Week 9 CELL WALLS are found in plant cells. They are made up of
... A collection of cells that perform the same function and that work together is called a TISSUE. Examples of tissues include nervous tissues, muscle tissue, and blood tissue. ...
... A collection of cells that perform the same function and that work together is called a TISSUE. Examples of tissues include nervous tissues, muscle tissue, and blood tissue. ...
Muscle Cells
... A. Unicellular Organisms- Single cell organisms including yeast, algae, bacteria and protozoa (Kingdom – Protista) B. Multicellular Organisms- organisms made of more than one cell 1. Cell specialization- the ways different cells have evolved to perform different tasks 2. Specialized Animal and Plant ...
... A. Unicellular Organisms- Single cell organisms including yeast, algae, bacteria and protozoa (Kingdom – Protista) B. Multicellular Organisms- organisms made of more than one cell 1. Cell specialization- the ways different cells have evolved to perform different tasks 2. Specialized Animal and Plant ...
science chapter 1 questions
... 1A. the cell wall helps to protect and support the cell. The cell membrane controls what goes in and out of the cell. 1b. the cellulose is a material in the cell wall. 1c. the cellulose gives the wall strength. 2a. Ribosomes: It makes proteins Golgi: it gets proteins packet them and distributes them ...
... 1A. the cell wall helps to protect and support the cell. The cell membrane controls what goes in and out of the cell. 1b. the cellulose is a material in the cell wall. 1c. the cellulose gives the wall strength. 2a. Ribosomes: It makes proteins Golgi: it gets proteins packet them and distributes them ...
AIM: How is the body organized?
... A group of cells working together form a tissue. Ex: Muscle cells working together form muscle tissue, skin cells working together form skin tissue. ...
... A group of cells working together form a tissue. Ex: Muscle cells working together form muscle tissue, skin cells working together form skin tissue. ...
Botany review What adaptive advantage does the large surface area
... What tissue is found in leaf veins? In which layer of cells in a leaf does most photosynthesis occur? What are the primary functions of leaves, stems, and roots? Which cells control the stomata opening? What are stomata? What materials are transported by xylem and phloem? Which types of cells are fo ...
... What tissue is found in leaf veins? In which layer of cells in a leaf does most photosynthesis occur? What are the primary functions of leaves, stems, and roots? Which cells control the stomata opening? What are stomata? What materials are transported by xylem and phloem? Which types of cells are fo ...
Nanotechnology and Heath: The use of nanostructure DDS
... The ability of the body to restore its integrity subsequent to many different kinds of injury is essential for the maintenance of life. Any living organism, in its constant interaction with the environment and with other organisms, eventually faces adverse situations, such as harsh climatic conditio ...
... The ability of the body to restore its integrity subsequent to many different kinds of injury is essential for the maintenance of life. Any living organism, in its constant interaction with the environment and with other organisms, eventually faces adverse situations, such as harsh climatic conditio ...
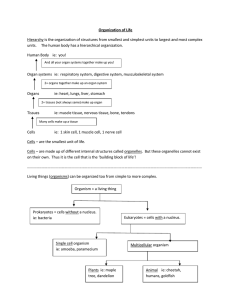
Organization of Life Hierarchy is the organization of structures from
... Organ systems ie: respiratory system, digestive system, musculoskeletal system 2+ organs together make up an organ system ...
... Organ systems ie: respiratory system, digestive system, musculoskeletal system 2+ organs together make up an organ system ...
Chapter 13: Cell Response to Surface Chemistry for Tissue
... Cell Response to Surface Chemistry for Tissue Engineering Applications M. Heyde* and C. Fotea ...
... Cell Response to Surface Chemistry for Tissue Engineering Applications M. Heyde* and C. Fotea ...
HW#1: Grey cell green
... 2. Why can’t a single-cell grow to be the size of an elephant? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. You’ve discovered a new single-celle ...
... 2. Why can’t a single-cell grow to be the size of an elephant? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. You’ve discovered a new single-celle ...
Tissue engineering

Tissue engineering is the use of a combination of cells, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to improve or replace biological functions. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field in its own right.While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e., bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. The term has also been applied to efforts to perform specific biochemical functions using cells within an artificially-created support system (e.g. an artificial pancreas, or a bio artificial liver). The term regenerative medicine is often used synonymously with tissue engineering, although those involved in regenerative medicine place more emphasis on the use of stem cells or progenitor cells to produce tissues.