![[ ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008815208_1-f64e86c2951532e412da02b66a87cc79-300x300.png)
[ ]
... S. Kirsch and U. Hartmann Multipotent adult progenitor cells (rMAPCs): The imaging of cell differentiation and the influence of nanostructured and functionalized surfaces Multipotent adult progenitor cells (MAPCs), characterized by Verfailles et al. in 2002, are a subpopulation of mesenchymal stem c ...
... S. Kirsch and U. Hartmann Multipotent adult progenitor cells (rMAPCs): The imaging of cell differentiation and the influence of nanostructured and functionalized surfaces Multipotent adult progenitor cells (MAPCs), characterized by Verfailles et al. in 2002, are a subpopulation of mesenchymal stem c ...
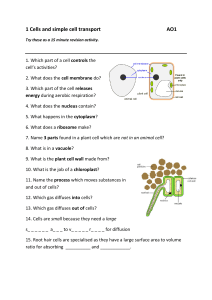
1 Cells and simple cell transport AO1
... 1. Which part of a cell controls the cell’s activities? 2. What does the cell membrane do? 3. Which part of the cell releases energy during aerobic respiration? 4. What does the nucleus contain? 5. What happens in the cytoplasm? 6. What does a ribosome make? 7. Name 3 parts found in a plant cell whi ...
... 1. Which part of a cell controls the cell’s activities? 2. What does the cell membrane do? 3. Which part of the cell releases energy during aerobic respiration? 4. What does the nucleus contain? 5. What happens in the cytoplasm? 6. What does a ribosome make? 7. Name 3 parts found in a plant cell whi ...
CELL CYCLE TEST REVIEW PAP Biology 1. List the three parts of a
... List the three parts of a nucleotide (the monomer of DNA). Which two parts make up the backbone of DNA? What are the base pairing rules for the nitrogen bases? What type of bond holds the N-bases together? What is helicase? What is DNA polymerase? When and why does DNA replication occur in the cell ...
... List the three parts of a nucleotide (the monomer of DNA). Which two parts make up the backbone of DNA? What are the base pairing rules for the nitrogen bases? What type of bond holds the N-bases together? What is helicase? What is DNA polymerase? When and why does DNA replication occur in the cell ...
Tour of the Cell Chapter 6
... Degree programs in cytology-also referred to as cell biology-train students to examine the composition, structure, function and interaction of cells. Curriculum prepares individuals to work in clinical laboratory settings. Students learn basic science principles and complete a clinical practicum. Tr ...
... Degree programs in cytology-also referred to as cell biology-train students to examine the composition, structure, function and interaction of cells. Curriculum prepares individuals to work in clinical laboratory settings. Students learn basic science principles and complete a clinical practicum. Tr ...
cell theory
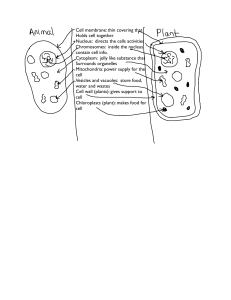
... Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of structure All living things are composed of cells Unicellular and multi cellular all cells come from pre-existing cell Important organs in a cell Nuclease: contains the cells DNA brain of the cell Mitochondria: site of respiring provides the energy for the c ...
... Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of structure All living things are composed of cells Unicellular and multi cellular all cells come from pre-existing cell Important organs in a cell Nuclease: contains the cells DNA brain of the cell Mitochondria: site of respiring provides the energy for the c ...
Unit 2 Cells Test Study Guide
... Answer the following questions using your textbook and notes. Study each of these questions and topics as all will appear on your test. ...
... Answer the following questions using your textbook and notes. Study each of these questions and topics as all will appear on your test. ...
http://en
... CELLS Visit this web page: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_%28biology%29 and answer the questions. ...
... CELLS Visit this web page: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_%28biology%29 and answer the questions. ...
Cells and Microscope Test Study Guide
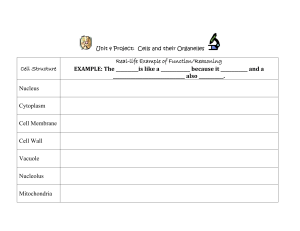
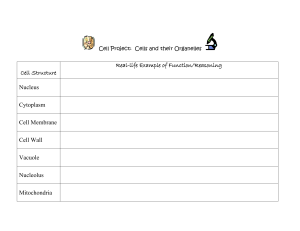
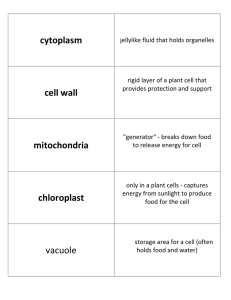
... Use your notes and handouts to help you study! Know different parts of cell and function of each part (what it does) Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Vacuole Mitochondria Chloroplast Cell wall Understand that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things Know what make ...
... Use your notes and handouts to help you study! Know different parts of cell and function of each part (what it does) Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Vacuole Mitochondria Chloroplast Cell wall Understand that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things Know what make ...
CELL ORGANELLES 1. How does the structure of a cell suggest its
... 7. In which kinds of human cells would you expect to find the most mitochondria? The most lysosomes? The most ribosomes? Explain your answers. ...
... 7. In which kinds of human cells would you expect to find the most mitochondria? The most lysosomes? The most ribosomes? Explain your answers. ...
I`m a real “powerhouse” That`s plain to see. I break down food To
... I’m strong and stiff Getting through me is tough. I’m found only in plants, But I guess that’s enough. CELL WALL ...
... I’m strong and stiff Getting through me is tough. I’m found only in plants, But I guess that’s enough. CELL WALL ...
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Objectives (Chapter 12)
... After reading this chapter and attending class, you should be able to: ...
... After reading this chapter and attending class, you should be able to: ...
Where do new cells come from?
... structures and functions of DNA, RNA, and protein. Standard Explanation-DNA-double helixcontains genetic info, RNA-singlestranded, copy of a section of DNA, protein-make up many parts of the body ...
... structures and functions of DNA, RNA, and protein. Standard Explanation-DNA-double helixcontains genetic info, RNA-singlestranded, copy of a section of DNA, protein-make up many parts of the body ...
The Cell Theory
... 1. Explain how cells got their name: _______________________________ __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 2. Why didn’t anyone know about cells before the late 17th century? _____________________________________________ ...
... 1. Explain how cells got their name: _______________________________ __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 2. Why didn’t anyone know about cells before the late 17th century? _____________________________________________ ...