Biology Notes 3-2
... 1. All living things are made of 1 or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit(s) of life’s function and structure. 3. All cells arise from existing cells. Most Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye: they are 5µm-20 µm (micrometers in diameter) Cells must have a high Surface Area-to-Volume ratio (S ...
... 1. All living things are made of 1 or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit(s) of life’s function and structure. 3. All cells arise from existing cells. Most Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye: they are 5µm-20 µm (micrometers in diameter) Cells must have a high Surface Area-to-Volume ratio (S ...
Cell Cycle & Mitosis
... workings of DNA and the processes it codes for DNA codes for the RNA and proteins that determine what happens in the cell, too big, and the DNA cannot keep up DNA overload ...
... workings of DNA and the processes it codes for DNA codes for the RNA and proteins that determine what happens in the cell, too big, and the DNA cannot keep up DNA overload ...
Answers to Review Questions
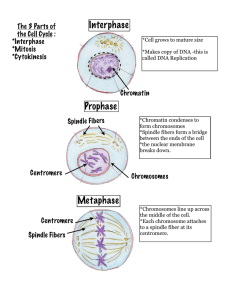
... 2. What are the stages of the cell cycle? During which stage does DNA replicate? The cell cycle is composed of interphase (G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phases) and the M phase (mitosis and cytokinesis). The genetic material is duplicated during interphase (the S phase, specifically). 3. What are sister ...
... 2. What are the stages of the cell cycle? During which stage does DNA replicate? The cell cycle is composed of interphase (G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phases) and the M phase (mitosis and cytokinesis). The genetic material is duplicated during interphase (the S phase, specifically). 3. What are sister ...
Cell Structure and Function Worksheet
... Cell Structure and Function Worksheet 1. Construct a Venn diagram of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells and give at least one example of each type of cell. ...
... Cell Structure and Function Worksheet 1. Construct a Venn diagram of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells and give at least one example of each type of cell. ...
Biology Chapter 7 Notes I. Cell Theory A. Discovered since 1600 by
... Only can magnify to a maximum of 1000x and light refracts therefore cannot see extremely small cells or parts of small cells ...
... Only can magnify to a maximum of 1000x and light refracts therefore cannot see extremely small cells or parts of small cells ...
Chapter 12
... Thus, all the DNA must be copied so there are two complete sets, one set for each daughter cell. The outline of the replication process for a chromosome is given in Figure 12.4 (p. 220): Chromosome duplication and distribution during mitosis. Remember the terms used in this Figure! ...
... Thus, all the DNA must be copied so there are two complete sets, one set for each daughter cell. The outline of the replication process for a chromosome is given in Figure 12.4 (p. 220): Chromosome duplication and distribution during mitosis. Remember the terms used in this Figure! ...
Lecture Quiz 2, Biol-1, C. Briggs, ver 9.13 (1pt each, unless noted
... Lecture Quiz 2, Biol-1, C. Briggs, ver 9.13 (1pt each, unless noted) ...
... Lecture Quiz 2, Biol-1, C. Briggs, ver 9.13 (1pt each, unless noted) ...
Bio07_TR_U03_CH10.QXD
... • Color the phase in which most cell growth occurs blue. • Color the phase in which DNA replication occurs red. • Color the phase in which preparation for mitosis occurs yellow. • Color the phase in which mitosis and cytokinesis occur orange. ...
... • Color the phase in which most cell growth occurs blue. • Color the phase in which DNA replication occurs red. • Color the phase in which preparation for mitosis occurs yellow. • Color the phase in which mitosis and cytokinesis occur orange. ...
Name
... 8. Telophase: How many daughter nuclei are formed during Telophase? _______ Are the chromosomes visible inside each new nuclei? _______ What happens to the cell’s membrane near the end of telophase? ...
... 8. Telophase: How many daughter nuclei are formed during Telophase? _______ Are the chromosomes visible inside each new nuclei? _______ What happens to the cell’s membrane near the end of telophase? ...
Genetic Control of Protein Synthesis, Cell Function, and Cell
... proceeds in both directions. • Entire genome is replicated once - further replication is blocked • involves DNA polymerase and other proteins that function to unwind and stabilize the DNA and “prime” DNA replication of the “lagging” strand. ...
... proceeds in both directions. • Entire genome is replicated once - further replication is blocked • involves DNA polymerase and other proteins that function to unwind and stabilize the DNA and “prime” DNA replication of the “lagging” strand. ...
mitosis
... require more DNA (to make the necessary proteins) than can be supported by a single nucleus. ...
... require more DNA (to make the necessary proteins) than can be supported by a single nucleus. ...
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
... organism has a specific number of chromosomes. During cell division chromatin condenses into chromosomes. In order for each cell to get the right number the chromosomes have to double ...
... organism has a specific number of chromosomes. During cell division chromatin condenses into chromosomes. In order for each cell to get the right number the chromosomes have to double ...
Interphase Prophase Metaphase
... form chromosomes *Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell *the nuclear membrane breaks down. ...
... form chromosomes *Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell *the nuclear membrane breaks down. ...
The Cell Cycle
... much longer than that--up to a year in certain ________ cells. Generally, however, for fastdividing mammalian cells, the length of the cycle is approximately _______ hours. ...
... much longer than that--up to a year in certain ________ cells. Generally, however, for fastdividing mammalian cells, the length of the cycle is approximately _______ hours. ...
Cell Test Review
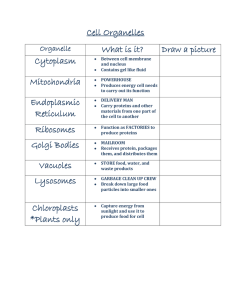
... Cells work together to form a __________________. Tissue What organelles are used to store water, food, or waste materials? Vacuoles What threadlike structures contain information about the organism? Chromosomes What is the jelly-like substance between the cell membrane and the nucleus? Cytoplasm Wh ...
... Cells work together to form a __________________. Tissue What organelles are used to store water, food, or waste materials? Vacuoles What threadlike structures contain information about the organism? Chromosomes What is the jelly-like substance between the cell membrane and the nucleus? Cytoplasm Wh ...
Levels of Organization/Cells/Cell Organelle Notes
... Their are five levels of organization in living organisms beginning with the process going from cells tissue organ organ system organism. 2. Cells are the structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. 3. The Cell Theory states that all living things are made up of cells. 4. The t wo ...
... Their are five levels of organization in living organisms beginning with the process going from cells tissue organ organ system organism. 2. Cells are the structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. 3. The Cell Theory states that all living things are made up of cells. 4. The t wo ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.