Online Onion Root Tips
... http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/activities/cell_cycle/cell_cycle.html ...
... http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/activities/cell_cycle/cell_cycle.html ...
CELL DIVISION
... *Cell Life Cycle: Series of changes a cell goes through from time it is formed until it divides -Cycle has three major phases: 1. Interphase: Cell grows and carries on normal metabolic functions; longest phase; majority of cell’s life spent here 2. Mitosis: Cell reproduces itself; get two daughter c ...
... *Cell Life Cycle: Series of changes a cell goes through from time it is formed until it divides -Cycle has three major phases: 1. Interphase: Cell grows and carries on normal metabolic functions; longest phase; majority of cell’s life spent here 2. Mitosis: Cell reproduces itself; get two daughter c ...
answers - Biology Resources
... 4 (a) Plant and animal cells have cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, nucleus and chromosomes. (b) Only plant cells have a cell wall, central vacuole and cell sap. 5 The most likely sequence is as shown below. ...
... 4 (a) Plant and animal cells have cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, nucleus and chromosomes. (b) Only plant cells have a cell wall, central vacuole and cell sap. 5 The most likely sequence is as shown below. ...
Slide 1
... – To identify cell parts – To compare and contrast various cell types• Plant and animal cells ...
... – To identify cell parts – To compare and contrast various cell types• Plant and animal cells ...
Cell Review Cell Theory Levels of Organization Organelle
... 6. Cell Membrane – Barrier of protection for the cell (Allows nutrients in and waste out) 8. Vacuole – Stores water and waste. 4. Chloroplasts – Makes food for the plant cell. 2. Cell Wall – Only in plants to give a rigid structure and add barrier of protection. 7. Ribosome – Creates protein Plant C ...
... 6. Cell Membrane – Barrier of protection for the cell (Allows nutrients in and waste out) 8. Vacuole – Stores water and waste. 4. Chloroplasts – Makes food for the plant cell. 2. Cell Wall – Only in plants to give a rigid structure and add barrier of protection. 7. Ribosome – Creates protein Plant C ...
Robert Hooke (1665) saw cells while looking at a piece of cork
... Cell Theory: 1. all organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. the cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. ...
... Cell Theory: 1. all organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. the cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. ...
Important organells in a Cell 2
... Nucleus: contains the cell’s DNA. ‘Brain’ of the cell. Mitochondnon: Site of respiration. Provides the energy for the cell to function. Ribosomes: Site where proteins are made (including enzymes). Vacuole: Storage Cytoplasm: Watery fluid that all the cell organelles float in. _______________________ ...
... Nucleus: contains the cell’s DNA. ‘Brain’ of the cell. Mitochondnon: Site of respiration. Provides the energy for the cell to function. Ribosomes: Site where proteins are made (including enzymes). Vacuole: Storage Cytoplasm: Watery fluid that all the cell organelles float in. _______________________ ...
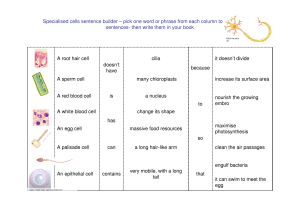
engulf bacteria to change its shape has A white blood cell nourish
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
Chapter 3 Lesson 3.2
... Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Chloroplasts Golgi Complex Vesicle Lysosomes Vacuoles ...
... Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Chloroplasts Golgi Complex Vesicle Lysosomes Vacuoles ...
Asexual Reproduction
... 3. Cell division also enables sexually reproducing organisms to develop from a single cell (fertilized egg, or zygote) into and adult organism. 4. Cell division continues to function in renewal and repair (replacing cells that die from normal wear) ...
... 3. Cell division also enables sexually reproducing organisms to develop from a single cell (fertilized egg, or zygote) into and adult organism. 4. Cell division continues to function in renewal and repair (replacing cells that die from normal wear) ...
Mitosis Cell Division
... Why do cells undergo Cell Division? Cell size- larger cells are less efficient, cells divide to keep cells small Growth of an organism- the more cells an organism has, the larger it is. All multicelled life starts as a single cell after fertilization then grows. Reproduction- single celled organism ...
... Why do cells undergo Cell Division? Cell size- larger cells are less efficient, cells divide to keep cells small Growth of an organism- the more cells an organism has, the larger it is. All multicelled life starts as a single cell after fertilization then grows. Reproduction- single celled organism ...
Cellular Processes
... semi-permeable cell membrane do so by passive transport Diffusion: the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration ...
... semi-permeable cell membrane do so by passive transport Diffusion: the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration ...