How to Make Red Cabbage pH Indicator Acid
... a plant? There are two things that combine to move water through plants – TRANSPIRATION and COHESION! Water evaporating from the leaves and flowers pulls water up the stem of the plant (Transpiration) like a straw! Water is pulled up the stem of the plant because it is very “sticky”. Water molecules ...
... a plant? There are two things that combine to move water through plants – TRANSPIRATION and COHESION! Water evaporating from the leaves and flowers pulls water up the stem of the plant (Transpiration) like a straw! Water is pulled up the stem of the plant because it is very “sticky”. Water molecules ...
Plants with Seeds
... • depend on osmosis and diffusion • plants are small • live in wet environments Mosses and Liverworts • live in wet environments • rhizoids are root like structures to anchor ...
... • depend on osmosis and diffusion • plants are small • live in wet environments Mosses and Liverworts • live in wet environments • rhizoids are root like structures to anchor ...
e. Clustered, staled sporangia called sori
... b. Groups of vascular tissues scattered throughout the stem c. Groups of vascular tissues in a ring d. Flower parts mostly in threes or multiples of three e. Seeds with one cotyledon 13. Primary growth in plants results from activity of a. Apical meristems b. Lateral meristems c. Vascular cambium d. ...
... b. Groups of vascular tissues scattered throughout the stem c. Groups of vascular tissues in a ring d. Flower parts mostly in threes or multiples of three e. Seeds with one cotyledon 13. Primary growth in plants results from activity of a. Apical meristems b. Lateral meristems c. Vascular cambium d. ...
CHAPTER 10 “INTRO TO PLANTS” p. 259
... vessels or tubes to transport water or food. -called bryophytes - the most simple of plants. -are seedless. ...
... vessels or tubes to transport water or food. -called bryophytes - the most simple of plants. -are seedless. ...
Yellow flag iris
... your home pond or waterfront shorelines; research nursery and catalogue specimens before buying Biological – None known or likely at this time due to it’s similarity to garden iris Cultural – Healthy native plant communities help reduce likelihood of establishment but don’t stop it Mechanical – Pull ...
... your home pond or waterfront shorelines; research nursery and catalogue specimens before buying Biological – None known or likely at this time due to it’s similarity to garden iris Cultural – Healthy native plant communities help reduce likelihood of establishment but don’t stop it Mechanical – Pull ...
Week 13
... A genetically modified organism (GMO) is any organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering technique ...
... A genetically modified organism (GMO) is any organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering technique ...
Science 8* Plant Processes and Reproduction
... energy, water, and carbon dioxide into the foodenergy molecule glucose and give off oxygen ...
... energy, water, and carbon dioxide into the foodenergy molecule glucose and give off oxygen ...
How a Plant Works
... 14. Name two ways in which the pollen of one plant is brought into contact with the stigma of another plant of the same species. ...
... 14. Name two ways in which the pollen of one plant is brought into contact with the stigma of another plant of the same species. ...
Review - Plant Systems 15
... 11. What is the function of the xylem? Transport water and minerals from soil into root hairs roots stem leaves 12. What is the function of the phloem? Transport sugar from leaves to rest of the plant 13. Compare and Contrast gymnosperms and angiosperms. ...
... 11. What is the function of the xylem? Transport water and minerals from soil into root hairs roots stem leaves 12. What is the function of the phloem? Transport sugar from leaves to rest of the plant 13. Compare and Contrast gymnosperms and angiosperms. ...
Plant Vocabulary You`ll Need
... Parenchyma- “typical” plant cells; primary walls are thin and flexible and they make and store various plant products; most fruit is made of parenchyma cells, and photosynthetic cells in the leaf and stem are usually parenchyma cells Collenchyma- cells that support the plant organs; usually found in ...
... Parenchyma- “typical” plant cells; primary walls are thin and flexible and they make and store various plant products; most fruit is made of parenchyma cells, and photosynthetic cells in the leaf and stem are usually parenchyma cells Collenchyma- cells that support the plant organs; usually found in ...
File
... Vascular bundles are arranged in a circle in the middle of the stem surrounding a central pith. To the outside of the vascular bundles is the cortex which is covered by a single layer of epidermis cells. The xylem orientated towards the middle of the stem and the phloem towards the outside. ...
... Vascular bundles are arranged in a circle in the middle of the stem surrounding a central pith. To the outside of the vascular bundles is the cortex which is covered by a single layer of epidermis cells. The xylem orientated towards the middle of the stem and the phloem towards the outside. ...
Odontoglossum, Odontioda and Burrageara
... temperatures of 7 to 28C (45 to 82F). Avoid frost. These plants appreciate lots of air movement, especially at higher temperatures. Keep out of draft. Light: The low to intermediate light of a bright north or east facing window or a shaded west window are best. Too much light will result in red pi ...
... temperatures of 7 to 28C (45 to 82F). Avoid frost. These plants appreciate lots of air movement, especially at higher temperatures. Keep out of draft. Light: The low to intermediate light of a bright north or east facing window or a shaded west window are best. Too much light will result in red pi ...
Chapter 4 Lesson 1: How do leaves help a plant
... c. Plants need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. Sunlight gives the cell energy for photosynthesis. It gets water from its root hairs and enters the chloroplasts. Carbon dioxide comes from the atmosphere and enters through the leaves. d. The process of photosynthesis uses water ...
... c. Plants need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. Sunlight gives the cell energy for photosynthesis. It gets water from its root hairs and enters the chloroplasts. Carbon dioxide comes from the atmosphere and enters through the leaves. d. The process of photosynthesis uses water ...
"Make Your Plants Happy with Proper Watering”
... A: You need enough water to get to as much of the root system as possible to make your plants happy. Plants need enough water to properly transport essential nutrients from the bottom of the plant to the very top of the plant. To get water down to the very bottom or edges of your root system, you ne ...
... A: You need enough water to get to as much of the root system as possible to make your plants happy. Plants need enough water to properly transport essential nutrients from the bottom of the plant to the very top of the plant. To get water down to the very bottom or edges of your root system, you ne ...
Chapters 17, 18 and 19
... A. cell walls made of cellulose that lend support to the plant cell B. roots and root hairs absorb water and nutrients from the soil C. stomates open to exchange photosynthetic gases and close to limit water loss D. cutin – waxy coating on leaves – prevents water loss from the leaves E. gametangia – ...
... A. cell walls made of cellulose that lend support to the plant cell B. roots and root hairs absorb water and nutrients from the soil C. stomates open to exchange photosynthetic gases and close to limit water loss D. cutin – waxy coating on leaves – prevents water loss from the leaves E. gametangia – ...
06-PlantsCN
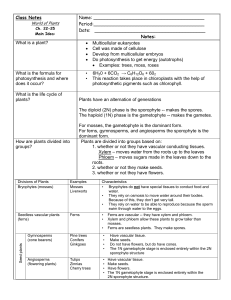
... For mosses, the gametophyte is the dominant form. For ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms the sporophyte is the dominant form. Plants are divided into groups based on: 1. whether or not they have vascular conducting tissues. Xylem – moves water from the roots up to the leaves Phloem – moves sugars m ...
... For mosses, the gametophyte is the dominant form. For ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms the sporophyte is the dominant form. Plants are divided into groups based on: 1. whether or not they have vascular conducting tissues. Xylem – moves water from the roots up to the leaves Phloem – moves sugars m ...
Plant Structure
... •Symplast is when water moves through cells (when water reaches the endoplast, this is the only way to travel through xylem •In general, there are 3 mechanisms for water to move through plant: •Osmosis is the movement of water through membranes of high concentration to lower concentration. This crea ...
... •Symplast is when water moves through cells (when water reaches the endoplast, this is the only way to travel through xylem •In general, there are 3 mechanisms for water to move through plant: •Osmosis is the movement of water through membranes of high concentration to lower concentration. This crea ...
Kingdom plants Ch.22-25
... Transporting water and food Some plant stems have the additional job of food storage. EX: The potato is a special stem that stores starch. ...
... Transporting water and food Some plant stems have the additional job of food storage. EX: The potato is a special stem that stores starch. ...
Plantae: Anthophyta
... winter, the plant is dormant, although food reserves in the roots allow some root growth when the soil isn't cold. These reserves fuel the initial growth of new leaves in spring. • Fertilizer is often marketed as plant food., Fertilizer is not food to plants but are nutrients absorbed by the roots f ...
... winter, the plant is dormant, although food reserves in the roots allow some root growth when the soil isn't cold. These reserves fuel the initial growth of new leaves in spring. • Fertilizer is often marketed as plant food., Fertilizer is not food to plants but are nutrients absorbed by the roots f ...
Possible Essay Questions:
... Explain how the same chemical signal can lead to totally different responses in different cell types. ...
... Explain how the same chemical signal can lead to totally different responses in different cell types. ...
Plant Kingdom Slides
... light. Function: photosynthesis – Spongy mesophyll: air spaces for gas and water movement. • Cuticle: Waxy coating that protects leaf and prevent water loss. • Veins – contain vascular tissue (xylem and phloem) ...
... light. Function: photosynthesis – Spongy mesophyll: air spaces for gas and water movement. • Cuticle: Waxy coating that protects leaf and prevent water loss. • Veins – contain vascular tissue (xylem and phloem) ...
Ch 29 - MsBabbey
... transport water and nutrients throughout a plant. Vascular plants either are seedless (mosses, horsetails, and ferns) or have seeds (gymnosperms like pine trees, angiosperms like flowers) Non-vascular plants include liverworts, hornworts, and mosses ...
... transport water and nutrients throughout a plant. Vascular plants either are seedless (mosses, horsetails, and ferns) or have seeds (gymnosperms like pine trees, angiosperms like flowers) Non-vascular plants include liverworts, hornworts, and mosses ...
Xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants, phloem being the other. The word xylem is derived from the Greek word ξύλον (xylon), meaning ""wood""; the best-known xylem tissue is wood, though it is found throughout the plant.The basic function of xylem is to transport water, but it also transports some nutrients.