Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
... Enthalpy is defined as: H = E + PV A change in Enthalpy would imply: ∆H = ∆E + ∆(PV) = ∆E + P∆V + V∆P Since: ∆E = q + w; and W = - P∆V; we find: ∆H = q - P∆V + P∆V + V∆P From this it follows that at constant P (process open to the atmosphere): ∆H = qp (equals heat at constant P) Why Define Enthalpy? ...
... Enthalpy is defined as: H = E + PV A change in Enthalpy would imply: ∆H = ∆E + ∆(PV) = ∆E + P∆V + V∆P Since: ∆E = q + w; and W = - P∆V; we find: ∆H = q - P∆V + P∆V + V∆P From this it follows that at constant P (process open to the atmosphere): ∆H = qp (equals heat at constant P) Why Define Enthalpy? ...
Solute
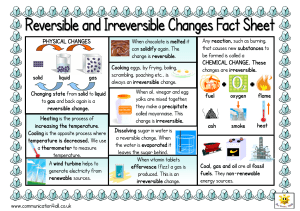
... • Change which results in one or more new substances being formed • The new substance has different chemical properties!!! • Examples • Paper burns, iron rusts, silver tarnishes ...
... • Change which results in one or more new substances being formed • The new substance has different chemical properties!!! • Examples • Paper burns, iron rusts, silver tarnishes ...
Course Overview - Colorado State University College of Engineering
... transducers to generate the above plot of pressure vs. volume for a single pocket of gas. The polytropic exponent was measured to be 1.175. Based on the temperatures and pressures at the inlet and exit, the specific internal energy, u, at each state is known to be 234.9 kJ/kg to 267.5 kJ/kg, respect ...
... transducers to generate the above plot of pressure vs. volume for a single pocket of gas. The polytropic exponent was measured to be 1.175. Based on the temperatures and pressures at the inlet and exit, the specific internal energy, u, at each state is known to be 234.9 kJ/kg to 267.5 kJ/kg, respect ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS
... two out of four long questions. Each section carries equal marks. The minimum mathematical requirements of the syllabus are the same as those for the SEC examination in Chemistry. Questions will be set in SI units except that pressures may be expressed in atmospheres (atm.). The Periodic Table, comp ...
... two out of four long questions. Each section carries equal marks. The minimum mathematical requirements of the syllabus are the same as those for the SEC examination in Chemistry. Questions will be set in SI units except that pressures may be expressed in atmospheres (atm.). The Periodic Table, comp ...
S2-2-07 - Classifying Chemical Reactions
... from notes. Think of other analogies for this type of reaction and fill in notes sheet. Teacher’s analogy: Blackeye + Pinkpanther Blackpanther + Pinkeye. (10 minutes) Have students follow the directions found with material at the center of their table and perform the double displacement reaction B ...
... from notes. Think of other analogies for this type of reaction and fill in notes sheet. Teacher’s analogy: Blackeye + Pinkpanther Blackpanther + Pinkeye. (10 minutes) Have students follow the directions found with material at the center of their table and perform the double displacement reaction B ...
Electrochemistry I
... As we have been doing all along, we make a Legendre transformation to obtain the Gibbs free energy, G = U + pV TS, ...
... As we have been doing all along, we make a Legendre transformation to obtain the Gibbs free energy, G = U + pV TS, ...
Classification of Matter
... Matter that can not be broken down into simpler substances under normal lab conditions Contains only one kind of element Atom ...
... Matter that can not be broken down into simpler substances under normal lab conditions Contains only one kind of element Atom ...
What You Need to Know to Pass the Chemistry
... Filtration and distillation are examples of processes used to separate mixtures. 2. An element is a substance composed of atoms with the same atomic number. They cannot be broken down by chemical change. 3. A compound is two or more elements bonded together. It can only be broken down by chemical ...
... Filtration and distillation are examples of processes used to separate mixtures. 2. An element is a substance composed of atoms with the same atomic number. They cannot be broken down by chemical change. 3. A compound is two or more elements bonded together. It can only be broken down by chemical ...
IB1 Introduction to Ch
... but retains the properties of the substance Undergoes a chemical reaction. A new substance is formed with new physical and chemical properties ...
... but retains the properties of the substance Undergoes a chemical reaction. A new substance is formed with new physical and chemical properties ...
objective - Humble ISD
... 2. List and explain the functions necessary for maintaining life (characteristics of life) 3. Define metabolism and apply this term to the characteristics of life. ...
... 2. List and explain the functions necessary for maintaining life (characteristics of life) 3. Define metabolism and apply this term to the characteristics of life. ...
Atoms Matter Energy Notes
... Thermal Energy: is all of the energy of all of the particles in an object. o This is the most common change in energy when you have a change in matter o Temperature is used to measure the average energy of the motion of particles in an object. o The flow of thermal energy will always be from warme ...
... Thermal Energy: is all of the energy of all of the particles in an object. o This is the most common change in energy when you have a change in matter o Temperature is used to measure the average energy of the motion of particles in an object. o The flow of thermal energy will always be from warme ...
Exam only.
... the enthalpy of reaction is the difference between product and reactant enthalpies. the Gibbs free energy is a function of both enthalpy and entropy. ...
... the enthalpy of reaction is the difference between product and reactant enthalpies. the Gibbs free energy is a function of both enthalpy and entropy. ...
Ch. 5 --Thermochemistry (I)
... Enthalpy Chemical reactions can absorb or release heat. They also have the ability to do work. For example, when a gas is produced, the gas can be used to push a piston, doing work. Zn(s) + 2H+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + H2(g) The work performed by the above reaction is called pressure-volume work. ...
... Enthalpy Chemical reactions can absorb or release heat. They also have the ability to do work. For example, when a gas is produced, the gas can be used to push a piston, doing work. Zn(s) + 2H+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + H2(g) The work performed by the above reaction is called pressure-volume work. ...
FORM 1 GEOGRAPHY REVISION GRID
... Explain what happens in terms of particles during a change of state Describe the properties of solids, liquids and gases Draw diagrams of the arrangement of particles in solids, liquids and gases ...
... Explain what happens in terms of particles during a change of state Describe the properties of solids, liquids and gases Draw diagrams of the arrangement of particles in solids, liquids and gases ...
Chapter 6-student notes
... b) Stalactites form in caves when calcium bicarbonate reacts to form calcium carbonate, water and carbon dioxide gas. Can you figure out what is missing in the following chemical reactions? 1. Aluminum resists corrosion (rust) because it reacts with a gas in the air to form a protective coating of a ...
... b) Stalactites form in caves when calcium bicarbonate reacts to form calcium carbonate, water and carbon dioxide gas. Can you figure out what is missing in the following chemical reactions? 1. Aluminum resists corrosion (rust) because it reacts with a gas in the air to form a protective coating of a ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.