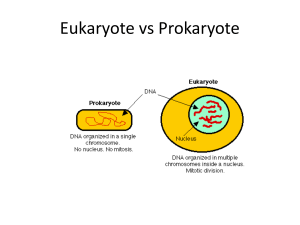
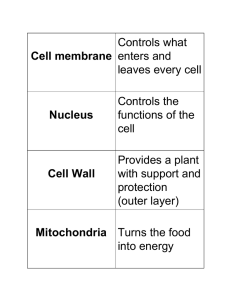
Activity: Cell Levels of Organization
... 4. Answer the following based on the activity in class: a. Main organ of Excretory system _____________ b. Cells which fight off foreign substances ____________ c. Helps blood to clot when there is a cut _____________ d. Blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart ___________ e. Has four ch ...
... 4. Answer the following based on the activity in class: a. Main organ of Excretory system _____________ b. Cells which fight off foreign substances ____________ c. Helps blood to clot when there is a cut _____________ d. Blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart ___________ e. Has four ch ...
study guide for final
... Dominant vs. Recessive traits: dominant appears in every generation Recessive usually skips generations Punnett Squares: need to be able to fill in punnett and determine % & fraction results ** DNA Structure & Mitosis and Meiosis Nucleotides: three parts: sugar, phosphate, base Chargaff’s Rule: A-T, ...
... Dominant vs. Recessive traits: dominant appears in every generation Recessive usually skips generations Punnett Squares: need to be able to fill in punnett and determine % & fraction results ** DNA Structure & Mitosis and Meiosis Nucleotides: three parts: sugar, phosphate, base Chargaff’s Rule: A-T, ...
Organic Molecules - Riverdale Middle School
... Proteins – Organic Molecule • Made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen • Makes up many cell structures (cell membrane and parts of the organelles) • Responsible for many cell functions • Enzymes – a group of proteins that speed up chemical reactions ...
... Proteins – Organic Molecule • Made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen • Makes up many cell structures (cell membrane and parts of the organelles) • Responsible for many cell functions • Enzymes – a group of proteins that speed up chemical reactions ...
CELLS UNIT 1 Learning Targets - Milton
... Draw/create a bacteria, plant, and animal cell and place the appropriate organelles in each cell type. Name the four cell structures in common to all cell types. Describe Anton Van Leeuwen hoek’s contribution to cellular biology. List the three principles of the cell theory. Describe the function of ...
... Draw/create a bacteria, plant, and animal cell and place the appropriate organelles in each cell type. Name the four cell structures in common to all cell types. Describe Anton Van Leeuwen hoek’s contribution to cellular biology. List the three principles of the cell theory. Describe the function of ...
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Objectives (Chapter 12)
... After reading this chapter and attending class, you should be able to: ...
... After reading this chapter and attending class, you should be able to: ...
L4 Prokaryotes eukaryotes and onion cheek preps
... Eukaryotes. • Cytoplasm. Contains all the enzymes needed for all metabolic reactions, since there are no organelles. Contains glycogen (CHO storage) and lipid droplets. • Ribosomes. The smaller (70 S) type, scattered in the ...
... Eukaryotes. • Cytoplasm. Contains all the enzymes needed for all metabolic reactions, since there are no organelles. Contains glycogen (CHO storage) and lipid droplets. • Ribosomes. The smaller (70 S) type, scattered in the ...
Chapter 7 Cells Test Review
... No. They need a host to reproduce. They do not exhibit the characteristics of living things. ...
... No. They need a host to reproduce. They do not exhibit the characteristics of living things. ...
I`m the prokaryotic cell
... From the biggest to the least My simplest form Is in everyday yeast ...
... From the biggest to the least My simplest form Is in everyday yeast ...
Microorganisms as Cells
... structures and chemicals that make it possible for the cell to function. Key structures are the nucleus or nucleoid, where the genetic information, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), needed to make more cells is stored, and the cytoplasm, where the machinery for cell growth and function is present. All ce ...
... structures and chemicals that make it possible for the cell to function. Key structures are the nucleus or nucleoid, where the genetic information, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), needed to make more cells is stored, and the cytoplasm, where the machinery for cell growth and function is present. All ce ...
Chapter 4
... 3. Exocytosis—Vesicles fuse with outer cell membrane for final export outside cell. ...
... 3. Exocytosis—Vesicles fuse with outer cell membrane for final export outside cell. ...
Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology
... this tissue are the skin and the linings of internal organs. Muscle Tissue expands and contracts, allowing the body to move. Nervous Tissue carries messages from all parts of the body to the central nervous system (CNS). ...
... this tissue are the skin and the linings of internal organs. Muscle Tissue expands and contracts, allowing the body to move. Nervous Tissue carries messages from all parts of the body to the central nervous system (CNS). ...
Cell Vocabulary
... Cell-the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism, typically microscopic and consisting of cytoplasm and a nucleus enclosed in a membrane. Microscopic organisms typically consist of a single cell, which is either eukaryotic or prokaryotic. Microscope-an optical instrument used for view ...
... Cell-the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism, typically microscopic and consisting of cytoplasm and a nucleus enclosed in a membrane. Microscopic organisms typically consist of a single cell, which is either eukaryotic or prokaryotic. Microscope-an optical instrument used for view ...
Cell Structure PPT Part 2
... (ECM) or glycocalyx. The ECM is made of glycoproteins such as collagen, proteoglycan, and fibronectins. These glycoproteins are connected to receptor proteins in the cell membrane called integrins. Used for support, adhesion, movement and identity. ...
... (ECM) or glycocalyx. The ECM is made of glycoproteins such as collagen, proteoglycan, and fibronectins. These glycoproteins are connected to receptor proteins in the cell membrane called integrins. Used for support, adhesion, movement and identity. ...
Cells, Tissues, & Organs
... • Cytoskeleton - The “skeleton” of the cell. Consists of microtubules and microfilaments • Vacuoles - Large membranous bubbles which store substances inside the cell ...
... • Cytoskeleton - The “skeleton” of the cell. Consists of microtubules and microfilaments • Vacuoles - Large membranous bubbles which store substances inside the cell ...
Reading Guide 02- Cellular Structures
... Now that we understand the many different types of organisms that make up our food, if we looked at our food and at ourselves under the microscope we would see that they and we are made up of cells – sometimes trillions of them! If we looked even closer, we would see that these cells are also made u ...
... Now that we understand the many different types of organisms that make up our food, if we looked at our food and at ourselves under the microscope we would see that they and we are made up of cells – sometimes trillions of them! If we looked even closer, we would see that these cells are also made u ...
Chapter 4 : Cells - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... for transporting molecules needed in protein making. 6. Ribosomes – makes proteins 7. Golgi body or apparatus – packages proteins and lipids. ...
... for transporting molecules needed in protein making. 6. Ribosomes – makes proteins 7. Golgi body or apparatus – packages proteins and lipids. ...
Cell Organelles - Bath.k12.ky.us
... Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) A system of folded membranes that transport ...
... Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) A system of folded membranes that transport ...
cell test review 15-16 - Mercer Island School District
... B. Understand the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. C. Understand the hierarchy of multicellular organisms (what makes up what) atomsmolecules organellescells tissues organs organ systems multicellular organism D. Review your labs and understand the concepts that were ...
... B. Understand the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. C. Understand the hierarchy of multicellular organisms (what makes up what) atomsmolecules organellescells tissues organs organ systems multicellular organism D. Review your labs and understand the concepts that were ...
Life is Cellular
... 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
... 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
Mitosis Cell Division
... Why do cells undergo Cell Division? Cell size- larger cells are less efficient, cells divide to keep cells small Growth of an organism- the more cells an organism has, the larger it is. All multicelled life starts as a single cell after fertilization then grows. Reproduction- single celled organism ...
... Why do cells undergo Cell Division? Cell size- larger cells are less efficient, cells divide to keep cells small Growth of an organism- the more cells an organism has, the larger it is. All multicelled life starts as a single cell after fertilization then grows. Reproduction- single celled organism ...
All About Cells
... All living things are made up of cells There are millions of cells in your body New cells are constantly growing to replace old cells Cells in our body have many different jobs, but they all contain similar parts called ...
... All living things are made up of cells There are millions of cells in your body New cells are constantly growing to replace old cells Cells in our body have many different jobs, but they all contain similar parts called ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.