1. Nutrients enter cells through the _____. 2. Which cell organelle is
... 10. Which of the following types of organelles are most important in providing a cell with energy? A. nuclei B. vacuoles C. cell membranes D. mitochondria ...
... 10. Which of the following types of organelles are most important in providing a cell with energy? A. nuclei B. vacuoles C. cell membranes D. mitochondria ...
Cell Organelle Organelle Function City Part Cell Membrane
... Cell Organelle Cell Membrane Nucleus ...
... Cell Organelle Cell Membrane Nucleus ...
chapter 4.3 notes
... Attach to spindle fibers at ____________________ What happens during Anaphase? Centromeres ________________ Chromatids separate = new __________________ Cells stretches out What happens during Telophase? Chromosomes stretch out Nuclear ____________________ forms ...
... Attach to spindle fibers at ____________________ What happens during Anaphase? Centromeres ________________ Chromatids separate = new __________________ Cells stretches out What happens during Telophase? Chromosomes stretch out Nuclear ____________________ forms ...
9 Weeks Assessment Review (You can use your notebook, green
... 2. How big are cells? And how does using a model help us understand cells? 3. What is the difference between the plant cell and the animal cell? 4. What does the nucleus do? 5. What does a vacuole do? 6. What does the cell membrane do? 7. What part releases waste from the cell? (think of the mall an ...
... 2. How big are cells? And how does using a model help us understand cells? 3. What is the difference between the plant cell and the animal cell? 4. What does the nucleus do? 5. What does a vacuole do? 6. What does the cell membrane do? 7. What part releases waste from the cell? (think of the mall an ...
Cell
... A structure made up of different kinds of TISSUES that all work together to perform the same JOB. ...
... A structure made up of different kinds of TISSUES that all work together to perform the same JOB. ...
Parts of a Cell Note Sheet:
... Surrounds the nucleus. Controls what enters and exits the nucleus. ...
... Surrounds the nucleus. Controls what enters and exits the nucleus. ...
What are the two basic categories of cells and
... how do they differ? Living cells are divided into two major classifications—prokaryotic and eukaryotic. This division is based on internal complexity. Eukaryotic: The cells of protozoa, higher plants and animals are highly structures. The eukaryotes have a nucleus and comprise all plant and animal c ...
... how do they differ? Living cells are divided into two major classifications—prokaryotic and eukaryotic. This division is based on internal complexity. Eukaryotic: The cells of protozoa, higher plants and animals are highly structures. The eukaryotes have a nucleus and comprise all plant and animal c ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
... an antibody). Antibodies to each determinant are produced in the spleen. One spleen cell produces a single type of antibody. A spleen cell has a finite lifetime and cannot be cultured indefinitely in vitro. B. In the mouse, the antibody-producing cells from the spleen secrete into the blood. The liq ...
... an antibody). Antibodies to each determinant are produced in the spleen. One spleen cell produces a single type of antibody. A spleen cell has a finite lifetime and cannot be cultured indefinitely in vitro. B. In the mouse, the antibody-producing cells from the spleen secrete into the blood. The liq ...
Lectures 18-21 - Biology Courses Server
... 3. Explain the mechanism of muscular contraction using actin, myosin, and ATPase. a. Would a muscle contract in the absence of calcium? Explain. 4. If both the thick and thin filaments of muscle are made up of subunits held together by weak non-covalent bonds, how is it possible for a human being to ...
... 3. Explain the mechanism of muscular contraction using actin, myosin, and ATPase. a. Would a muscle contract in the absence of calcium? Explain. 4. If both the thick and thin filaments of muscle are made up of subunits held together by weak non-covalent bonds, how is it possible for a human being to ...
Video Worksheet: Bill Nye~Cells
... _______ 6. ___________ is our body’s fastest growing organ because we shed millions of these cells every day _______ 7. Genes are made of _______________ _______ 8. Humans have ______ pairs of chromosomes (46 total) _______ 9. Name one large single cell that is very easy to see. _______ 10.Red blood ...
... _______ 6. ___________ is our body’s fastest growing organ because we shed millions of these cells every day _______ 7. Genes are made of _______________ _______ 8. Humans have ______ pairs of chromosomes (46 total) _______ 9. Name one large single cell that is very easy to see. _______ 10.Red blood ...
Cell story book project
... grader would be able to understand. The editor gives you a list of the book requirements. The book needs to include: The two different types of cells (animal and plant) The different parts of the cells (cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes, ribosomes, golgi bodies, endoplas ...
... grader would be able to understand. The editor gives you a list of the book requirements. The book needs to include: The two different types of cells (animal and plant) The different parts of the cells (cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes, ribosomes, golgi bodies, endoplas ...
Marine Biology Cell Assessment 1) Cyanide is a poison that
... different light intensities. A gas was produced by the cell process. The amount of this gas was measured. The rate of the cell process was determined by the amount of gas produced. A graph of the students' measurements is shown below. ...
... different light intensities. A gas was produced by the cell process. The amount of this gas was measured. The rate of the cell process was determined by the amount of gas produced. A graph of the students' measurements is shown below. ...
The Cell Theory .ppt
... Biology • Biology is the study of life • It helps answer the questions: – How do we function? – Why do we act and like the things we do? ...
... Biology • Biology is the study of life • It helps answer the questions: – How do we function? – Why do we act and like the things we do? ...
Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells
... -‐Be able to label at least 10 organelles in a Eukaryotic cell -‐Know how eukaryotic cells obtain energy -‐Be able to compare and contrast Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (size, age, complexity, struc ...
... -‐Be able to label at least 10 organelles in a Eukaryotic cell -‐Know how eukaryotic cells obtain energy -‐Be able to compare and contrast Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (size, age, complexity, struc ...
Chapter 3
... 3. Many bacteria commonly carry extrachromosomal pieces of DNA called ___________, which are able to ___________ independently of the bacterial chromosome. 4. Protein synthesis takes place at ___________. 5. The main components of cell membranes are ___________ and ___________ 6. Gram-positive cell ...
... 3. Many bacteria commonly carry extrachromosomal pieces of DNA called ___________, which are able to ___________ independently of the bacterial chromosome. 4. Protein synthesis takes place at ___________. 5. The main components of cell membranes are ___________ and ___________ 6. Gram-positive cell ...
Plant and Animal cells by: Cody Mills
... Ribosomes consist of two sub units and functioning as the site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. Endoplasmic reticulum makes up more then half the membrane of the cell. There are two different kinds of endoplasmic reticulum: smooth and rough. Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed sac of hydrolytic en ...
... Ribosomes consist of two sub units and functioning as the site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. Endoplasmic reticulum makes up more then half the membrane of the cell. There are two different kinds of endoplasmic reticulum: smooth and rough. Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed sac of hydrolytic en ...
Chapter 40
... b. Coevolution occurs more often in homologous structures c. Sympatric and Allopatric isolation can create homologies ...
... b. Coevolution occurs more often in homologous structures c. Sympatric and Allopatric isolation can create homologies ...
Cell Theory - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... These combined discoveries are known as the cell theory, which states that: o All living organisms are made of cells; o The cell is the basic unit of structure and function of a living organism; and o All new cells are created from living existing cells. ...
... These combined discoveries are known as the cell theory, which states that: o All living organisms are made of cells; o The cell is the basic unit of structure and function of a living organism; and o All new cells are created from living existing cells. ...
Plant Cell
... The nucleus directs all of the cell‘s activities, including reproduction. Endoplasmic Reticulum This network of passageways carries materials from one part of the cell to another. ...
... The nucleus directs all of the cell‘s activities, including reproduction. Endoplasmic Reticulum This network of passageways carries materials from one part of the cell to another. ...
Slide ()
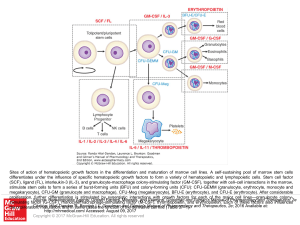
... stimulate stem cells to form a series of burst-forming units (BFU) and colony-forming units (CFU): CFU-GEMM (granulocyte, erythrocyte, monocyte and megakaryocyte), CFU-GM (granulocyte and macrophage), CFU-Meg (megakaryocyte), BFU-E (erythrocyte), and CFU-E (erythrocyte). After considerable prolifera ...
... stimulate stem cells to form a series of burst-forming units (BFU) and colony-forming units (CFU): CFU-GEMM (granulocyte, erythrocyte, monocyte and megakaryocyte), CFU-GM (granulocyte and macrophage), CFU-Meg (megakaryocyte), BFU-E (erythrocyte), and CFU-E (erythrocyte). After considerable prolifera ...
Exam III Sample Questions
... B) A mutation that destroyed the kinase activity of S-CDK complex C) A mutation that removed the phosphorylation sites of Rb protein. D) A mutation that prevents RAS from hydrolyzing GTP. E) None of the Above 15. Which of the following can be associated with an adherens junctions, but not desmosomes ...
... B) A mutation that destroyed the kinase activity of S-CDK complex C) A mutation that removed the phosphorylation sites of Rb protein. D) A mutation that prevents RAS from hydrolyzing GTP. E) None of the Above 15. Which of the following can be associated with an adherens junctions, but not desmosomes ...
NAME - SchoolNotes
... 9. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM: Channels for transport, breakdown of chemicals and toxins, production of complex chemicals like hormones, and production site of lipids used for cell membrane construction. 10. RIBOSOMES: Makes proteins from directions given by the DNA. 11. GOLGI APPARATUS: Storage for cell ...
... 9. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM: Channels for transport, breakdown of chemicals and toxins, production of complex chemicals like hormones, and production site of lipids used for cell membrane construction. 10. RIBOSOMES: Makes proteins from directions given by the DNA. 11. GOLGI APPARATUS: Storage for cell ...
Lipids and solutions/ inside of the cell Explain what it means to
... 1. Explain what it means to be selectively permeable Selectively permeable means the cell membrane only let a certain molecules to move through them. 2. What happens to a cell that has been dropped into a hypotonic solution?(explain in case of animal cell and plant cell and what makes the difference ...
... 1. Explain what it means to be selectively permeable Selectively permeable means the cell membrane only let a certain molecules to move through them. 2. What happens to a cell that has been dropped into a hypotonic solution?(explain in case of animal cell and plant cell and what makes the difference ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.