CH 3 Biochemistry - Belle Vernon Area School District
... • Lipids that have tail chains with only single bonds between the carbon atoms are called saturated fats. • Lipids that have at least one double bond between carbon atoms in the tail chain are called unsaturated ...
... • Lipids that have tail chains with only single bonds between the carbon atoms are called saturated fats. • Lipids that have at least one double bond between carbon atoms in the tail chain are called unsaturated ...
Atomic Theory Part 1
... An element has a FIXED number of protons in its nucleus. (This information is contained within the element‟s Atomic Number. E.g. All hydrogen (H) atoms have 1 proton in their nuclei, while all carbon (C) atoms have 6 protons in their nuclei). HOWEVER, an element can have a VARIABLE number of neutron ...
... An element has a FIXED number of protons in its nucleus. (This information is contained within the element‟s Atomic Number. E.g. All hydrogen (H) atoms have 1 proton in their nuclei, while all carbon (C) atoms have 6 protons in their nuclei). HOWEVER, an element can have a VARIABLE number of neutron ...
Chapter 2 Notes The Chemistry of Life
... excellent vehicle for carrying substances in living systems. One way to move substances is by diffusion. • Diffusion is the net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. ...
... excellent vehicle for carrying substances in living systems. One way to move substances is by diffusion. • Diffusion is the net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. ...
Atomic Theory 1
... An element has a FIXED number of protons in its nucleus. (This information is contained within the element’s Atomic Number. E.g. All hydrogen (H) atoms have 1 proton in their nuclei, while all carbon (C) atoms have 6 protons in their nuclei). HOWEVER, an element can have a VARIABLE number of neutron ...
... An element has a FIXED number of protons in its nucleus. (This information is contained within the element’s Atomic Number. E.g. All hydrogen (H) atoms have 1 proton in their nuclei, while all carbon (C) atoms have 6 protons in their nuclei). HOWEVER, an element can have a VARIABLE number of neutron ...
Isotope
... Mass of Atoms (cont.) • Key Concept 27: The average atomic mass of an element is the weighted average mass of the isotopes of that ...
... Mass of Atoms (cont.) • Key Concept 27: The average atomic mass of an element is the weighted average mass of the isotopes of that ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... COMPOUNDS are composed of the SAME TWO ELEMENTS then the RATIO of the masses of the SECOND ELEMENT combined with a certain mass of the FIRST ELEMENT is always a ratio of ...
... COMPOUNDS are composed of the SAME TWO ELEMENTS then the RATIO of the masses of the SECOND ELEMENT combined with a certain mass of the FIRST ELEMENT is always a ratio of ...
Nuclear Chemistry PowerPoint
... parts, releasing a large amount of energy in the process. Most commonly this is done by "firing" a neutron at the nucleus of an atom. The energy of the neutron "bullet" causes the target element to split into two (or more) elements that are lighter than the parent atom. • During the fission of U235, ...
... parts, releasing a large amount of energy in the process. Most commonly this is done by "firing" a neutron at the nucleus of an atom. The energy of the neutron "bullet" causes the target element to split into two (or more) elements that are lighter than the parent atom. • During the fission of U235, ...
Atoms! - Holtmeyerhouse
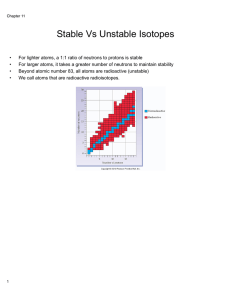
... Neutrons have no force, so they do not repel, they are like the glue helping hold together. When get too many protons ( above 83) not enough neutrons to hold. So all elements above 83 are radioactive. (state some) Also isotopes of stable atoms that have too many neutrons makes an atom unstable! ...
... Neutrons have no force, so they do not repel, they are like the glue helping hold together. When get too many protons ( above 83) not enough neutrons to hold. So all elements above 83 are radioactive. (state some) Also isotopes of stable atoms that have too many neutrons makes an atom unstable! ...
Atomic structure packets
... available and explain how this is different from Dalton’s original postulates. ...
... available and explain how this is different from Dalton’s original postulates. ...
Alpha Beta Fission Fusion
... In 1902, Frederick Soddy proposed the theory that "radioactivity is the result of a natural change of an isotope of one element into an isotope of a different element." Nuclear reactions involve changes in particles in an atom's nucleus and thus cause a change in the atom itself. All elements heavie ...
... In 1902, Frederick Soddy proposed the theory that "radioactivity is the result of a natural change of an isotope of one element into an isotope of a different element." Nuclear reactions involve changes in particles in an atom's nucleus and thus cause a change in the atom itself. All elements heavie ...
Physical Science
... A2: How are elements and compounds related? A. Elements and compounds are not related. Elements and compounds ARE related. It takes two or more elements chemically combined to make a compound. B. An element can be broken down into compounds. Elements cannot be broken down into compounds, but compou ...
... A2: How are elements and compounds related? A. Elements and compounds are not related. Elements and compounds ARE related. It takes two or more elements chemically combined to make a compound. B. An element can be broken down into compounds. Elements cannot be broken down into compounds, but compou ...
Unit 2 Outline - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... The unique properties of water make it essential to the existence of life. Properties of Water The many hydrogen bonds that link water molecules help water absorb heat without a great change in temperature. Water has a high heat of vaporization because hydrogen bonds must be broken before water boil ...
... The unique properties of water make it essential to the existence of life. Properties of Water The many hydrogen bonds that link water molecules help water absorb heat without a great change in temperature. Water has a high heat of vaporization because hydrogen bonds must be broken before water boil ...
Development of atomic theory
... indestructible particles. These particles, called atoms, maintain their identity when the element undergoes physical or chemical change. • 2. All atoms of the same element are identical and different from the atoms of every other element. • 3. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form comp ...
... indestructible particles. These particles, called atoms, maintain their identity when the element undergoes physical or chemical change. • 2. All atoms of the same element are identical and different from the atoms of every other element. • 3. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form comp ...
Metric Unit – Chapter 1
... combine in simple wholenumbered ratios to form 5. In chemical reactions, atoms ___________________________. are _____________________ 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are _______________________. ___________________________ ___________________________. ...
... combine in simple wholenumbered ratios to form 5. In chemical reactions, atoms ___________________________. are _____________________ 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are _______________________. ___________________________ ___________________________. ...
What do the numbers 238, 235 written against the name of the
... For most nuclei, the average binding energy per nucleon is about 8 MeV. Consequently, this amount of energy needs to be supplied to price a proton or neutron out of a nucleus. Is there any connection between the nuclear binding energy and the strong nuclear force? The strong force, due to gluon exch ...
... For most nuclei, the average binding energy per nucleon is about 8 MeV. Consequently, this amount of energy needs to be supplied to price a proton or neutron out of a nucleus. Is there any connection between the nuclear binding energy and the strong nuclear force? The strong force, due to gluon exch ...
Biology – The Living Environment
... Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter. That is to say that matter is composed of atoms. In chemistry, atoms can be represented by symbols. For example an oxygen atom is represented by the symbol O, carbon by the symbol C, nitrogen by the symbol N, and iron by the symbol Fe. Atoms are c ...
... Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter. That is to say that matter is composed of atoms. In chemistry, atoms can be represented by symbols. For example an oxygen atom is represented by the symbol O, carbon by the symbol C, nitrogen by the symbol N, and iron by the symbol Fe. Atoms are c ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... by 2 protons + 2 neutrons) AZ My AZ X + 4 He 5. Illustrate beta emission using new isotope in step 4 with equation and marshmallows AZ Y + 0-1 β 6. Label the following decay sequence as α or β emission: 238 U 234 Th 234 Pa 230 Th 226 Ra 222 Rn ...
... by 2 protons + 2 neutrons) AZ My AZ X + 4 He 5. Illustrate beta emission using new isotope in step 4 with equation and marshmallows AZ Y + 0-1 β 6. Label the following decay sequence as α or β emission: 238 U 234 Th 234 Pa 230 Th 226 Ra 222 Rn ...
Chapter 2-3 PPT
... b. They have different numbers of electrons. c. They have the same chemical properties but differ in atomic mass. d. They have the same number of protons and neutrons. ...
... b. They have different numbers of electrons. c. They have the same chemical properties but differ in atomic mass. d. They have the same number of protons and neutrons. ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... 2. **All atoms of the same element are identical in mass, volume, and properties. 3. Atoms can’t be created, destroyed, or divided. 4. Atoms combine in small, whole number ratios 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated or rearranged, NOT turned into another element. ...
... 2. **All atoms of the same element are identical in mass, volume, and properties. 3. Atoms can’t be created, destroyed, or divided. 4. Atoms combine in small, whole number ratios 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated or rearranged, NOT turned into another element. ...
Chapter 10 Test A
... c. there are no elements associated with these light sources. d. all elements have the same spectral pattern. ____ 18. Heisenburg’s uncertainty principle tells us that: a. the act of observing in the quantum world changes the very system you are trying to measure. b. we are always uncertain about th ...
... c. there are no elements associated with these light sources. d. all elements have the same spectral pattern. ____ 18. Heisenburg’s uncertainty principle tells us that: a. the act of observing in the quantum world changes the very system you are trying to measure. b. we are always uncertain about th ...
2. Chemistry of Living Things Outline
... catalyze. In organisms, _____________ allow the chemical reactions of ______________ to take place more efficiently than they otherwise would at body temperature. For example, amino acids are produced from protein digestion. The enzymes needed for this reaction are not changed but must be present fo ...
... catalyze. In organisms, _____________ allow the chemical reactions of ______________ to take place more efficiently than they otherwise would at body temperature. For example, amino acids are produced from protein digestion. The enzymes needed for this reaction are not changed but must be present fo ...
Chemistry of Living Things Outline
... reaction they catalyze. In organisms, _____________ allow the chemical reactions of ______________ to take place more efficiently than they otherwise would at body temperature. For example, amino acids are produced from protein digestion. The enzymes needed for this reaction are not changed but ...
... reaction they catalyze. In organisms, _____________ allow the chemical reactions of ______________ to take place more efficiently than they otherwise would at body temperature. For example, amino acids are produced from protein digestion. The enzymes needed for this reaction are not changed but ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.