Atomic Mass Units
... How to calculate the average atomic mass of an element: List all isotopes, mass numbers, and percent relative abundance of an element Multiply the mass number of each isotope by its relative abundance Add all the products together = atomic mass ...
... How to calculate the average atomic mass of an element: List all isotopes, mass numbers, and percent relative abundance of an element Multiply the mass number of each isotope by its relative abundance Add all the products together = atomic mass ...
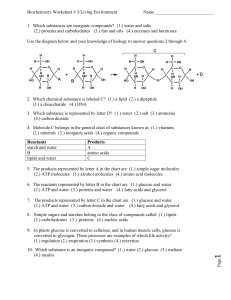
1. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
... 8. Simple sugars and starches belong to the class of compounds called (1.) lipids (2.) carbohydrates (3.) proteins (4.) nucleic acids ...
... 8. Simple sugars and starches belong to the class of compounds called (1.) lipids (2.) carbohydrates (3.) proteins (4.) nucleic acids ...
Interesting and Helpful Websites Early Models of the Atom
... First to suggest idea of atoms, they are invisible and indestructible. Law of conservation of matter. Law of constant composition, compounds contain the same elements in the same proportions by mass. – FORM A BASIC UNDERSTANDING… All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms ...
... First to suggest idea of atoms, they are invisible and indestructible. Law of conservation of matter. Law of constant composition, compounds contain the same elements in the same proportions by mass. – FORM A BASIC UNDERSTANDING… All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms ...
Atoms - Sterlingwikisci
... disagreed with Democritus’s ideas. He believed that you would never end up with a particle that could not be cut. Democritus was right, though: Matter is made of particles, which we call atoms. An atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still be the same substance. ...
... disagreed with Democritus’s ideas. He believed that you would never end up with a particle that could not be cut. Democritus was right, though: Matter is made of particles, which we call atoms. An atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still be the same substance. ...
Review Problems week 11 plus any problems left over from last week
... 9) Inhibition of a key enzyme activity by the end product of a biosynthetic pathway is known as what? 10) Why is it useful to have multiple isozymes of enzymes that comprise common pathways to multiple amino acids? 11) Partial inhibition of a key enzyme activity by multiple compounds derived from an ...
... 9) Inhibition of a key enzyme activity by the end product of a biosynthetic pathway is known as what? 10) Why is it useful to have multiple isozymes of enzymes that comprise common pathways to multiple amino acids? 11) Partial inhibition of a key enzyme activity by multiple compounds derived from an ...
Atomic Structure - s3.amazonaws.com
... Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
1.2 Atomic Structure
... atom of krypton must contain 36 electrons since it contains 36 protons. ...
... atom of krypton must contain 36 electrons since it contains 36 protons. ...
Atomic masses are weighted averages.
... chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. This is known as the Law of Definite Proportions – very important. ...
... chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. This is known as the Law of Definite Proportions – very important. ...
PRACTICE PROBLEMS EXAM 1,2 and 3 1311
... Practice problems Chapter 1 Chemical Foundations 1) A small amount of salt dissolved in water is an example of a __________. 2) Which one of the following is a pure substance? A) concrete B) wood C) salt water D) elemental copper E) milk 3) For which of the following can the composition vary? A) pur ...
... Practice problems Chapter 1 Chemical Foundations 1) A small amount of salt dissolved in water is an example of a __________. 2) Which one of the following is a pure substance? A) concrete B) wood C) salt water D) elemental copper E) milk 3) For which of the following can the composition vary? A) pur ...
Chemistry Scavenger Hunt
... Go to the “ChemTime Clock” area to find the answers to these questions. http://scifun.chem.wisc.edu/ChemTime/ChemTime.html 1. All materials, whether solid, liquid or gas, are made of _______________. Atoms are the smallest _______ of ___________. Scientists have found over _______ different kinds of ...
... Go to the “ChemTime Clock” area to find the answers to these questions. http://scifun.chem.wisc.edu/ChemTime/ChemTime.html 1. All materials, whether solid, liquid or gas, are made of _______________. Atoms are the smallest _______ of ___________. Scientists have found over _______ different kinds of ...
VOCABULARY name, date, hour: Fill in the number of each term
... ___ positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ stable, orbiting particle of an atom with a negative charge ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as groups ___ number of protons carried by the nucleus of an atom ___ el ...
... ___ positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ stable, orbiting particle of an atom with a negative charge ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as groups ___ number of protons carried by the nucleus of an atom ___ el ...
Chapter 4 - Atomic Structure - A
... Used experimental methods to develop a theory All elements composed of tiny indivisible particles = atoms Atoms in the same element are identical; atoms from 1 element are different form atoms of another element Atoms of different elements can physically mix or chemically combine in whole-number rat ...
... Used experimental methods to develop a theory All elements composed of tiny indivisible particles = atoms Atoms in the same element are identical; atoms from 1 element are different form atoms of another element Atoms of different elements can physically mix or chemically combine in whole-number rat ...
Chapter 2 - Saint Joseph High School
... 2.1: Chemical Bonds • Ionic Bonds are formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another • A loss or gain of electrons results in a positively or negatively charged atom known as an Ion ...
... 2.1: Chemical Bonds • Ionic Bonds are formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another • A loss or gain of electrons results in a positively or negatively charged atom known as an Ion ...
Biology 2.3 Carbon Compounds
... bones and muscles. Other proteins transport substances into or out of cells or help to fight disease. ...
... bones and muscles. Other proteins transport substances into or out of cells or help to fight disease. ...
PowerPoint - Models of the Atom
... Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. Often, at least one isotope is unstable. It breaks down, releasing radioactivity. These types of isotopes are called radioisotopes Q- Sometimes an isotope is written without its atomic number - e.g. 35S (or S-35). Why? A- The atomic # of an element do ...
... Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. Often, at least one isotope is unstable. It breaks down, releasing radioactivity. These types of isotopes are called radioisotopes Q- Sometimes an isotope is written without its atomic number - e.g. 35S (or S-35). Why? A- The atomic # of an element do ...
File - Ms M - EARL MARRIOTT SECONDARY
... Early discoveries of radiation relied on photographic equipment. Later, more sophisticated devices such as the Geiger-Müller counter were developed to more precisely measure radioactivity. Isotopes are different atoms of the same element, with the difference between the two atoms being the number of ...
... Early discoveries of radiation relied on photographic equipment. Later, more sophisticated devices such as the Geiger-Müller counter were developed to more precisely measure radioactivity. Isotopes are different atoms of the same element, with the difference between the two atoms being the number of ...
Article 2: Key Concepts and Vocabulary
... collisions with the surrounding material, transforming their kinetic energy into thermal energy. Some of the thermal energy sustains the plasma temperature, and some is converted into electricity. Finally, some of the electricity is used within the power plant to power magnets and other auxiliary sy ...
... collisions with the surrounding material, transforming their kinetic energy into thermal energy. Some of the thermal energy sustains the plasma temperature, and some is converted into electricity. Finally, some of the electricity is used within the power plant to power magnets and other auxiliary sy ...
Understanding Biochemistry
... • Much of our planet is covered in water • Water is necessary for life to exist • If life exists on other planets, there most likely is water present • Water has many properties that make life possible ...
... • Much of our planet is covered in water • Water is necessary for life to exist • If life exists on other planets, there most likely is water present • Water has many properties that make life possible ...
Macromolecules - Georgetown ISD
... 3. Carbon has how many electrons in its outer energy shell? 4. Carbon can form up to ______ covalent bonds with other atoms (elements) 5. Elements that carbon usually bonds with: _____, _____, _____, or _____. Example: ___________________ 6. Macromolecules are also called ___________________. 7. Mad ...
... 3. Carbon has how many electrons in its outer energy shell? 4. Carbon can form up to ______ covalent bonds with other atoms (elements) 5. Elements that carbon usually bonds with: _____, _____, _____, or _____. Example: ___________________ 6. Macromolecules are also called ___________________. 7. Mad ...
Chapter14
... Redox reactions can be separated into half-cells to create a battery. Batteries do word, therefore we can calculate the work (or free energy change) of redox reactions ...
... Redox reactions can be separated into half-cells to create a battery. Batteries do word, therefore we can calculate the work (or free energy change) of redox reactions ...
NATURE`S BIOLOGICAL BUILDING BLOCKS
... Composition: mostly carbon and hydrogen with some oxygen Includes fatty, greasy and waxy compounds relatively insoluble in water, but soluble in organic solvents such as ether and benzene. Neutral Fats - high energy molecules consisting of glycerol and fatty acids. Phospholipids - neutral fat with o ...
... Composition: mostly carbon and hydrogen with some oxygen Includes fatty, greasy and waxy compounds relatively insoluble in water, but soluble in organic solvents such as ether and benzene. Neutral Fats - high energy molecules consisting of glycerol and fatty acids. Phospholipids - neutral fat with o ...
genchm 113 - Angelfire
... Laws of Chemical Combination 1. Law of constant composition In a given compound, the relative numbers and kinds of atoms are constant. 2. Law of conservation of mass The total mass of materials present after a chemical reaction is the same as the total mass before the reaction. ...
... Laws of Chemical Combination 1. Law of constant composition In a given compound, the relative numbers and kinds of atoms are constant. 2. Law of conservation of mass The total mass of materials present after a chemical reaction is the same as the total mass before the reaction. ...
Atomic Structure
... mass. Joseph Proust (French chemist, 1754-1826) demonstrated that compounds have a constant (definite) composition by mass – “Proust’s law” is also known as the law of definite proportion. John Dalton (English school teacher, 1766-1844) discovered that elements can combine in different ratios to for ...
... mass. Joseph Proust (French chemist, 1754-1826) demonstrated that compounds have a constant (definite) composition by mass – “Proust’s law” is also known as the law of definite proportion. John Dalton (English school teacher, 1766-1844) discovered that elements can combine in different ratios to for ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.