Cells Alive- Internet Lesson
... Objective: You will look at computer models of cells, learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and their components. Navigating the site: Cells.alive has a navigation bar at the left. After accessing the page, click on CELL BIOLOGY on the leftside navigation bar. From here, you will acc ...
... Objective: You will look at computer models of cells, learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and their components. Navigating the site: Cells.alive has a navigation bar at the left. After accessing the page, click on CELL BIOLOGY on the leftside navigation bar. From here, you will acc ...
Microscopes allow us to see inside the cell
... its genetic material. (most multicellular) • PROKARYOTIC cells have its genetic material float throughout the cytoplasm with no nucleus. (most unicellular are prokaryotes) • ORGANELLES are any part of a cell enclosed within its own membrane. ...
... its genetic material. (most multicellular) • PROKARYOTIC cells have its genetic material float throughout the cytoplasm with no nucleus. (most unicellular are prokaryotes) • ORGANELLES are any part of a cell enclosed within its own membrane. ...
Organic Molecules - Riverdale Middle School
... – Cholesterol – found in your blood – Phosopholipids – make up cell membrane ...
... – Cholesterol – found in your blood – Phosopholipids – make up cell membrane ...
Cell Comparison *All in the Family*
... They are were energy (food) is produced so it can be used by all parts of the family (cell). ...
... They are were energy (food) is produced so it can be used by all parts of the family (cell). ...
Oct. 5, 2015 Cells - AP Biology Study Guide
... 3. Contrast the general features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 4. Be able to distinguish the organelles and structures typical of eukaryotic plant and animal cells. 5. Describe the nucleus of eukaryotes with respect to structure and function. 6. Describe the organelles associated with the end ...
... 3. Contrast the general features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 4. Be able to distinguish the organelles and structures typical of eukaryotic plant and animal cells. 5. Describe the nucleus of eukaryotes with respect to structure and function. 6. Describe the organelles associated with the end ...
Cell Organelles and Their Functions
... materials. Animal cell vacuoles form and reform over and over again. ...
... materials. Animal cell vacuoles form and reform over and over again. ...
Horticulture
... • Control Center: regulates activities – Nuclear Membrane: controls materials in and out – Chromosomes: thin, rod-shaped, carry on traits – Nucleolus: makes ribosomes ...
... • Control Center: regulates activities – Nuclear Membrane: controls materials in and out – Chromosomes: thin, rod-shaped, carry on traits – Nucleolus: makes ribosomes ...
Test Review Sheet - Lyndhurst School District
... Word Banks: Be able to label the parts of the cell (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm). Be able to label the parts of the cell membrane (lipids, proteins, carbohydrates). Be able to identify if a cell is in a hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic solution based on what happens to it. Be able to identif ...
... Word Banks: Be able to label the parts of the cell (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm). Be able to label the parts of the cell membrane (lipids, proteins, carbohydrates). Be able to identify if a cell is in a hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic solution based on what happens to it. Be able to identif ...
Cells Alive
... Part A: Bacterial Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button) ...
... Part A: Bacterial Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button) ...
EUKARYOTES ppt
... Cell/plasma membrane allows cell to be selective in what gets in/leaves the cell Separates the cell from its environment Made of a double layer with proteins and ...
... Cell/plasma membrane allows cell to be selective in what gets in/leaves the cell Separates the cell from its environment Made of a double layer with proteins and ...
Cell Theory and Basic Structures - CGW-Life-Science
... Example = plant cells and animal cells Complex cells with organelles and specialization Usually at least 10X bigger than prokaryotes. Prokaryotes “before nucleus” No nucleus, DNA floats around in cytoplasm example = bacteria Simpler or “more primitive” cells Smaller than Eukaryotes ...
... Example = plant cells and animal cells Complex cells with organelles and specialization Usually at least 10X bigger than prokaryotes. Prokaryotes “before nucleus” No nucleus, DNA floats around in cytoplasm example = bacteria Simpler or “more primitive” cells Smaller than Eukaryotes ...
Biology genetics hw Due: 26th November 2013 Name
... see strands that contain a chemical called DNA. A photograph of these strands can be cut up and re-arranged. The diagram shows an arrangement of the strands from a human cell. ...
... see strands that contain a chemical called DNA. A photograph of these strands can be cut up and re-arranged. The diagram shows an arrangement of the strands from a human cell. ...
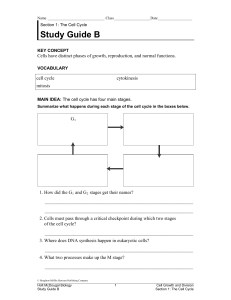
Study Guide B
... 9. Which typically increases faster as a cell grows, surface area or volume? _______________________________________________________________ 10. For cells to stay the same size from generation to generation, what two things must be coordinated? _______________________________________________________ ...
... 9. Which typically increases faster as a cell grows, surface area or volume? _______________________________________________________________ 10. For cells to stay the same size from generation to generation, what two things must be coordinated? _______________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 2 “Cells” Section 1: “Cell Structure
... found on a hereditary material called DNA Usually the largest organelle ...
... found on a hereditary material called DNA Usually the largest organelle ...
Honors Biology Midterm
... 26. Catalase, ligase, polymerase, etc. These are all examples of: 27. Is water a polar compound? 28. Is fructose a monosaccharide? 29. The bonding of water molecules on one another is called: 30. The _________________ of DNA is a nucleotide. 31. Does a decrease in hydrogen ions leads to a decrease i ...
... 26. Catalase, ligase, polymerase, etc. These are all examples of: 27. Is water a polar compound? 28. Is fructose a monosaccharide? 29. The bonding of water molecules on one another is called: 30. The _________________ of DNA is a nucleotide. 31. Does a decrease in hydrogen ions leads to a decrease i ...