Framework for Cell division 2
... When watching the yeast cells under the microscope, do all cells look the same? If the cells do not look the same, what is happening? Explain why the cells in a person’s body are all genetically identical? If meiosis did not occur, why would sexual reproduction be a problem? Can you describe the sta ...
... When watching the yeast cells under the microscope, do all cells look the same? If the cells do not look the same, what is happening? Explain why the cells in a person’s body are all genetically identical? If meiosis did not occur, why would sexual reproduction be a problem? Can you describe the sta ...
Get a PDF of this story
... the cell remains in an uncontrolled state. By principles governing differentiation pinpointing this noise and its “off” switch, in complex animals.” ...
... the cell remains in an uncontrolled state. By principles governing differentiation pinpointing this noise and its “off” switch, in complex animals.” ...
Postassessment Study Guide
... ______________ are cells that DO NOT have a nucleus. ______________ is a type of material that is made from specialized cells. ______________ is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus. ______________ the process where dead organism are broken down and important materials are returned to the e ...
... ______________ are cells that DO NOT have a nucleus. ______________ is a type of material that is made from specialized cells. ______________ is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus. ______________ the process where dead organism are broken down and important materials are returned to the e ...
7.1_Life_is_Cellular
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek Early master lens maker Made early microscopes Looked at pond water. ...
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek Early master lens maker Made early microscopes Looked at pond water. ...
Class 3
... THAN OUR BODY; FREES UP WATER TO GO TO CELL; TOO MUCH = HEMOLYSIS (0.45% NaCl) HYPERTONIC – MORE SOLUTE THAN OUR BODY; PULLS WATER TOWARD IT; TOO MUCH DEHYDRATED CELL = CRENATION (3% NaCl) ...
... THAN OUR BODY; FREES UP WATER TO GO TO CELL; TOO MUCH = HEMOLYSIS (0.45% NaCl) HYPERTONIC – MORE SOLUTE THAN OUR BODY; PULLS WATER TOWARD IT; TOO MUCH DEHYDRATED CELL = CRENATION (3% NaCl) ...
Cells: The Basic Unit of Life
... It directs all of the cells activities. Inside the nucleus is the nucleolus. Also in the nucleus there are chromosomes which contain all of the genetic information (the stuff passed down by the parent cells). The chromosomes look like balled up strings. ...
... It directs all of the cells activities. Inside the nucleus is the nucleolus. Also in the nucleus there are chromosomes which contain all of the genetic information (the stuff passed down by the parent cells). The chromosomes look like balled up strings. ...
organelles - La Paz Wiki
... with enzymes that can break down molecules into smaller ones that can be used. • If a lysosome breaks open inside the cell, it dissolves the cell itself! ...
... with enzymes that can break down molecules into smaller ones that can be used. • If a lysosome breaks open inside the cell, it dissolves the cell itself! ...
Multi-celled and Single-Celled Notes
... passes directly form cell to cell. They must live close to a water source The lack of a transport system also prevents them from growing very tall. Many barely reach a few inches full-grown. Mosses Liverworts Hornworts ...
... passes directly form cell to cell. They must live close to a water source The lack of a transport system also prevents them from growing very tall. Many barely reach a few inches full-grown. Mosses Liverworts Hornworts ...
4/20 & 4/21 - 7th Grade Agenda
... Golgi Bodies can be thought of as the The ___________ cell’s mailroom. It receive proteins from endoplasmic reticulum and distribute them to other parts of the cell. ...
... Golgi Bodies can be thought of as the The ___________ cell’s mailroom. It receive proteins from endoplasmic reticulum and distribute them to other parts of the cell. ...
Centrioles are self-replicating organelles made up
... outside the cell into simple compounds, which are transferred to the cytoplasm as new cell-building materials. Microfilaments - Microfilaments are solid rods made of globular proteins called actin. These filaments are primarily structural in function and are an important component of the cytoskeleto ...
... outside the cell into simple compounds, which are transferred to the cytoplasm as new cell-building materials. Microfilaments - Microfilaments are solid rods made of globular proteins called actin. These filaments are primarily structural in function and are an important component of the cytoskeleto ...
CELL DIVISION
... CELL DIVISION As cells grow they must divide Why?…(write your own answer) DNA and cell division Both daughter cells need a complete set of DNA, nothing missing, nothing extra DNA starts out as Chromatin (spread out DNA molecules) ...
... CELL DIVISION As cells grow they must divide Why?…(write your own answer) DNA and cell division Both daughter cells need a complete set of DNA, nothing missing, nothing extra DNA starts out as Chromatin (spread out DNA molecules) ...
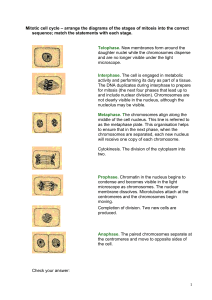
Mitotic cell cycle – arrange the diagrams of the stages of mitosis into
... Interphase. The cell is engaged in metabolic activity and performing its duty as part of a tissue. The DNA duplicates during interphase to prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Chromosomes are not clearly visible in the nucleus, although the nucleol ...
... Interphase. The cell is engaged in metabolic activity and performing its duty as part of a tissue. The DNA duplicates during interphase to prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Chromosomes are not clearly visible in the nucleus, although the nucleol ...
Chapter 1 The Science of Biology
... Using the light microscope Electron microscopes Scientists prokaryotes and eukaryotes cell organelles, structure and function Identification of cell structures from a diagram plant cell and animal cell characteristics Cell membrane- fluid mosaic model- structure and function Passive transport- diffu ...
... Using the light microscope Electron microscopes Scientists prokaryotes and eukaryotes cell organelles, structure and function Identification of cell structures from a diagram plant cell and animal cell characteristics Cell membrane- fluid mosaic model- structure and function Passive transport- diffu ...
TEACHER NOTES AND ANSWERS Section 5.5
... Organ systems: organs that carry out similar functions Organs: groups of tissues that work together to perform similar or related functions Tissues: groups of cells that work together to perform a similar function Cells: smallest, most basic structural unit of life; typically become specialized home ...
... Organ systems: organs that carry out similar functions Organs: groups of tissues that work together to perform similar or related functions Tissues: groups of cells that work together to perform a similar function Cells: smallest, most basic structural unit of life; typically become specialized home ...
Mitosis ppt
... identical daughter cells Divided into 4 stages of Mitosis: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase ...
... identical daughter cells Divided into 4 stages of Mitosis: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase ...
Cells ( Think of the analogy of the factory) Cell parts are called
... **Nucleolus builds ribosomes which build proteins. Differences between Plant and Animal Cells ...
... **Nucleolus builds ribosomes which build proteins. Differences between Plant and Animal Cells ...
High
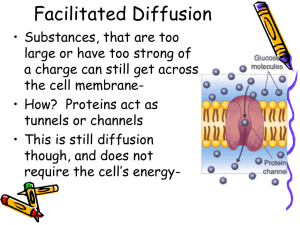
... Diffusion makes materials move through the cell membrane and the cells environment from___________ concentration to ____________concentration ...
... Diffusion makes materials move through the cell membrane and the cells environment from___________ concentration to ____________concentration ...
sParamecium: Paramecium is a genus of unicellular ciliate protozoa
... Paramecium is a genus of unicellular ciliate protozoa. It is covered with simple cilia, allowing the cell to move. If the Paramecium hits an obstacle it moves back, turns slightly and goes forward again. If it runs into the solid object again, it will repeat this process until it can get past the ob ...
... Paramecium is a genus of unicellular ciliate protozoa. It is covered with simple cilia, allowing the cell to move. If the Paramecium hits an obstacle it moves back, turns slightly and goes forward again. If it runs into the solid object again, it will repeat this process until it can get past the ob ...
1. Nutrients enter cells through the _____. 2. Which cell organelle is
... 5. In a living organism, what is an organ? A. a group of similar cells that perform a common function B. the shell or skin of an organism C. a structure composed of a number of tissues that work together to perform a specific task D. functional unit, or building block, of all organisms; smallest uni ...
... 5. In a living organism, what is an organ? A. a group of similar cells that perform a common function B. the shell or skin of an organism C. a structure composed of a number of tissues that work together to perform a specific task D. functional unit, or building block, of all organisms; smallest uni ...
Biology - edl.io
... Cheek cell + methylene blue (make your own) 4. Data: - Make drawings of the above observation. - Label the name and the total magnification of each drawing - Color the drawings - Label the following cell structures: cytoplasm, nucleus, vacuole, chloroplast, cell wall, cell membrane ...
... Cheek cell + methylene blue (make your own) 4. Data: - Make drawings of the above observation. - Label the name and the total magnification of each drawing - Color the drawings - Label the following cell structures: cytoplasm, nucleus, vacuole, chloroplast, cell wall, cell membrane ...
Stage 1: INTERPHASE
... • Interphase is the first stage of the cell cycle • During interphase, cells grow, make copies of their DNA, and prepare to divide into two new cells • CELL CYCLE: The regular sequence of growth and division that cells go through ...
... • Interphase is the first stage of the cell cycle • During interphase, cells grow, make copies of their DNA, and prepare to divide into two new cells • CELL CYCLE: The regular sequence of growth and division that cells go through ...
The Cell Cycle: Interphase, Mitosis
... and draw you’re the cells under scanning power or low power. As you can clearly see, it is too difficult to make out the different phases of mitosis under low power ...
... and draw you’re the cells under scanning power or low power. As you can clearly see, it is too difficult to make out the different phases of mitosis under low power ...
File
... Conclude the type of organelle affected by the symptoms portrayed by the cell. Hypothesize the effects on the cells of hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic blood concentrations in patients given a range of symptoms. Students will be able to: Compare and contrast the general structures of plant a ...
... Conclude the type of organelle affected by the symptoms portrayed by the cell. Hypothesize the effects on the cells of hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic blood concentrations in patients given a range of symptoms. Students will be able to: Compare and contrast the general structures of plant a ...
Cells
... Cells Cell Theory: 1. Every organism is composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the smallest unit that has the properties of life. 3. The continuity of life arises directly from the growth and division of single cells. ...
... Cells Cell Theory: 1. Every organism is composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the smallest unit that has the properties of life. 3. The continuity of life arises directly from the growth and division of single cells. ...