UShape Representation in the Inferior Temporal Cortex of MonkeysU
... best fit to a set of training data corresponding to the object's familiar views. A view is considered as a vector, the elements of which can be any image features, including non-geometrical ones, such as color or texture. In the simplest case, one hidden-layer unit is assumed to store each familiar ...
... best fit to a set of training data corresponding to the object's familiar views. A view is considered as a vector, the elements of which can be any image features, including non-geometrical ones, such as color or texture. In the simplest case, one hidden-layer unit is assumed to store each familiar ...
neural mechanisms for detecting and remembering novel events
... and classification10, as well as during passive viewing and even under general anaesthesia11. The effects of repetition suppression are stimulus specific, in that a particular neuron will show reduced responses to repeated stimuli whereas the responses of the same neuron to novel stimuli will be lar ...
... and classification10, as well as during passive viewing and even under general anaesthesia11. The effects of repetition suppression are stimulus specific, in that a particular neuron will show reduced responses to repeated stimuli whereas the responses of the same neuron to novel stimuli will be lar ...
Theory of Mind: A Neural Prediction Problem
... dominated by error neurons (Friston, 2009; Wacongne et al., 2012; Egner et al., 2010; Keller et al., 2012; Meyer and Sauerland, 2009). The result is that the classic signature of predictive coding, reduced activity to predictable stimuli, is typically observed when averaging across large samples of ...
... dominated by error neurons (Friston, 2009; Wacongne et al., 2012; Egner et al., 2010; Keller et al., 2012; Meyer and Sauerland, 2009). The result is that the classic signature of predictive coding, reduced activity to predictable stimuli, is typically observed when averaging across large samples of ...
Trait Conceptualization and Measurement of
... processing of advertisements is affected by internal frames of reference or “contexts,” that are present at the time of ad exposure. Internal contexts are “concepts or categories previously formed by the individual during the course of encounters with the stimuli in question” (Sherif and Hovland 196 ...
... processing of advertisements is affected by internal frames of reference or “contexts,” that are present at the time of ad exposure. Internal contexts are “concepts or categories previously formed by the individual during the course of encounters with the stimuli in question” (Sherif and Hovland 196 ...
The Influence of Target Properties and the Possible
... of interest to another, allow us to interact with our visual environment. Latency and peak velocity are among the most studied parameters of saccades with their characteristics pretty well known. However, much less is known about how the possible lateralization of saccades and how target properties, ...
... of interest to another, allow us to interact with our visual environment. Latency and peak velocity are among the most studied parameters of saccades with their characteristics pretty well known. However, much less is known about how the possible lateralization of saccades and how target properties, ...
Predictability Modulates Human Brain Response to Reward
... body transformation. Because swallowing unavoidably causes significant head movement, the motion-correction parameters were also used to determine whether head motion differed significantly between the conditions. The mean of the motion-corrected images was then coregistered to the individual’s 24-s ...
... body transformation. Because swallowing unavoidably causes significant head movement, the motion-correction parameters were also used to determine whether head motion differed significantly between the conditions. The mean of the motion-corrected images was then coregistered to the individual’s 24-s ...
Representation of naturalistic image structure in the primate visual
... However, in the area immediately downstream, V2, cells respond more vigorously to these stimuli than to matched control stimuli. Humans show BOLD fMRI responses in V1 and V2 that are consistent with the neuronal measurements in macaque. These fMRI measurements, as well as neurophysiological work by ...
... However, in the area immediately downstream, V2, cells respond more vigorously to these stimuli than to matched control stimuli. Humans show BOLD fMRI responses in V1 and V2 that are consistent with the neuronal measurements in macaque. These fMRI measurements, as well as neurophysiological work by ...
The representation of Kanizsa illusory contours in the monkey
... salivation. Body temperature, heart rate, respiratory rate, end-tidal CO2 and peripheral O2 saturation were monitored throughout the surgery. Analgesic was given after surgery (Nalbuphine, 0.15 mg ⁄ kg) for 5 days. We used a controlled water-access paradigm during the training of the animals and for ...
... salivation. Body temperature, heart rate, respiratory rate, end-tidal CO2 and peripheral O2 saturation were monitored throughout the surgery. Analgesic was given after surgery (Nalbuphine, 0.15 mg ⁄ kg) for 5 days. We used a controlled water-access paradigm during the training of the animals and for ...
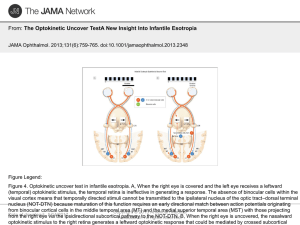
The Optokinetic Uncover TestA New Insight Into Infantile Esotropia
... JAMA Ophthalmol. 2013;131(6):759-765. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2013.2348 ...
... JAMA Ophthalmol. 2013;131(6):759-765. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2013.2348 ...
Attention induces synchronization-based response gain in steady
... The three hypotheses have not previously been examined at the level of the neural population. This examination is important for two reasons. First, it is intrinsically difficult to compare the contrastresponse functions of individual neurons with behavioral results because it is unclear how neural s ...
... The three hypotheses have not previously been examined at the level of the neural population. This examination is important for two reasons. First, it is intrinsically difficult to compare the contrastresponse functions of individual neurons with behavioral results because it is unclear how neural s ...
file
... motion when the cortex is abruptly engaged by a stimulus12,17,18,20–25, one might predict that this elemental input sampling/recovery property of cortical circuits is immutable. However, a large body of evidence has indicated that temporal response properties of cortical neurons can be substantially ...
... motion when the cortex is abruptly engaged by a stimulus12,17,18,20–25, one might predict that this elemental input sampling/recovery property of cortical circuits is immutable. However, a large body of evidence has indicated that temporal response properties of cortical neurons can be substantially ...
Neural coding of behavioral relevance in parietal cortex
... in neuronal responses in MT were generally too small to account for the behavioral changes, whereas the changes in VIP responses were generally stronger than expected to explain the behavioral effect. These results suggest that comparing the neuronal and behavioral effects of attention may be a reas ...
... in neuronal responses in MT were generally too small to account for the behavioral changes, whereas the changes in VIP responses were generally stronger than expected to explain the behavioral effect. These results suggest that comparing the neuronal and behavioral effects of attention may be a reas ...
Functional Properties of Neurons in Middle Temporal Visual Area of
... great majority of MT neurons (16, 6 1). Although this suggests that MT may somehow be involved in the analysis of motion, it does not resolve the nature of the processing actually occurring within MT nor does it identify which specific aspects of motion analysis might be served. Motion analysis is a ...
... great majority of MT neurons (16, 6 1). Although this suggests that MT may somehow be involved in the analysis of motion, it does not resolve the nature of the processing actually occurring within MT nor does it identify which specific aspects of motion analysis might be served. Motion analysis is a ...
A coincidence detector neural network model of selective attention
... In addition to influence from top-down spatial goals, the neural activation of each stimulus is progressively modulated by top-down signals of semantic information. We propose that a correlation control mechanism that includes coincidence detector neurons determines the correlation between semantic ...
... In addition to influence from top-down spatial goals, the neural activation of each stimulus is progressively modulated by top-down signals of semantic information. We propose that a correlation control mechanism that includes coincidence detector neurons determines the correlation between semantic ...
Vibration Sensitivity and a Computational Theory for Prey
... SYNOPSIS. As burrowing, nocturnal predators of small arthropods, sand scorpions have evolved exquisite sensitivity to vibrational information that comes to them through the substrate they live on, dry sand. Over distances of a few decimeters, sand conducts low velocity (;50 m/sec) surface (Rayleigh) ...
... SYNOPSIS. As burrowing, nocturnal predators of small arthropods, sand scorpions have evolved exquisite sensitivity to vibrational information that comes to them through the substrate they live on, dry sand. Over distances of a few decimeters, sand conducts low velocity (;50 m/sec) surface (Rayleigh) ...
Scale-Invariant Adaptation in Response to
... variance through receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) analysis of a neuron’s firing rate. We computed the probability distributions of firing rate for a single cell over the course of a 0.1 Hz switch by separating the time course into 500 ms bins, computing the firing rate during each bin over ea ...
... variance through receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) analysis of a neuron’s firing rate. We computed the probability distributions of firing rate for a single cell over the course of a 0.1 Hz switch by separating the time course into 500 ms bins, computing the firing rate during each bin over ea ...
Gestalt Issues in Modern Neuroscience
... apparent motion to an intracortical short-circuit between two foci of excitation. Apparent motion occurs when two static lights are presented briefly in a proper sequence. Under these conditions one can perceive either pure motion without object displacement (phi motion) or, when the time interval b ...
... apparent motion to an intracortical short-circuit between two foci of excitation. Apparent motion occurs when two static lights are presented briefly in a proper sequence. Under these conditions one can perceive either pure motion without object displacement (phi motion) or, when the time interval b ...
STDP produces robust oscillatory architectures that exhibit precise
... For potentiation, the learning rate value λ is 0.3, and the window τ is 20 ms. For depression, the learning rate value λ is 0.3105 and the window τ is 10 ms. F. Evolution of oscillatory nodes Although groups of neurons firing together rhythmically can occur because of intrinsic firing patterns of ex ...
... For potentiation, the learning rate value λ is 0.3, and the window τ is 20 ms. For depression, the learning rate value λ is 0.3105 and the window τ is 10 ms. F. Evolution of oscillatory nodes Although groups of neurons firing together rhythmically can occur because of intrinsic firing patterns of ex ...
Receptive Field Properties of Single Neurons in Rat Primary Visual
... unusual characteristic of responding to two stimulus orientations which were nearly orthogonal to one another. This surprising observation has also been made in the cat V1 (Shevelev et al. 1995). We recorded these cells for a long enough (from 1 to 3 h in several cases) to document this fact and sho ...
... unusual characteristic of responding to two stimulus orientations which were nearly orthogonal to one another. This surprising observation has also been made in the cat V1 (Shevelev et al. 1995). We recorded these cells for a long enough (from 1 to 3 h in several cases) to document this fact and sho ...
Preprint - University of Pennsylvania School of Arts and Sciences
... dot on the screen. Our experimental design included four images presented in all possible combinations as a visual stimulus, and as an intended target, resulting in 16 experimental conditions. We held the target image fixed for short blocks of trials and we presented the same images as both targets ...
... dot on the screen. Our experimental design included four images presented in all possible combinations as a visual stimulus, and as an intended target, resulting in 16 experimental conditions. We held the target image fixed for short blocks of trials and we presented the same images as both targets ...
stimulus conditions area MT of the macaque monkey under matched
... cortical circuits adjust to recent visual input, but they have left unclear how a particular sensory event alters the distributed representation of information in the visual system. This is because studies, understandably, have focused on measuring effects with stimuli that are most appropriate for ...
... cortical circuits adjust to recent visual input, but they have left unclear how a particular sensory event alters the distributed representation of information in the visual system. This is because studies, understandably, have focused on measuring effects with stimuli that are most appropriate for ...
Feedforward, horizontal, and feedback processing
... is left identical (see [33]). The initial transients are identical in all three cases, but from 80–100 ms after stimulus onset, responses are larger (shaded in gray) for positions of the RF on the figure boundary or surface than on the background. (c) Responses in V1 with the RF at 15 different posi ...
... is left identical (see [33]). The initial transients are identical in all three cases, but from 80–100 ms after stimulus onset, responses are larger (shaded in gray) for positions of the RF on the figure boundary or surface than on the background. (c) Responses in V1 with the RF at 15 different posi ...
Multiplication and stimulus invariance in a looming
... (Fig. 4B, inset). It can be shown from Eq. (1) that such a linear relation is equivalent to the angular size subtended by the object being a fixed constant d ms prior to the peak, independent of the stimulation parameter l=jvj ([19, Appendix 1]). This angular threshold size can be computed from the s ...
... (Fig. 4B, inset). It can be shown from Eq. (1) that such a linear relation is equivalent to the angular size subtended by the object being a fixed constant d ms prior to the peak, independent of the stimulation parameter l=jvj ([19, Appendix 1]). This angular threshold size can be computed from the s ...
Interactions Between Premotor and Motor Cortices in Non
... based on the properties of particular cortical areas, but focused on the transmission of information between areas: They suggested that ‘‘the transformation of an object’s intrinsic properties into specific grips takes place in a circuit that is formed by the inferior parietal lobule and the inferio ...
... based on the properties of particular cortical areas, but focused on the transmission of information between areas: They suggested that ‘‘the transformation of an object’s intrinsic properties into specific grips takes place in a circuit that is formed by the inferior parietal lobule and the inferio ...
JERZY KONORSKI`S THEORY OF CONDITIONED
... to their association. As the result of association, the conditioned stimulus becomes, according to Pavlov, a "substitute" for the unconditioned stimulus and evokes a response similar to that observed to the unconditioned stimulus presented alone (24). In contrast to that in instrumental canditionin ...
... to their association. As the result of association, the conditioned stimulus becomes, according to Pavlov, a "substitute" for the unconditioned stimulus and evokes a response similar to that observed to the unconditioned stimulus presented alone (24). In contrast to that in instrumental canditionin ...
Response priming

In the psychology of perception and motor control, the term response priming denotes a special form of priming. Generally, priming effects take place whenever a response to a target stimulus is influenced by a prime stimulus presented at an earlier time. The distinctive feature of response priming is that prime and target are presented in quick succession (typically, less than 100 milliseconds apart) and are coupled to identical or alternative motor responses. When a speeded motor response is performed to classify the target stimulus, a prime immediately preceding the target can thus induce response conflicts when assigned to a different response as the target. These response conflicts have observable effects on motor behavior, leading to priming effects, e.g., in response times and error rates. A special property of response priming is its independence from visual awareness of the prime.