Bio07_TR_U03_CH10.QXD
... • How is the cell cycle regulated? • How are cancer cells different from other cells? ...
... • How is the cell cycle regulated? • How are cancer cells different from other cells? ...
The eukaryotic cell cycle
... Isolation of cell-division cycle (CDC) genes from a S. cerevisiae genomic library by functional complementation of cdc mutants ...
... Isolation of cell-division cycle (CDC) genes from a S. cerevisiae genomic library by functional complementation of cdc mutants ...
(null): Can You Identify These Cell Structures.doc, filename=Can
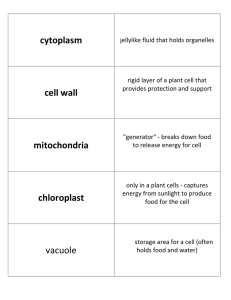
... You can find me in the cytoplasm Or attached to the E.R.’s wall What am I?__________________ I’ve been called a “storage tank” ...
... You can find me in the cytoplasm Or attached to the E.R.’s wall What am I?__________________ I’ve been called a “storage tank” ...
Meiosis And Mitosis - Bloomfield Public Schools
... The process of Meiosis Meiosis is the process by which sex cells divide. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. They line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Then move to opposite ends of the cell. 2 new cells are formed. Again, they line up in the middle. Then they divide and ...
... The process of Meiosis Meiosis is the process by which sex cells divide. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. They line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Then move to opposite ends of the cell. 2 new cells are formed. Again, they line up in the middle. Then they divide and ...
Cell Cycle - Canyon ISD
... There are several factors that regulate the cell cycle and assure a cell divides correctly. Before a cell divides, the DNA is checked to make sure it has replicated correctly. If DNA does not copy itself correctly, a gene mutation occurs. Neighboring cells also communicate with dividing cells to re ...
... There are several factors that regulate the cell cycle and assure a cell divides correctly. Before a cell divides, the DNA is checked to make sure it has replicated correctly. If DNA does not copy itself correctly, a gene mutation occurs. Neighboring cells also communicate with dividing cells to re ...
1. Describe two functions of centromere during mitosis. 2. a) Look at
... formation during the mitotic cell cycle. ...
... formation during the mitotic cell cycle. ...
Test Review for DNA, Cell Cycle, and Mitosis The
... What is a spindle and what is it used for? What is a centriole? What does it do with regards to cell division? List the phases of mitosis in order. What are the 2 main stages of cell division? What is mitosis and what happens there? What is cytokinesis and what happens there? What comes “after” cyto ...
... What is a spindle and what is it used for? What is a centriole? What does it do with regards to cell division? List the phases of mitosis in order. What are the 2 main stages of cell division? What is mitosis and what happens there? What is cytokinesis and what happens there? What comes “after” cyto ...
The Cell Cycle
... • THE LIFE OF A CELL CAN BE BROKEN DOWN INTO TWO MAJOR STAGES: INTERPHASE AND CELL DIVISION (M PHASE) • DURING INTERPHASE, THE CELL PERFORMS NORMAL FUNCTIONS AND PREPARES FOR DIVISION • INTERPHASE IS MADE UP OF THREE PHASES: G1 – CELL GROWS AND ...
... • THE LIFE OF A CELL CAN BE BROKEN DOWN INTO TWO MAJOR STAGES: INTERPHASE AND CELL DIVISION (M PHASE) • DURING INTERPHASE, THE CELL PERFORMS NORMAL FUNCTIONS AND PREPARES FOR DIVISION • INTERPHASE IS MADE UP OF THREE PHASES: G1 – CELL GROWS AND ...
Mitosis, Cell division and aging
... How to remember the different stages of the cell cycle, and the 4 phases of mitosis? Make this pledge: ...
... How to remember the different stages of the cell cycle, and the 4 phases of mitosis? Make this pledge: ...
Mitosis Lab Activity: 1. Diagram a cell in interphase, prophase
... 5. Calculate the time a cell spends in each phase. Consider that it takes, on average, 24 hours (or 1,440 minutes) for onion root tip cells to complete the cell cycle. You can calculate the amou ...
... 5. Calculate the time a cell spends in each phase. Consider that it takes, on average, 24 hours (or 1,440 minutes) for onion root tip cells to complete the cell cycle. You can calculate the amou ...
cell theory
... Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of structure All living things are composed of cells Unicellular and multi cellular all cells come from pre-existing cell Important organs in a cell Nuclease: contains the cells DNA brain of the cell Mitochondria: site of respiring provides the energy for the c ...
... Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of structure All living things are composed of cells Unicellular and multi cellular all cells come from pre-existing cell Important organs in a cell Nuclease: contains the cells DNA brain of the cell Mitochondria: site of respiring provides the energy for the c ...
CELL ORGANELLES 1. How does the structure of a cell suggest its
... 1. How does the structure of a cell suggest its function? ...
... 1. How does the structure of a cell suggest its function? ...
TEACHER NOTES AND ANSWERS Section 5.1
... 2. cell growth, normal functions, replications of organelles 3. synthesis 4. copies DNA 5. gap 2 6. additional growth and carrying out of normal functions 7. mitosis 8. cell division 9. prophase 10. metaphase 11. anaphase 12. telophase 13. cytokinesis 14. mitosis 15. interphase Cells divide at diffe ...
... 2. cell growth, normal functions, replications of organelles 3. synthesis 4. copies DNA 5. gap 2 6. additional growth and carrying out of normal functions 7. mitosis 8. cell division 9. prophase 10. metaphase 11. anaphase 12. telophase 13. cytokinesis 14. mitosis 15. interphase Cells divide at diffe ...
Quiz D - exam Q`s
... D. Glycogen 2. mRNA is A. A double-stranded molecule B. Found only in eukaryotic cells C. Found exclusively in the nucleus D. Formed during transcription of DNA 3. Lipids are A. Used as an energy source B. Involved in active transport C. Part of glycoproteins D. Transported by rough ER ...
... D. Glycogen 2. mRNA is A. A double-stranded molecule B. Found only in eukaryotic cells C. Found exclusively in the nucleus D. Formed during transcription of DNA 3. Lipids are A. Used as an energy source B. Involved in active transport C. Part of glycoproteins D. Transported by rough ER ...
Unit 2 Review: Cells
... 7) In the space below, draw an animal cell in each phase of mitosis and cytokinesis. Assume the animal cell has 4 chromosomes (2 pairs). Include, where appropriate, centrioles, spindle fibers, nuclear membrane, and nucleolus. ...
... 7) In the space below, draw an animal cell in each phase of mitosis and cytokinesis. Assume the animal cell has 4 chromosomes (2 pairs). Include, where appropriate, centrioles, spindle fibers, nuclear membrane, and nucleolus. ...
Chapter 12 – The Cell Cycle – Homework
... 10. Chemicals, such as colchicine from the Autumn Crocus plant, are known to disrupt spindle fibers. What affect will this have on a cell undergoing mitosis? What will be the result? ...
... 10. Chemicals, such as colchicine from the Autumn Crocus plant, are known to disrupt spindle fibers. What affect will this have on a cell undergoing mitosis? What will be the result? ...
Chapter 9 How Cells Reproduce
... checks for DNA errors Figure 2: p53 re-enforces G1 and G2 cell cycle arrest after DNA damage through the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/CIPI Mdm2 and Bax are other p53 transcriptional targets, with Mdm2 regulating p53 levels and Bax mediating apoptosis ...
... checks for DNA errors Figure 2: p53 re-enforces G1 and G2 cell cycle arrest after DNA damage through the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/CIPI Mdm2 and Bax are other p53 transcriptional targets, with Mdm2 regulating p53 levels and Bax mediating apoptosis ...
File
... Chapter 12 – Cell Cycle and Mitosis 1. How are the three subphases of interphase alike? How are they different? 2. What key event happens during the S phase? 3. Is binary fission the same as mitosis? Explain. 4. During prometaphase, the nuclear envelope disappears. Where does it go? 5. Imagine a cel ...
... Chapter 12 – Cell Cycle and Mitosis 1. How are the three subphases of interphase alike? How are they different? 2. What key event happens during the S phase? 3. Is binary fission the same as mitosis? Explain. 4. During prometaphase, the nuclear envelope disappears. Where does it go? 5. Imagine a cel ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.