Meiosis & Mitosis Process
... chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. Then line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Move to upset ends of the cell. Two new cells are formed. Line up in the center of the cell. Then the chromosomes divide and move upset of the cel ...
... chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. Then line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Move to upset ends of the cell. Two new cells are formed. Line up in the center of the cell. Then the chromosomes divide and move upset of the cel ...
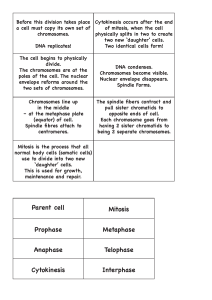
Parent cell Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
... Before this division takes place Cytokinesis occurs after the end a cell must copy its own set of of mitosis, when the cell chromosomes. physically splits in two to create two new ‘daughter’ cells. DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at ...
... Before this division takes place Cytokinesis occurs after the end a cell must copy its own set of of mitosis, when the cell chromosomes. physically splits in two to create two new ‘daughter’ cells. DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at ...
Ch. 7 Rd Assign.
... You will be quizzed over the information in this assignment. Use your books and notes Reading Assignment: Pages 169-173 1. List three scientists that contributed to the study of cells and what each of their contributions where. ...
... You will be quizzed over the information in this assignment. Use your books and notes Reading Assignment: Pages 169-173 1. List three scientists that contributed to the study of cells and what each of their contributions where. ...
Cell Cycle Check
... 5. Centromeres attach to centrioles. 6. The nuclear membrane reforms in anaphase. 7. Chromatids form as a result of replication. 8. Centromeres break apart in telophase. 9. DNA strands in eukaryotic cells exist in multiples of two. 10. The “poles” are creaked by the spindle fibers. 11. Two pairs of ...
... 5. Centromeres attach to centrioles. 6. The nuclear membrane reforms in anaphase. 7. Chromatids form as a result of replication. 8. Centromeres break apart in telophase. 9. DNA strands in eukaryotic cells exist in multiples of two. 10. The “poles” are creaked by the spindle fibers. 11. Two pairs of ...
I`m a real “powerhouse” That`s plain to see. I break down food To
... I’m strong and stiff Getting through me is tough. I’m found only in plants, But I guess that’s enough. CELL WALL ...
... I’m strong and stiff Getting through me is tough. I’m found only in plants, But I guess that’s enough. CELL WALL ...
The Cell Theory
... __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 2. Why didn’t anyone know about cells before the late 17th century? __________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
... __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 2. Why didn’t anyone know about cells before the late 17th century? __________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
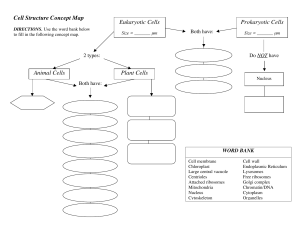
Study Guide for Cell Structure, Function, and Division
... 3. What is the cell theory? 4. List differences between prokaryote and eukaryote. 5. What is the magnification of an electron microscope? 6. What is the difference between active and passive transport 7. Define the following transport mechanisms: a. Diffusion b. Osmosis c. Facilitated Diffusion ...
... 3. What is the cell theory? 4. List differences between prokaryote and eukaryote. 5. What is the magnification of an electron microscope? 6. What is the difference between active and passive transport 7. Define the following transport mechanisms: a. Diffusion b. Osmosis c. Facilitated Diffusion ...
MS Word worksheet
... 1. Regarding the mitotic phase of the cell cycle: How does its length compare to the S phase of the cycle? ...
... 1. Regarding the mitotic phase of the cell cycle: How does its length compare to the S phase of the cycle? ...
How Do Cells Divide? 1. Regarding the mitotic phase of the cell
... 1. Regarding the mitotic phase of the cell cycle: How does its length compare to the S phase of the cycle? What are the two major events that occur during the mitotic phase? What "choices" does a cell have at the end of the mitotic phase? How does the nature of chromatin change at the end of the mit ...
... 1. Regarding the mitotic phase of the cell cycle: How does its length compare to the S phase of the cycle? What are the two major events that occur during the mitotic phase? What "choices" does a cell have at the end of the mitotic phase? How does the nature of chromatin change at the end of the mit ...
The Process of Cell Division
... Name the main events of the cell cycle. Describe what happens during the four stages of mitosis. Describe the process of cytokinesis. ...
... Name the main events of the cell cycle. Describe what happens during the four stages of mitosis. Describe the process of cytokinesis. ...
Mitosis PPT
... • Cell grows in size. • Genetic material (DNA) is replicated (S Phase of Interphase) in preparation for division. ...
... • Cell grows in size. • Genetic material (DNA) is replicated (S Phase of Interphase) in preparation for division. ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.