. List three scientists that contributed to the study of cells and what each of their contributions where. ...
... You will be quizzed over the information in this assignment. Use your books and notes Reading Assignment: Pages 169-173 1. List three scientists that contributed to the study of cells and what each of their contributions where. ...
Cell Processes notes 11/21
... •Take out notebook and open to next available page. •Write: Cell Processes and get ready for notes…there’s not many! ...
... •Take out notebook and open to next available page. •Write: Cell Processes and get ready for notes…there’s not many! ...
Unit A, Chapter 1, Lesson 1
... Mitochondria – release energy from food (powerhouse/power plant) ...
... Mitochondria – release energy from food (powerhouse/power plant) ...
Gross anatomy Microscopic anatomy Physiology Histology Organ
... organism and its parts The study of tissue ...
... organism and its parts The study of tissue ...
Cell culture on high-extension surfaces
... surfaces. The technology consists of a computer-controlled iris-like mechanical device which can slowly expand (or contract) a transparent, high-extension silicone rubber culture surface. These developments led to a CHRP-funded collaboration between our laboratory in the Department of Chemical Engin ...
... surfaces. The technology consists of a computer-controlled iris-like mechanical device which can slowly expand (or contract) a transparent, high-extension silicone rubber culture surface. These developments led to a CHRP-funded collaboration between our laboratory in the Department of Chemical Engin ...
Vertebrate Body Structure - Saint Demetrios Astoria School
... • Covers internal and external structures • Purpose – Protection – Secretion – Gas exchange ...
... • Covers internal and external structures • Purpose – Protection – Secretion – Gas exchange ...
session 12 File - E-Learning/An
... An-Najah National University Faculty of Medicine Department of Physiology ...
... An-Najah National University Faculty of Medicine Department of Physiology ...
TEACHER NOTES AND ANSWERS Section 5.5
... Organs: groups of tissues that work together to perform similar or related functions Tissues: groups of cells that work together to perform a similar function Cells: smallest, most basic structural unit of life; typically become specialized homeostasis: maintained by the interaction of different org ...
... Organs: groups of tissues that work together to perform similar or related functions Tissues: groups of cells that work together to perform a similar function Cells: smallest, most basic structural unit of life; typically become specialized homeostasis: maintained by the interaction of different org ...
Establishing a Territory Goal/Move 2
... Cell source is a major issue for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. An exciting breakthrough in stem cell biology is that adult somatic cells can be reprogrammed into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) by the activation of a limited number of genes1. The iPSCs derived from somatic cel ...
... Cell source is a major issue for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. An exciting breakthrough in stem cell biology is that adult somatic cells can be reprogrammed into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) by the activation of a limited number of genes1. The iPSCs derived from somatic cel ...
Chapter II.6.11 - Cardiac Muscle Tissue Engineering
... to encourage cells to pull on it, and elastic enough to respond to deform under cell tension. You may include properties that encourage signal propagation or gas diffusion while shielding cells from shear stress, as well as hybrid biomaterials that take advantage of one or more physical properties o ...
... to encourage cells to pull on it, and elastic enough to respond to deform under cell tension. You may include properties that encourage signal propagation or gas diffusion while shielding cells from shear stress, as well as hybrid biomaterials that take advantage of one or more physical properties o ...
Levels of Organization
... Tissues—the 3rd level • In any multi-cellular organism, cells rarely work alone. • Cells that are similar in structure and function are usually joined together to form tissues. • Tissues have specialized functions and including many types including connective, muscle, epithelial, nerve, bone, etc. ...
... Tissues—the 3rd level • In any multi-cellular organism, cells rarely work alone. • Cells that are similar in structure and function are usually joined together to form tissues. • Tissues have specialized functions and including many types including connective, muscle, epithelial, nerve, bone, etc. ...
Mammalian Differentiated Cell Types, Part1
... move substances (such as mucus) over the epithelial sheet. ...
... move substances (such as mucus) over the epithelial sheet. ...
cells-study-guide
... Be able to explain how surface area/volume ratio limits the size of cells. (textbook) Understand that in order for organisms (and individual cells) to survive, nutrients need to come in and wastes need to go out. ...
... Be able to explain how surface area/volume ratio limits the size of cells. (textbook) Understand that in order for organisms (and individual cells) to survive, nutrients need to come in and wastes need to go out. ...
Plant Tissues
... a. Simple Tissues - composed of only one cell type. Epidermis - the thin layer (the cuticle) on its outer surface. Epidermal cells protect the underlying tissues. Parenchyma - the most common and least specialized of all tissues; occurring throughout the plant. The cells are typically large, isodiam ...
... a. Simple Tissues - composed of only one cell type. Epidermis - the thin layer (the cuticle) on its outer surface. Epidermal cells protect the underlying tissues. Parenchyma - the most common and least specialized of all tissues; occurring throughout the plant. The cells are typically large, isodiam ...
7.3 From Cell To Organism
... a. ex – the heart - made up of muscle, nerve, & other tissues C. Organ System 1. Various organs that carry out a major body function a. ex- circulatory system – carries blood throughout the body ...
... a. ex – the heart - made up of muscle, nerve, & other tissues C. Organ System 1. Various organs that carry out a major body function a. ex- circulatory system – carries blood throughout the body ...
biology exam review
... 19. Tendons connect ___________ to ____________. When muscle _____________ they pull the bone Muscles can only _________and therefore work in groups. (3.8) 20. Differentiate between the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. (3.10) 21. Describe the functions of the following organ ...
... 19. Tendons connect ___________ to ____________. When muscle _____________ they pull the bone Muscles can only _________and therefore work in groups. (3.8) 20. Differentiate between the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. (3.10) 21. Describe the functions of the following organ ...
Epithelial Cells
... 1. What are Epithelial Cells? 2. How does the shape of the epithelial cell aid in creating a barrier of protection in the body? 3. How does the epithelium aid to maintain homeostasis? 4. Which body system do epithelial cells most likely work with the majority of the time? ...
... 1. What are Epithelial Cells? 2. How does the shape of the epithelial cell aid in creating a barrier of protection in the body? 3. How does the epithelium aid to maintain homeostasis? 4. Which body system do epithelial cells most likely work with the majority of the time? ...
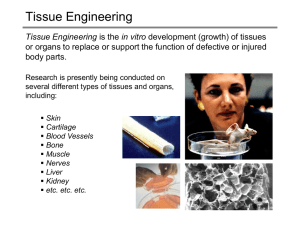
Tissue engineering

Tissue engineering is the use of a combination of cells, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to improve or replace biological functions. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field in its own right.While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e., bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. The term has also been applied to efforts to perform specific biochemical functions using cells within an artificially-created support system (e.g. an artificial pancreas, or a bio artificial liver). The term regenerative medicine is often used synonymously with tissue engineering, although those involved in regenerative medicine place more emphasis on the use of stem cells or progenitor cells to produce tissues.