Heat of reaction
... • The heat absorbed or released by a system usually depends on the conditions under which the reaction is performed. • Normally, reactions are performed in vessels open to the atmosphere and hence at constant atmospheric pressure. • Enthalpy is an extensive property of a substance that can be used t ...
... • The heat absorbed or released by a system usually depends on the conditions under which the reaction is performed. • Normally, reactions are performed in vessels open to the atmosphere and hence at constant atmospheric pressure. • Enthalpy is an extensive property of a substance that can be used t ...
國立嘉義大學95學年度
... 2NO(g) + Br (g) . After equilibrium was reached, the volume was increased to 2.0 liters, while the temperature was 44. 2NOBr(g) ...
... 2NO(g) + Br (g) . After equilibrium was reached, the volume was increased to 2.0 liters, while the temperature was 44. 2NOBr(g) ...
Internal Energy Energy is defined as the capacity to do work. There
... Energy is defined as the capacity to do work. There are various forms of energy- potential energy by virtue of position, kinetic energy due to motion of the body, thermal energy, nuclear energy, mechanical energy etc. The energy possessed by a system due to translational, vibrational and rotational ...
... Energy is defined as the capacity to do work. There are various forms of energy- potential energy by virtue of position, kinetic energy due to motion of the body, thermal energy, nuclear energy, mechanical energy etc. The energy possessed by a system due to translational, vibrational and rotational ...
Review Sheet for Chemistry* First Semester Final
... Hydrogen sulfide, a foul-smelling gas, is found in nature in volcanic areas. The balanced chemical equation for the burning of hydrogen sulfide is given below. Interpret this equation in terms of the interaction of the following three relative quantities. 1. The coefficients in this balanced reactio ...
... Hydrogen sulfide, a foul-smelling gas, is found in nature in volcanic areas. The balanced chemical equation for the burning of hydrogen sulfide is given below. Interpret this equation in terms of the interaction of the following three relative quantities. 1. The coefficients in this balanced reactio ...
Synthesis/Decomposition Reactions
... Metal oxides and water react to produce a metal hydroxide (-OH). Nonmetal oxides and water react to produce an acid ...
... Metal oxides and water react to produce a metal hydroxide (-OH). Nonmetal oxides and water react to produce an acid ...
study guide first semester chemistry
... 6. Write the formula for hydrosulfuric acid. H2S Chapter 8 Molecular Shape Summary ...
... 6. Write the formula for hydrosulfuric acid. H2S Chapter 8 Molecular Shape Summary ...
A Thumbnail Review of Regents Chemistry
... COMPACT REGENTS REVIEW 2010-2011 MATTER Pure matter = substances, which are represented by (s), (l) or (g) Substances = elements (identical atoms) or compounds (fixed combinations of different elements) Compounds can be chemically decomposed, Elements cannot. Solution (aq) = homogeneous mixture = un ...
... COMPACT REGENTS REVIEW 2010-2011 MATTER Pure matter = substances, which are represented by (s), (l) or (g) Substances = elements (identical atoms) or compounds (fixed combinations of different elements) Compounds can be chemically decomposed, Elements cannot. Solution (aq) = homogeneous mixture = un ...
6.1 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, and COMPOUNDS
... by covalent bonds. • Can be a single, double, or triple bond depending on number of pairs of electrons shared. 2_____________________—forms when atom gives up electrons and another receives electrons in order to become stable • Electrical attraction between two oppositely charged atoms or groups of ...
... by covalent bonds. • Can be a single, double, or triple bond depending on number of pairs of electrons shared. 2_____________________—forms when atom gives up electrons and another receives electrons in order to become stable • Electrical attraction between two oppositely charged atoms or groups of ...
matter
... Endothermic Reactions • A reaction in which energy is absorbed • Often produces a decrease in ...
... Endothermic Reactions • A reaction in which energy is absorbed • Often produces a decrease in ...
Chapter 9 Balancing Equations
... atoms as the right side for EACH element. 4. Check your answer to see if: – The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. – The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ratios. (reduced) ...
... atoms as the right side for EACH element. 4. Check your answer to see if: – The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. – The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ratios. (reduced) ...
3 - CFD - Anna University
... mechanisms between a system and its surroundings. • Systems possess energy, but not heat or work. • Both are recognised at the boundaries of a system as they cross the boundaries. • Both are path functions ...
... mechanisms between a system and its surroundings. • Systems possess energy, but not heat or work. • Both are recognised at the boundaries of a system as they cross the boundaries. • Both are path functions ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... 1. Balance the different types of atoms one at a time 2. First balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only once on each side of the equation. (start with the largest ...
... 1. Balance the different types of atoms one at a time 2. First balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only once on each side of the equation. (start with the largest ...
Energy Notes - KLang Science
... Plants don’t produce energy from the sun, they transform light energy into chemical energy. Second Law of Thermodynamics: Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy (disorder) of the universe. The cheetah is converting chemical energy into to kinetic energy but it’s also inc ...
... Plants don’t produce energy from the sun, they transform light energy into chemical energy. Second Law of Thermodynamics: Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy (disorder) of the universe. The cheetah is converting chemical energy into to kinetic energy but it’s also inc ...
High School Curriculum Standards: Chemistry
... 3.4h Some chemical and physical changes can reach equilibrium. 3.4i At equilibrium the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. The measurable quantities of reactants and products remain constant at equilibrium. 3.4j LeChatelier's principle can be used to predict the eff ...
... 3.4h Some chemical and physical changes can reach equilibrium. 3.4i At equilibrium the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. The measurable quantities of reactants and products remain constant at equilibrium. 3.4j LeChatelier's principle can be used to predict the eff ...
Chapter 5 Notes: The Structure of Matter
... A molecule is formed from the sharing of electrons in a covalent bond Some can form more than one compound with each ...
... A molecule is formed from the sharing of electrons in a covalent bond Some can form more than one compound with each ...
Chapter Entropy Statistics
... δQ = dU + PdV Since V is constant, so δQ = dU Since δQ is infinitesimally small so the system is assumed to be in most probable state ds = δQ /T ...
... δQ = dU + PdV Since V is constant, so δQ = dU Since δQ is infinitesimally small so the system is assumed to be in most probable state ds = δQ /T ...
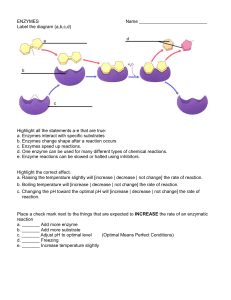
ENZYMES
... a. Raising the temperature slightly will [increase | decrease | not change] the rate of reaction. b. Boiling temperature will [increase | decrease | not change] the rate of reaction. c. Changing the pH toward the optimal pH will [increase | decrease | not change] the rate of reaction. ...
... a. Raising the temperature slightly will [increase | decrease | not change] the rate of reaction. b. Boiling temperature will [increase | decrease | not change] the rate of reaction. c. Changing the pH toward the optimal pH will [increase | decrease | not change] the rate of reaction. ...
chapter 6 sec 2 resonance structure
... But H2O is also a chemical formula because we use atomic symbols and subscripts to describe it. ...
... But H2O is also a chemical formula because we use atomic symbols and subscripts to describe it. ...
Chapter 2 - Chemical Context of Life
... The advantage of weak bonding is that the contact/bond between atoms can be brief. Hydrogen bonds occur when H is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom and ...
... The advantage of weak bonding is that the contact/bond between atoms can be brief. Hydrogen bonds occur when H is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom and ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.