Chapter 2 - Chemical Context of Life
... The advantage of weak bonding is that the contact/bond between atoms can be brief. Hydrogen bonds occur when H is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom and ...
... The advantage of weak bonding is that the contact/bond between atoms can be brief. Hydrogen bonds occur when H is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom and ...
Exam 2 Review - Iowa State University
... g/mL. The vinegar is titrated completely with 40.10 mL of 0.4100 M KOH. What is the percentage by mass of acetic acid in the vinegar? ...
... g/mL. The vinegar is titrated completely with 40.10 mL of 0.4100 M KOH. What is the percentage by mass of acetic acid in the vinegar? ...
Unit 10: Chemical Reactions
... The mole ratio between C3H8 and O2 is __1____C3H8:____5__O2. The mole ratio between C3H8 and CO2 is ___1___C3H8:__3____CO2. The mole ratio between C3H8 and H2O is ___1___C3H8:___4___H2O. The mole ratio between CO2 and O2 is __3____CO2:__5____O2. The mole ratio between H2O and CO2 is __4____H2O:___3_ ...
... The mole ratio between C3H8 and O2 is __1____C3H8:____5__O2. The mole ratio between C3H8 and CO2 is ___1___C3H8:__3____CO2. The mole ratio between C3H8 and H2O is ___1___C3H8:___4___H2O. The mole ratio between CO2 and O2 is __3____CO2:__5____O2. The mole ratio between H2O and CO2 is __4____H2O:___3_ ...
Thermochemistry Note
... Potential Energy – Stored energy in chemicals due to their composition. -The bonding forces between and within molecules. -It depends on the kinds of atoms and their arrangements within the substance. Eg. Fuels (coal, oil, gas) have high chemical potential energy whereas their combustion products (c ...
... Potential Energy – Stored energy in chemicals due to their composition. -The bonding forces between and within molecules. -It depends on the kinds of atoms and their arrangements within the substance. Eg. Fuels (coal, oil, gas) have high chemical potential energy whereas their combustion products (c ...
Thermodynamics
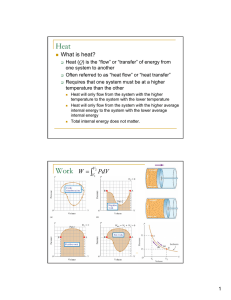
... Internal energy of a system can decrease if the system does work on its surroundings. Work is positive when it is done by the system and negative when it is done on the system. ...
... Internal energy of a system can decrease if the system does work on its surroundings. Work is positive when it is done by the system and negative when it is done on the system. ...
Heat Work
... Heat added +, heat lost -, work done by system +, work done on system – Internal Energy U is a state property Work W and heat Q are not But work and heat are involved in thermodynamic processes that change the state of the system ...
... Heat added +, heat lost -, work done by system +, work done on system – Internal Energy U is a state property Work W and heat Q are not But work and heat are involved in thermodynamic processes that change the state of the system ...
Energy - Rubin Gulaboski
... • Energy of (system + surroundings) is constant. • Any energy transferred from a system must be transferred to the surroundings (and vice versa). • From the first law of thermodynamics: when a system undergoes a physical or chemical change, the change in internal energy is given by the heat added to ...
... • Energy of (system + surroundings) is constant. • Any energy transferred from a system must be transferred to the surroundings (and vice versa). • From the first law of thermodynamics: when a system undergoes a physical or chemical change, the change in internal energy is given by the heat added to ...
MODULE 4
... Temperature & Heat • Heat is not the same as temperature • The more thermal energy, the more kinetic energy, the more motion the atoms and molecules will have • The total thermal energy of an object is the sum of all the individual energies • Thermal energy depends on the amount of substance as wel ...
... Temperature & Heat • Heat is not the same as temperature • The more thermal energy, the more kinetic energy, the more motion the atoms and molecules will have • The total thermal energy of an object is the sum of all the individual energies • Thermal energy depends on the amount of substance as wel ...
Chapter 21 Nonmetallic Elements and Their Compounds
... electrolysis of carbon tetrachloride. oxidation of chloride ion with F2(g). electrolysis of NaCl(aq). oxidation of chloride ion with Br2(aq). electrolysis of AlCl3(aq). ...
... electrolysis of carbon tetrachloride. oxidation of chloride ion with F2(g). electrolysis of NaCl(aq). oxidation of chloride ion with Br2(aq). electrolysis of AlCl3(aq). ...
Chemical Names and Formulas
... Copyright © 2004 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in her/his classroom. McGraw-Hill Ryerson shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. ...
... Copyright © 2004 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in her/his classroom. McGraw-Hill Ryerson shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. ...
Construction of Detailed Chemical Reaction Models
... products present in very small concentrations because depending on conditions their formation is dependent on complex chemistry involving stable and radical species, as well as reaction temperature. There is a need then to arrive at more complex mechanisms consisting of elementary reactions that are ...
... products present in very small concentrations because depending on conditions their formation is dependent on complex chemistry involving stable and radical species, as well as reaction temperature. There is a need then to arrive at more complex mechanisms consisting of elementary reactions that are ...
File
... Name: _______________________________________________________________________ Period: ____ 11.2: Types of Chemical Reactions Part A: Completion Directions: Each blank can be completed with a term, short phrase, or number. It is possible to __1__ the products of some chemical ...
... Name: _______________________________________________________________________ Period: ____ 11.2: Types of Chemical Reactions Part A: Completion Directions: Each blank can be completed with a term, short phrase, or number. It is possible to __1__ the products of some chemical ...
Outline
... B. Balanced by atoms AND charge AND mass 1. Coefficients 2. implied “1” if nothing written a. like you to write it anyway for now 3. lowest whole number ratio C. How to balance 1. method on p137 or… 2. another way a. find biggest, ugliest molecule b. put a “1” down as its coefficient c. work your wa ...
... B. Balanced by atoms AND charge AND mass 1. Coefficients 2. implied “1” if nothing written a. like you to write it anyway for now 3. lowest whole number ratio C. How to balance 1. method on p137 or… 2. another way a. find biggest, ugliest molecule b. put a “1” down as its coefficient c. work your wa ...
Review for SNC 2P Chemistry Unit(SPRING 2014)
... c) Na3P _______________________________________________ d) Ca(OH)2 + NaCl _______________________________________________ e) K3N + Cl2 _______________________________________________ f) silver nitrate + copper (II) sulfide _____________________________________________ g) Be3N2 ...
... c) Na3P _______________________________________________ d) Ca(OH)2 + NaCl _______________________________________________ e) K3N + Cl2 _______________________________________________ f) silver nitrate + copper (II) sulfide _____________________________________________ g) Be3N2 ...
AP Chemistry Ch. 3 Sections 3.7-3.8 Notes Chemical Equations
... Balancing Chemical Equations • When balancing a chemical equation you may add coefficients in front of the compounds to balance the equation but you may NOT change the subscripts. • Changing the subscripts changes the compound. • There are four basic steps to balancing a chemical equation. ...
... Balancing Chemical Equations • When balancing a chemical equation you may add coefficients in front of the compounds to balance the equation but you may NOT change the subscripts. • Changing the subscripts changes the compound. • There are four basic steps to balancing a chemical equation. ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.