Cell Growth and Division
... • Cells divide to allow the organism to grow and to repair damaged tissue • Cells grow, then divide. Why don’t they keep growing? • Large cells do not have enough DNA to function. • Large cells could not diffuse oxygen and nutrients efficiently. *Agar block lab* ...
... • Cells divide to allow the organism to grow and to repair damaged tissue • Cells grow, then divide. Why don’t they keep growing? • Large cells do not have enough DNA to function. • Large cells could not diffuse oxygen and nutrients efficiently. *Agar block lab* ...
Mitosis-Cell Division
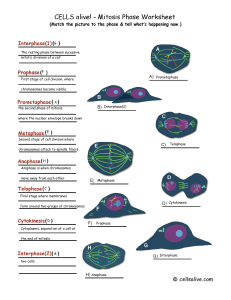
... c. Anaphase- Chromosomes are __________. _____________ move towards the “poles” of the cell ...
... c. Anaphase- Chromosomes are __________. _____________ move towards the “poles” of the cell ...
Curtis Science Dept. Biology Name: Period: Date: Chapter 10: Cell
... Chapter 10: Cell Growth and Division Vocabulary CARDS ...
... Chapter 10: Cell Growth and Division Vocabulary CARDS ...
Discover Cell Cycle Video
... 1. What phase duplicates the cytoplasmic organelles? 2. What phase duplicates the DNA? 3. What phase checks that duplication is completed? 4. What do we need to do to grow bigger? 5. What are the 4 phases of mitosis? 6. What are the structures at the ends of the cell during prophase? 7. During proph ...
... 1. What phase duplicates the cytoplasmic organelles? 2. What phase duplicates the DNA? 3. What phase checks that duplication is completed? 4. What do we need to do to grow bigger? 5. What are the 4 phases of mitosis? 6. What are the structures at the ends of the cell during prophase? 7. During proph ...
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Objectives (Chapter 12)
... After reading this chapter and attending class, you should be able to: ...
... After reading this chapter and attending class, you should be able to: ...
review for second six weeks common assessment
... 9. How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? 10. Know importance of meiosis 11. Functions of xylem and phloem 12. Describe the type of seed that would be dispersed by wind? insects? water? 13. What is the equation for photosynthesis? Where does it occur? 14. Levels of cell organization and define ...
... 9. How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? 10. Know importance of meiosis 11. Functions of xylem and phloem 12. Describe the type of seed that would be dispersed by wind? insects? water? 13. What is the equation for photosynthesis? Where does it occur? 14. Levels of cell organization and define ...
Cell Cycle - Southington Public Schools
... Cell Cycle—the sequence of growth and division of a cell. It is a cycle b/c it repeats itself over and over. Stages of the cell cycle ...
... Cell Cycle—the sequence of growth and division of a cell. It is a cycle b/c it repeats itself over and over. Stages of the cell cycle ...
Test 1 Study Guide
... 3. What must a cell do before it can pass from gap 2 to mitosis? 4. What is the main difference between healthy cells and cancerous cells? 5. When is DNA replicated? 6. During ______________ the contents inside the cell divide. 7. Why is mitosis important when you are injured? 8. What is a malignant ...
... 3. What must a cell do before it can pass from gap 2 to mitosis? 4. What is the main difference between healthy cells and cancerous cells? 5. When is DNA replicated? 6. During ______________ the contents inside the cell divide. 7. Why is mitosis important when you are injured? 8. What is a malignant ...
cell cycle - Explore Biology
... 12. What is the G1 checkpoint and where does it fit into the cycle? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 13. What evidence is there that regulation is chemical in nature? ________________ ...
... 12. What is the G1 checkpoint and where does it fit into the cycle? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 13. What evidence is there that regulation is chemical in nature? ________________ ...
Where do new cells come from?
... Explain the origin of new cells. Describe the structure and function of DNA. ...
... Explain the origin of new cells. Describe the structure and function of DNA. ...
The Cell Cycle - Haiku Learning
... What are the 3 phases of the cell cycle? What are the 4 phases of Mitosis? What is differentiation? ...
... What are the 3 phases of the cell cycle? What are the 4 phases of Mitosis? What is differentiation? ...
Online Onion Root Tips
... http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/activities/cell_cycle/cell_cycle.html ...
... http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/activities/cell_cycle/cell_cycle.html ...
HW#1: Grey cell green
... 2. Why can’t a single-cell grow to be the size of an elephant? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. You’ve discovered a new single-celle ...
... 2. Why can’t a single-cell grow to be the size of an elephant? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. You’ve discovered a new single-celle ...
Chapter 6 Exam – Part II
... Mitosis Study Guide - Biology 1. __________ is a process of eukaryotic cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. 2. Name the steps of the cell cycle in order. 3. Name the steps of mitosis in order. 4. What kind of cells undergo mitosis? 5. How man ...
... Mitosis Study Guide - Biology 1. __________ is a process of eukaryotic cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. 2. Name the steps of the cell cycle in order. 3. Name the steps of mitosis in order. 4. What kind of cells undergo mitosis? 5. How man ...
Cell cycle
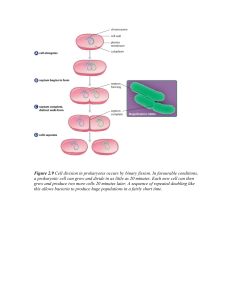
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.