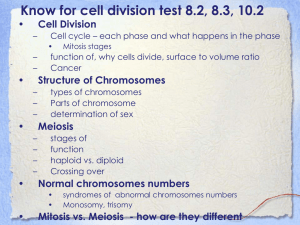
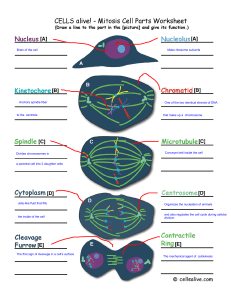
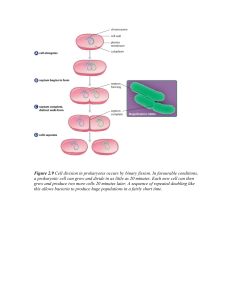
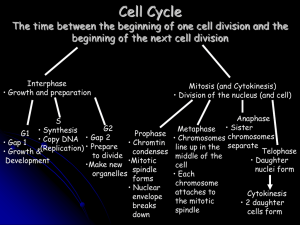
Mitosis-Cell Division
... c. Anaphase- Chromosomes are __________. _____________ move towards the “poles” of the cell ...
... c. Anaphase- Chromosomes are __________. _____________ move towards the “poles” of the cell ...
Discover Cell Cycle Video
... 1. What phase duplicates the cytoplasmic organelles? 2. What phase duplicates the DNA? 3. What phase checks that duplication is completed? 4. What do we need to do to grow bigger? 5. What are the 4 phases of mitosis? 6. What are the structures at the ends of the cell during prophase? 7. During proph ...
... 1. What phase duplicates the cytoplasmic organelles? 2. What phase duplicates the DNA? 3. What phase checks that duplication is completed? 4. What do we need to do to grow bigger? 5. What are the 4 phases of mitosis? 6. What are the structures at the ends of the cell during prophase? 7. During proph ...
Meiosis & Mitosis Process
... chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. Then line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Move to upset ends of the cell. Two new cells are formed. Line up in the center of the cell. Then the chromosomes divide and move upset of the cel ...
... chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. Then line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Move to upset ends of the cell. Two new cells are formed. Line up in the center of the cell. Then the chromosomes divide and move upset of the cel ...
Chapter 6 Exam – Part II
... Mitosis Study Guide - Biology 1. __________ is a process of eukaryotic cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. 2. Name the steps of the cell cycle in order. 3. Name the steps of mitosis in order. 4. What kind of cells undergo mitosis? 5. How man ...
... Mitosis Study Guide - Biology 1. __________ is a process of eukaryotic cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. 2. Name the steps of the cell cycle in order. 3. Name the steps of mitosis in order. 4. What kind of cells undergo mitosis? 5. How man ...
Meiosis And Mitosis - Bloomfield Public Schools
... The process of Meiosis Meiosis is the process by which sex cells divide. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. They line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Then move to opposite ends of the cell. 2 new cells are formed. Again, they line up in the middle. Then they divide and ...
... The process of Meiosis Meiosis is the process by which sex cells divide. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. They line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Then move to opposite ends of the cell. 2 new cells are formed. Again, they line up in the middle. Then they divide and ...
Meiosis & Mitosis process
... The process that occurs in the formation of sex cells (sperm and egg) by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. Then they line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Then they move to opposite ends of the cell. Then two new cells are formed. Th ...
... The process that occurs in the formation of sex cells (sperm and egg) by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. Then they line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Then they move to opposite ends of the cell. Then two new cells are formed. Th ...
review for second six weeks common assessment
... 1. Know stages of Mitosis and what happens in each phase 2. Passive and Active Transport 3. Diffusion, Osmosis 4. Functions of the cell membrane 5. Differences between plant and animal cells 6. What causes cells to stop growing when grown in a petri dish? 7. Cell organelle responsible for photosynth ...
... 1. Know stages of Mitosis and what happens in each phase 2. Passive and Active Transport 3. Diffusion, Osmosis 4. Functions of the cell membrane 5. Differences between plant and animal cells 6. What causes cells to stop growing when grown in a petri dish? 7. Cell organelle responsible for photosynth ...
HW#1: Grey cell green
... 2. Why can’t a single-cell grow to be the size of an elephant? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. You’ve discovered a new single-celle ...
... 2. Why can’t a single-cell grow to be the size of an elephant? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. You’ve discovered a new single-celle ...