Name - wwphs
... Which of the following features of cell division are very different for animal and plant cells? ...
... Which of the following features of cell division are very different for animal and plant cells? ...
Cell Cycle: Mitosis Labeling
... 1. What moves the chromatids during mitosis? __________________________________ 2. What do the spindle fibers attach to in order to pull apart the sister chromatids? _______________________________________________________________________ 3. What are the four phases of mitosis (in order)? ___________ ...
... 1. What moves the chromatids during mitosis? __________________________________ 2. What do the spindle fibers attach to in order to pull apart the sister chromatids? _______________________________________________________________________ 3. What are the four phases of mitosis (in order)? ___________ ...
powerpoint jeopardy
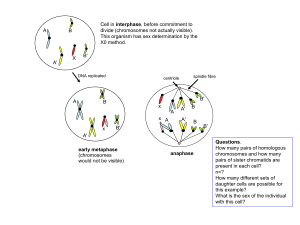
... In an animal with 90 chromosomes, it is the number of chromosomes contributed by the mother. ...
... In an animal with 90 chromosomes, it is the number of chromosomes contributed by the mother. ...
I`m a real “powerhouse.” That`s plain to see. I break down food to
... I’m a series of tubes, found throughout the cell. I transport proteins and other things as well ...
... I’m a series of tubes, found throughout the cell. I transport proteins and other things as well ...
Mitosis Cell Division
... Why do cells undergo Cell Division? Cell size- larger cells are less efficient, cells divide to keep cells small Growth of an organism- the more cells an organism has, the larger it is. All multicelled life starts as a single cell after fertilization then grows. Reproduction- single celled organism ...
... Why do cells undergo Cell Division? Cell size- larger cells are less efficient, cells divide to keep cells small Growth of an organism- the more cells an organism has, the larger it is. All multicelled life starts as a single cell after fertilization then grows. Reproduction- single celled organism ...
Notes Outline: How Cells Divide (4
... When a healthy, living cell reaches a certain size, it will either stop growing or divide ________________________________________________________________________ In bacteria, the hereditary information is encoded in a single circle of DNA ____________________________________________________________ ...
... When a healthy, living cell reaches a certain size, it will either stop growing or divide ________________________________________________________________________ In bacteria, the hereditary information is encoded in a single circle of DNA ____________________________________________________________ ...
Cancer - Wsfcs
... -a characteristic of normal cells in which cells will stop dividing (by entering a G0 phase) when they make contact with a surface -cancer cells do not have this characteristic ...
... -a characteristic of normal cells in which cells will stop dividing (by entering a G0 phase) when they make contact with a surface -cancer cells do not have this characteristic ...
Biology Chapter 7
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
The Magic Universe of Cells Directions
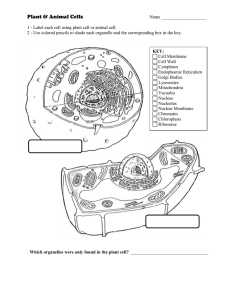
... draw, label, and define the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. You need to include at least: nucleus, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, vacuoles, centrioles, lysosomes, nuclear envelope, and chromatin. If there is ...
... draw, label, and define the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. You need to include at least: nucleus, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, vacuoles, centrioles, lysosomes, nuclear envelope, and chromatin. If there is ...
Robert Hooke (1665) saw cells while looking at a piece of cork
... Robert Hooke (1665) saw cells while looking at a piece of cork under the microscope. Anton Von Leeuwenhoek (1673) saw animalcules (“little animals”) in pond scum. Theodor Schwann (mid 1800’s) Cell Theory: 1. all organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. the cell is the basic unit of life in al ...
... Robert Hooke (1665) saw cells while looking at a piece of cork under the microscope. Anton Von Leeuwenhoek (1673) saw animalcules (“little animals”) in pond scum. Theodor Schwann (mid 1800’s) Cell Theory: 1. all organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. the cell is the basic unit of life in al ...
1. All living things are made of cell
... 10. Contrast osmosis and diffusion? -Osmosis is the passive movement of water across a cell membrane -Diffusion is the passive movement of substances other than water across a cell ...
... 10. Contrast osmosis and diffusion? -Osmosis is the passive movement of water across a cell membrane -Diffusion is the passive movement of substances other than water across a cell ...
Modeling the Phases of the Cell Cycle
... In a growing root, the cells at the tip of the root are constantly dividing. Because each cell divides independently of the others, a root tip contains many cells at different phases of the cell cycle. This makes a root tip an excellent tissue in which to study the cell cycle. In this investigation, ...
... In a growing root, the cells at the tip of the root are constantly dividing. Because each cell divides independently of the others, a root tip contains many cells at different phases of the cell cycle. This makes a root tip an excellent tissue in which to study the cell cycle. In this investigation, ...
Cells - biologybi
... control center for all activity. Nucleoplasm- contains chromosomes and DNA. Nucleolus- contains RNA. Cell membrane- separates the cell from other cells and allows molecules to pass through. Cell wall- protects and supports the cell. (Plant cells only) ...
... control center for all activity. Nucleoplasm- contains chromosomes and DNA. Nucleolus- contains RNA. Cell membrane- separates the cell from other cells and allows molecules to pass through. Cell wall- protects and supports the cell. (Plant cells only) ...
CELLULAR GROWTH 3 Reasons Why Cells Are Small
... B. DNA synthesis G2 checkpoint DNA synthesis is checked C. Mitosis checkpoint Signals the start of First Growth Phase ...
... B. DNA synthesis G2 checkpoint DNA synthesis is checked C. Mitosis checkpoint Signals the start of First Growth Phase ...
Cell Cycle Background
... and through the cell Cells need small size for simple communication with other cells and within themselves ...
... and through the cell Cells need small size for simple communication with other cells and within themselves ...
Mitosis Online Lab
... Use the following formula to calculate the duration of each stage: % of cells in stage x 1440 minutes (24 hours) = ___________ minutes of cell cycle spent in stage Analysis Questions ...
... Use the following formula to calculate the duration of each stage: % of cells in stage x 1440 minutes (24 hours) = ___________ minutes of cell cycle spent in stage Analysis Questions ...
3.2 Powerpoint
... • 2. List two reasons why cells divide. • 3. Volume: Cytoplasm :: Surface Area :________ ...
... • 2. List two reasons why cells divide. • 3. Volume: Cytoplasm :: Surface Area :________ ...
Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis
... Mitosis: nucleus is divided into two cells Cytokinesis: Cytoplasm divides ...
... Mitosis: nucleus is divided into two cells Cytokinesis: Cytoplasm divides ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.