Biology 109: Biology Today Laboratory 2 A literature review of cells
... Have a full understanding of the (many) events involved in a typical cell life cycle. Have extra help to study for Exam One!! ...
... Have a full understanding of the (many) events involved in a typical cell life cycle. Have extra help to study for Exam One!! ...
Biology Study guide
... Microscope use and calculations Diagram with parts and function Total magnification Field of view ...
... Microscope use and calculations Diagram with parts and function Total magnification Field of view ...
Mitosis
... Occurs in ALL eukaryotic cells except sex cells Broken down into the following stages: ...
... Occurs in ALL eukaryotic cells except sex cells Broken down into the following stages: ...
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
... The Metaphase to Anaphase Transition (also called the cyclosome NOT the tumor suppressor!!) ...
... The Metaphase to Anaphase Transition (also called the cyclosome NOT the tumor suppressor!!) ...
Mitosis Webquest
... 7. List the stages of mitosis (Notice – there’s an extra phase here…”prometaphase” – sometimes that is added as an “in-between” phase between prophase and metaphase. In our class you are only responsible for knowing PMAT) Write the steps of the cell cycle below. Provide one MAJOR thing that occurs i ...
... 7. List the stages of mitosis (Notice – there’s an extra phase here…”prometaphase” – sometimes that is added as an “in-between” phase between prophase and metaphase. In our class you are only responsible for knowing PMAT) Write the steps of the cell cycle below. Provide one MAJOR thing that occurs i ...
vocab flip chart - Effingham County Schools
... a membrane covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life. ...
... a membrane covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life. ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide
... _____ 9.One of the major differences in the cell division of prokaryotic cells compared to eukaryotic cell is that: a. cytokinesis does not occur in prokaryotic cells. b. genes are not replicated on chromosomes in prokaryotic cells. c. the duplicated chromosomes are attached to the nuclear membrane ...
... _____ 9.One of the major differences in the cell division of prokaryotic cells compared to eukaryotic cell is that: a. cytokinesis does not occur in prokaryotic cells. b. genes are not replicated on chromosomes in prokaryotic cells. c. the duplicated chromosomes are attached to the nuclear membrane ...
Cell Cycle-Binary Fission, Regulation
... • As the chromosome is replicated the copied regions move to the opposite ends of cell. • The bacteria grows until it reaches 2x its original size. • Fission only allows bacteria to produce identical copies, which leaves them vulnerable to being wiped out. • They do have ways to achieve genetic diff ...
... • As the chromosome is replicated the copied regions move to the opposite ends of cell. • The bacteria grows until it reaches 2x its original size. • Fission only allows bacteria to produce identical copies, which leaves them vulnerable to being wiped out. • They do have ways to achieve genetic diff ...
engulf bacteria to change its shape has A white blood cell nourish
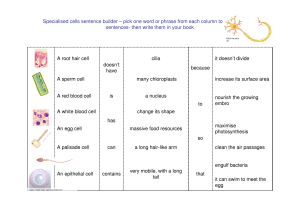
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
Check answers
... Growth; Cell is doing its job Includes G1, S, G2 Nuclear envelope/nucleoli are visible DNA is less condensed as chromatin S- DNA makes copy G2- Make organelles needed for new cell (EX: Centrosomes/centrioles are copied ) PROPHASE (1st dividing phase) Chromatin condenses; Chromosomes first visible Nu ...
... Growth; Cell is doing its job Includes G1, S, G2 Nuclear envelope/nucleoli are visible DNA is less condensed as chromatin S- DNA makes copy G2- Make organelles needed for new cell (EX: Centrosomes/centrioles are copied ) PROPHASE (1st dividing phase) Chromatin condenses; Chromosomes first visible Nu ...
Cell Review Cell Theory Levels of Organization Organelle
... 6. Cell Membrane – Barrier of protection for the cell (Allows nutrients in and waste out) 8. Vacuole – Stores water and waste. 4. Chloroplasts – Makes food for the plant cell. 2. Cell Wall – Only in plants to give a rigid structure and add barrier of protection. 7. Ribosome – Creates protein Plant C ...
... 6. Cell Membrane – Barrier of protection for the cell (Allows nutrients in and waste out) 8. Vacuole – Stores water and waste. 4. Chloroplasts – Makes food for the plant cell. 2. Cell Wall – Only in plants to give a rigid structure and add barrier of protection. 7. Ribosome – Creates protein Plant C ...
Mitosis
... • nuclear membrane starts to form around each gp of daughter chromosomes • cell appears to have 2 nuclei (nucleus) ...
... • nuclear membrane starts to form around each gp of daughter chromosomes • cell appears to have 2 nuclei (nucleus) ...
The cell cycle
... The pattern cannot be distinguished in hamster cells because G1 is too short. ...
... The pattern cannot be distinguished in hamster cells because G1 is too short. ...
Basic Bio 3
... M. This is a tiny fluid-filled cavity in the cytoplasm. It can be used for storage of biochemicals. ...
... M. This is a tiny fluid-filled cavity in the cytoplasm. It can be used for storage of biochemicals. ...
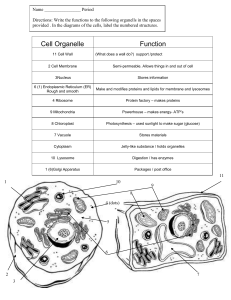
Cell Organelle
... Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
... Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
Text Book Reading Questions…The Cell
... NAME: ___________________________ Text Book Reading Questions…The Cell!!! (See chapter 7 in your book to answer these questions) 1. The size of a typical cell is _______________. 2. Who was the first person to observe “cells”? 3. The cell theory states: (3 parts) 4. What is the timeline for the hist ...
... NAME: ___________________________ Text Book Reading Questions…The Cell!!! (See chapter 7 in your book to answer these questions) 1. The size of a typical cell is _______________. 2. Who was the first person to observe “cells”? 3. The cell theory states: (3 parts) 4. What is the timeline for the hist ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.