1. Cell The basic unit (or piece) of life. 2. Cell Theory All living
... Cell or organism that must eat food; cannot create its own food. (Example: animals eat food to survive.) ...
... Cell or organism that must eat food; cannot create its own food. (Example: animals eat food to survive.) ...
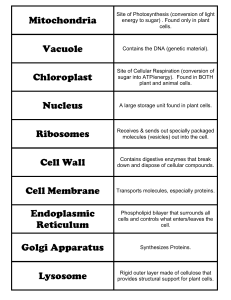
Cell Organelle Card Sort
... Gives the cell membrane added support. Gives plant cells their box-like shape. ...
... Gives the cell membrane added support. Gives plant cells their box-like shape. ...
By570PresAnimated
... – Identifying scientist who contributed to the Cell Theory – Defining important genetic terms (homozygous, dominant, etc) – Calculating genotypic and phenotypic percentages and ratios using a Punnett’s Square – Explaining relationships among DNA, genes & chromosomes – Relating genetic disorders and ...
... – Identifying scientist who contributed to the Cell Theory – Defining important genetic terms (homozygous, dominant, etc) – Calculating genotypic and phenotypic percentages and ratios using a Punnett’s Square – Explaining relationships among DNA, genes & chromosomes – Relating genetic disorders and ...
Live Casino Roulette System
... Cells have different shapes, according to the work they do. Cells might look like cubes, rods, snowflakes, or even blobs of jelly. Every cell’s outer layer is a thin skin called a membrane. It has openings to let materials in. Most of the cell is made of a jellylike fluid called cytoplasm. Cytoplasm ...
... Cells have different shapes, according to the work they do. Cells might look like cubes, rods, snowflakes, or even blobs of jelly. Every cell’s outer layer is a thin skin called a membrane. It has openings to let materials in. Most of the cell is made of a jellylike fluid called cytoplasm. Cytoplasm ...
CELL DIVISION
... 2. Mitosis: Cell reproduces itself; get two daughter cells 3. Cytokinesis: Cell’s cytoplasm divides, creating a new cell -Prior to cell division, must always have a duplication of genetic material DNA Replication Chromosome: Structure that contains genetic material passed from generation to genera ...
... 2. Mitosis: Cell reproduces itself; get two daughter cells 3. Cytokinesis: Cell’s cytoplasm divides, creating a new cell -Prior to cell division, must always have a duplication of genetic material DNA Replication Chromosome: Structure that contains genetic material passed from generation to genera ...
The Cell Cycle
... Instructions: Create a diagram that illustrates the continuous set of events (stages) that occur during the Cell Cycle. Your illustration should be proportional with the amount of time the cell remains in each stage. Draw arrows to illustrate the correct sequence in which the stages occur. Write a b ...
... Instructions: Create a diagram that illustrates the continuous set of events (stages) that occur during the Cell Cycle. Your illustration should be proportional with the amount of time the cell remains in each stage. Draw arrows to illustrate the correct sequence in which the stages occur. Write a b ...
Morphogenesis – the process of cell development.
... Morphogenesis – the process of cell development. 1. All cells begin as a single cell 2. A horse grows and develops into an adult with millions of cells through: a. Cell growth b. Mitosis c. Cell division 3. Many different types of cells in full grown horses. a. Differences in cell is controlled by g ...
... Morphogenesis – the process of cell development. 1. All cells begin as a single cell 2. A horse grows and develops into an adult with millions of cells through: a. Cell growth b. Mitosis c. Cell division 3. Many different types of cells in full grown horses. a. Differences in cell is controlled by g ...
BIO508: Cell Biology, Trimester III, 2016 Assignment Topics for
... Assignment Topics for Students 1. The 2016 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine to Prof. Yoshinori Ohsumi for his discoveries of mechanisms for autophagy. 2. Different types of cancer in Fiji: Factors concerning for emerging cancer in Fiji. 3. Principles of Electron Microscopy: Contribution in Cell ...
... Assignment Topics for Students 1. The 2016 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine to Prof. Yoshinori Ohsumi for his discoveries of mechanisms for autophagy. 2. Different types of cancer in Fiji: Factors concerning for emerging cancer in Fiji. 3. Principles of Electron Microscopy: Contribution in Cell ...
1. Name 4 bases (subunits) of DNA. 2. Write series of bases will
... b) Golgi apparatus, lysosome, cell wall c) Chloroplast, nucleus, mitochondria d) Central vacuole, chloroplast, cell wall ...
... b) Golgi apparatus, lysosome, cell wall c) Chloroplast, nucleus, mitochondria d) Central vacuole, chloroplast, cell wall ...
7.013 LEGO MITOSIS/MEIOSIS SECTION
... 2. How many cells does this process produce at the end? 3. How do the chromosomes line up at the middle of the cell before the first division? 4. Are the new cells identical to the original or are they genetically different? 5. Compare the total amount of DNA in each new cell with the amount of DNA ...
... 2. How many cells does this process produce at the end? 3. How do the chromosomes line up at the middle of the cell before the first division? 4. Are the new cells identical to the original or are they genetically different? 5. Compare the total amount of DNA in each new cell with the amount of DNA ...
Vacuoles
... Keeps harmful materials away from cell Holds cell waste Stores protein for seeds Lets plants have leaves and flowers because of the high pressure in the cell • Vacuoles are found in plant and fungi cells ...
... Keeps harmful materials away from cell Holds cell waste Stores protein for seeds Lets plants have leaves and flowers because of the high pressure in the cell • Vacuoles are found in plant and fungi cells ...
Unit 6 - Lonoke School District
... Cell functions are regulated. Regulation occurs both through changes in the activity of the functions performed by proteins and through the selective expression of individual genes. This regulation allows cells to respond to their environment and to control and coordinate cell growth and division. ...
... Cell functions are regulated. Regulation occurs both through changes in the activity of the functions performed by proteins and through the selective expression of individual genes. This regulation allows cells to respond to their environment and to control and coordinate cell growth and division. ...
Homework: Respiration - Fall River Public Schools
... 1. How is a human muscle cell similar to a plant cell? a. They both have cell walls for protection. b. They both move with flagella. c. They both need energy. d. They both consume oxygen. 2. Which of the following best describes respiration? a. When cells divide to make new cells. b. When materials ...
... 1. How is a human muscle cell similar to a plant cell? a. They both have cell walls for protection. b. They both move with flagella. c. They both need energy. d. They both consume oxygen. 2. Which of the following best describes respiration? a. When cells divide to make new cells. b. When materials ...
The Cell Cycle - Lake Stevens High School / Overview
... ◦ Eukaryotes--gametes (sperm and egg) meiosis (non-identical cells) ...
... ◦ Eukaryotes--gametes (sperm and egg) meiosis (non-identical cells) ...
• Individual chromosomes are made up of 2 identical strands of
... The whole cell cycle of body cells typically lasts from 8 to 24 hours in humans. As the pie chart shows, the part of the cell during which the nucleus of the cell is dividing (mitosis) occupies approximately 10% of the time taken for the whole cycle. The Cytokinesis phase (part of the division phase ...
... The whole cell cycle of body cells typically lasts from 8 to 24 hours in humans. As the pie chart shows, the part of the cell during which the nucleus of the cell is dividing (mitosis) occupies approximately 10% of the time taken for the whole cycle. The Cytokinesis phase (part of the division phase ...
Layout
... In order to meet the Given Signal to interference ratio, We need to try N( Reuse factor) with different combination of Sectoring(60 120 180 360) and through this calculating Number of First level interfering channels n. The aim here is to minimize the Reuse factor N. ...
... In order to meet the Given Signal to interference ratio, We need to try N( Reuse factor) with different combination of Sectoring(60 120 180 360) and through this calculating Number of First level interfering channels n. The aim here is to minimize the Reuse factor N. ...
Cell Size Limitations
... Movement from higher concentration to lower concentration Larger the distance, slower the diffusion rate A cell 20 cm would require months for nutrients to get to the center ...
... Movement from higher concentration to lower concentration Larger the distance, slower the diffusion rate A cell 20 cm would require months for nutrients to get to the center ...
Raven (7th) Guided Notes Chapter 11
... 21. What cell conditions are being monitored at the G1/S checkpoint? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 22. What is the G2/M checkpoint and where does it fit into the cell cycle? ______ ...
... 21. What cell conditions are being monitored at the G1/S checkpoint? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 22. What is the G2/M checkpoint and where does it fit into the cell cycle? ______ ...
The Cell Cycle
... • G1 check point before S phase (DNA replication) can start, pass if: – Nutrients sufficient – Growth factors present- there is a need for more cells – Cell is big enough – DNA is undamaged ...
... • G1 check point before S phase (DNA replication) can start, pass if: – Nutrients sufficient – Growth factors present- there is a need for more cells – Cell is big enough – DNA is undamaged ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.