* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Notes - cloudfront.net
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Cultivated plant taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Hydroponics wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Embryophyte wikipedia , lookup
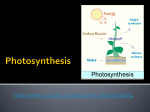
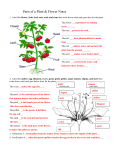
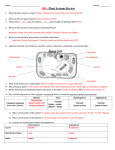
Agenda Bell Work Plant Notes Finish All Questions Plants Plant Characteristics All plants are autotrophs or producers; they use the sun’s energy to make their own food (photosynthesis) They are multi-cellular eukaryotes (their cells have a nucleus) They are typically green because they contain chlorophyll, a pigment that allows them to perform photosynthesis Plant Parts Roots – Mainly absorb water from the soil; also absorb nutrients, like nitrogen, used for growth and development. Stems – Full of xlyem, which transports water from the roots up to the leaves for photosynthesis, and phloem, which transports glucose down from the leave to other parts of the plant Flower – Reproductive organ of the plant Leaves – Site of photosynthesis Flower Parts Stamen – The male part of the flower; contains the anther (produces pollen) and filament (holds anther up) Pistol – Female part of the plant; contain the stigma (sticky part that collects pollen), style (long tub pollen travels down), and ovary (contains the eggs) Petals – Brightly colored structures used to attracted pollinators like bees or butterflies Plant Reproduction Plants rely on other organisms to help them reproduce. Bees, birds, other insects, and sometimes the wind carry pollen (flower sperm) from one plant to another. When the pollen attaches to the stigma it is then transferred down the style to the ovary where the eggs are. The ovary grows into a fruit, and the eggs within it turn into seeds Other animals eat the fruit and poop the seeds out far away from the parent plant, in some nice fertilizer so it can germinate Photosynthesis Plants use the energy from the sun to create organic stored energy in the form of glucose. They also require carbon dioxide and water to complete this process. Sun + H2O + CO2 Glucose (C6H12O6) + O2 For photosynthesis to occur plants need enough water and CO2, but when plants open the stomata in their leaves to take in CO2 they lose water Stomata On the bottom sides of leaves there are tiny pores called stomata A stomate regulates how much water will leave the plant and how much CO2 will enter the leaf When the plants are losing too much water and beginning to wilt, stomates close to conserve water. When the plants have plenty of water stomates open to take in CO2 for photosynthesis This is one way plants maintain homeostasis Guard Cells Guard cells regulate when the stomate is opened or closed The guard cells do this by taking water into their cells and becoming turgid, thus closing the stomate, or removing water from their cells to become flaccid and open the stomate. This is done through osmosis Plant Adaptations Just like animals, plants have evolved adaptations to help them survive. Some plants have evolved spines to keep predators from eating them (cacti) Other have developed chemicals that inhibit other plants from growing near them (black walnut tree) Some have developed ways to catch insects for nutrients, so they can grow in nutrient poor areas (venus fly trap and pitcher plants) Some plants have adapted to crawl up other plants to reach the sunlight above (vines and ivy)