Chapter 2 Cells to Systems
... True or False. All plant and animal cells have a cell membrane. What type of cell makes up your skin? ...
... True or False. All plant and animal cells have a cell membrane. What type of cell makes up your skin? ...
By570PresAnimated
... – Identifying scientist who contributed to the Cell Theory – Defining important genetic terms (homozygous, dominant, etc) – Calculating genotypic and phenotypic percentages and ratios using a Punnett’s Square – Explaining relationships among DNA, genes & chromosomes – Relating genetic disorders and ...
... – Identifying scientist who contributed to the Cell Theory – Defining important genetic terms (homozygous, dominant, etc) – Calculating genotypic and phenotypic percentages and ratios using a Punnett’s Square – Explaining relationships among DNA, genes & chromosomes – Relating genetic disorders and ...
Cell Cycle - Southington Public Schools
... a cycle b/c it repeats itself over and over. Stages of the cell cycle ...
... a cycle b/c it repeats itself over and over. Stages of the cell cycle ...
Mitosis Matching Worksheet
... _______ 5. The chromosomes continue to move until they have separated into two groups near the ends of the cell . _______ 6. Chromosome replication takes place. Because of this, each chromosome consists of two identical “sister” chromatids. _______ 7. The DNA starts to unwind in the nucleus. _______ ...
... _______ 5. The chromosomes continue to move until they have separated into two groups near the ends of the cell . _______ 6. Chromosome replication takes place. Because of this, each chromosome consists of two identical “sister” chromatids. _______ 7. The DNA starts to unwind in the nucleus. _______ ...
1. All living things are made of cell
... Cells carry out all of life’s functions and processes. All cells come from other cells. What are the previous statements collectively referred to as? Cell theory ...
... Cells carry out all of life’s functions and processes. All cells come from other cells. What are the previous statements collectively referred to as? Cell theory ...
Organelle Notes
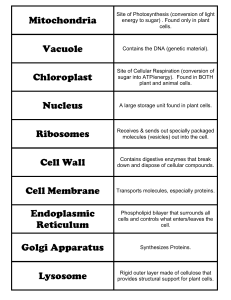
... Essential Question: What organelles are found in Eukaryotic Cells? Notes: Questions/Main Ideas: Nucleus Contains the cell’s DNA Control center of cell, the cell’s brain Ribosomes ...
... Essential Question: What organelles are found in Eukaryotic Cells? Notes: Questions/Main Ideas: Nucleus Contains the cell’s DNA Control center of cell, the cell’s brain Ribosomes ...
Cell specialisation
... 4 Find out why red blood cells have no nucleus, and what effect this has on them. ...
... 4 Find out why red blood cells have no nucleus, and what effect this has on them. ...
Quiz D - exam Q`s
... D. Glycogen 2. mRNA is A. A double-stranded molecule B. Found only in eukaryotic cells C. Found exclusively in the nucleus D. Formed during transcription of DNA 3. Lipids are A. Used as an energy source B. Involved in active transport C. Part of glycoproteins D. Transported by rough ER ...
... D. Glycogen 2. mRNA is A. A double-stranded molecule B. Found only in eukaryotic cells C. Found exclusively in the nucleus D. Formed during transcription of DNA 3. Lipids are A. Used as an energy source B. Involved in active transport C. Part of glycoproteins D. Transported by rough ER ...
Cell Organelle Card Sort
... Gives the cell membrane added support. Gives plant cells their box-like shape. ...
... Gives the cell membrane added support. Gives plant cells their box-like shape. ...
Ch.7.4 Homeostasis Notes
... o Fungi – yeast Multicellular organisms are composed of specialized cells that work together and communicate to maintain homeostasis. Cell specialization – a specific job a cell has within the organism The shape of a cell can determine the role it will have within the organism. Levels of organizat ...
... o Fungi – yeast Multicellular organisms are composed of specialized cells that work together and communicate to maintain homeostasis. Cell specialization – a specific job a cell has within the organism The shape of a cell can determine the role it will have within the organism. Levels of organizat ...
Product Information
... phase of the cell cycle. Thereby a cell in the interphase (“resting phase”) of G 418-BC is less affected than in the mitosis (“separating phase”). But also on separating-active cells, the cells’ death occurs only after 3 to 7 days. The recommended concentration at G 418-BC in the medium has for euka ...
... phase of the cell cycle. Thereby a cell in the interphase (“resting phase”) of G 418-BC is less affected than in the mitosis (“separating phase”). But also on separating-active cells, the cells’ death occurs only after 3 to 7 days. The recommended concentration at G 418-BC in the medium has for euka ...
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A cell, whether it is one part of a larger
... Interphase is not really a stage in mitosis, but the part of the cell cycle immediately preceding it (the S phase from the diagram). ...
... Interphase is not really a stage in mitosis, but the part of the cell cycle immediately preceding it (the S phase from the diagram). ...
Biology Study guide
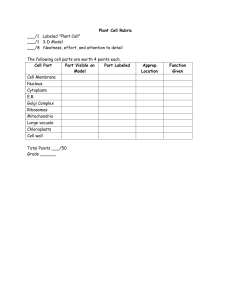
... Microscope use and calculations Diagram with parts and function Total magnification Field of view ...
... Microscope use and calculations Diagram with parts and function Total magnification Field of view ...
I`m a real “powerhouse.” That`s plain to see. I break down food to
... Or so they say. I regulate activities from day to day. ...
... Or so they say. I regulate activities from day to day. ...
The Process of Cell Division
... Name the main events of the cell cycle. Describe what happens during the four stages of mitosis. Describe the process of cytokinesis. ...
... Name the main events of the cell cycle. Describe what happens during the four stages of mitosis. Describe the process of cytokinesis. ...
Chapter 7 test review 2015
... 6. Know the structure and function of the organelles we discussed in class (we talked about 15) ...
... 6. Know the structure and function of the organelles we discussed in class (we talked about 15) ...