chapter 12.rtf - HCC Learning Web
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If cells in the process of dividing are subjected to colchicine, a drug that interferes with the formation of the spindle apparatus, at which stage will mitosis be arrested? A) anaphase B) inter ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If cells in the process of dividing are subjected to colchicine, a drug that interferes with the formation of the spindle apparatus, at which stage will mitosis be arrested? A) anaphase B) inter ...
Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... The cell cycle can be regulated at any of the phases, but typically, variability in the length of the cell cycle is based on cells exiting the cell cycle at the G1 and G2 phases. ...
... The cell cycle can be regulated at any of the phases, but typically, variability in the length of the cell cycle is based on cells exiting the cell cycle at the G1 and G2 phases. ...
AP Biology - Mitosis and Meiosis Experiments
... 2. Observe at least 200 different cells in the apical meristem region. 3. Catagorize each cell as to the cell cycle phase (Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis). 4. Calculate the percentage of cells in each phase and the time (in minutes) that the onion cells are in each ...
... 2. Observe at least 200 different cells in the apical meristem region. 3. Catagorize each cell as to the cell cycle phase (Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis). 4. Calculate the percentage of cells in each phase and the time (in minutes) that the onion cells are in each ...
Cell Cycle Control System - Santa Susana High School
... • Cdks - cyclin-dependent kinase (remember that a kinase is an enzyme that activate or inactivate by phosphorylating) – cyclin is always present in the cell and is activated when phosphorylated – synthesized during the S-phase ...
... • Cdks - cyclin-dependent kinase (remember that a kinase is an enzyme that activate or inactivate by phosphorylating) – cyclin is always present in the cell and is activated when phosphorylated – synthesized during the S-phase ...
Cancer and the cell cycle
... • Cancer is caused by unregulated cell growth. Cancer is not contagious. However, people can be genetically more likely to develop cancer. Most cells spend a much greater amount of time in interphase and not duplicating. ...
... • Cancer is caused by unregulated cell growth. Cancer is not contagious. However, people can be genetically more likely to develop cancer. Most cells spend a much greater amount of time in interphase and not duplicating. ...
Product Information
... The required dose of G 418-BC for the selection of resistant cells varies in dependence of the cell type and the current phase of the cell cycle. Thereby a cell in the interphase (“resting phase”) of G 418-BC is less affected than in the mitosis (“separating phase”). But also on separating-active ce ...
... The required dose of G 418-BC for the selection of resistant cells varies in dependence of the cell type and the current phase of the cell cycle. Thereby a cell in the interphase (“resting phase”) of G 418-BC is less affected than in the mitosis (“separating phase”). But also on separating-active ce ...
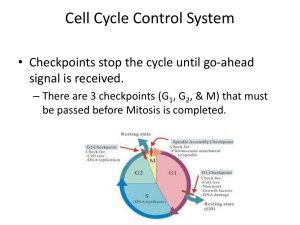
Cell Cycle Control System
... signal is received. – There are 3 checkpoints (G1, G2, & M) that must be passed before Mitosis is completed. ...
... signal is received. – There are 3 checkpoints (G1, G2, & M) that must be passed before Mitosis is completed. ...
Biology Final Semester 1 Study Guide
... 71. Where does the calvin cycle take place? 72. Products of calvin cycle 73. sequence of cellular respiration 74. equation for respiration 75. glycolysis—how many ATPs, what does it start with? 76. lactic acid ferm. 77. Alcoholic ferm. 78. Oxygen debt 79. after 90 secs. Of activity how can our bodie ...
... 71. Where does the calvin cycle take place? 72. Products of calvin cycle 73. sequence of cellular respiration 74. equation for respiration 75. glycolysis—how many ATPs, what does it start with? 76. lactic acid ferm. 77. Alcoholic ferm. 78. Oxygen debt 79. after 90 secs. Of activity how can our bodie ...
CHAPTER 12 THE CELL CYCLE
... 2. Explain how chromatin, chromosomes and genomes relate to one another 3. Describe the difference between a somatic cell and a gamete. The Mitotic Cell Cycle 1. Describe the process of binary fission in bacteria. 2. List the phases of the cell cycle and describe the sequence of events that occurs d ...
... 2. Explain how chromatin, chromosomes and genomes relate to one another 3. Describe the difference between a somatic cell and a gamete. The Mitotic Cell Cycle 1. Describe the process of binary fission in bacteria. 2. List the phases of the cell cycle and describe the sequence of events that occurs d ...
Cell Cycle Analysis Questions
... 1. What 2 things does cell division (mitosis) do for multicellular organisms? 2. What is the cell cycle? How many stages are there? Name the stages. 3. What is interphase? Roughly how much of the cell’s life cycle will be spent in interphase? 4. During what part of interphase is DNA replicated (or s ...
... 1. What 2 things does cell division (mitosis) do for multicellular organisms? 2. What is the cell cycle? How many stages are there? Name the stages. 3. What is interphase? Roughly how much of the cell’s life cycle will be spent in interphase? 4. During what part of interphase is DNA replicated (or s ...
Mitosis - Mahopac Voyagers!
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
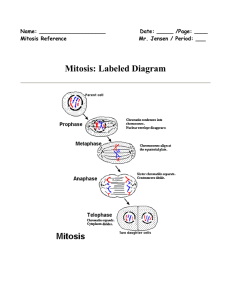
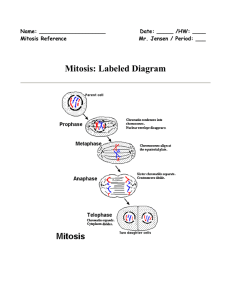
Mitosis: Labeled Diagram
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A cell, whether it is one part of a larger
... The entire process is best studied in stages, but remember they are a continual process! IPMAT - an anagram for remembering the stages. INTERPHASE Interphase is not really a stage in mitosis, but the part of the cell cycle immediately preceding it (the S phase from the diagram). ...
... The entire process is best studied in stages, but remember they are a continual process! IPMAT - an anagram for remembering the stages. INTERPHASE Interphase is not really a stage in mitosis, but the part of the cell cycle immediately preceding it (the S phase from the diagram). ...
Unit 2 Part1 wksht
... come from __________________________________ and all organisms are made of _____________. ...
... come from __________________________________ and all organisms are made of _____________. ...
Cell Cycle & Cancer
... The Cell Cycle • Interphase Cell Growth and Preparation for Division • Mitosis Division of the Nucleus and its DNA • Cytokinesis Division of the Cytoplasm ...
... The Cell Cycle • Interphase Cell Growth and Preparation for Division • Mitosis Division of the Nucleus and its DNA • Cytokinesis Division of the Cytoplasm ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.