Atomic number.
... part of a living organism is the atom. Atoms are the smallest part of an element. An element is a pure substance. • There are 25 different elements necessary to life can be classiffied into: SPONCH (98%) and Trace elements (elements that the body needs in small amounts). • The smallest particle of a ...
... part of a living organism is the atom. Atoms are the smallest part of an element. An element is a pure substance. • There are 25 different elements necessary to life can be classiffied into: SPONCH (98%) and Trace elements (elements that the body needs in small amounts). • The smallest particle of a ...
Calculation of Average Atomic Masses
... When calculating the atomic mass of an isotope, we will assume that the mass of the electrons are negligible, and the each proton and neutron contributes 1 amu to the mass of the isotope. These calculations will prove to be close but not exact since the sum of the mass of the individual protons and ...
... When calculating the atomic mass of an isotope, we will assume that the mass of the electrons are negligible, and the each proton and neutron contributes 1 amu to the mass of the isotope. These calculations will prove to be close but not exact since the sum of the mass of the individual protons and ...
Basic Atomic Structure and Isotope Symbols
... The Atomic Number is found in the element's box on the Periodic Table. The Mass Number depends on which isotope it is and is NOT found on the Periodic Table. Atomic Mass - is the weight of a particle as compared to Carbon - 12. Atomic Weight - is the average weight of all the atoms of all the isotop ...
... The Atomic Number is found in the element's box on the Periodic Table. The Mass Number depends on which isotope it is and is NOT found on the Periodic Table. Atomic Mass - is the weight of a particle as compared to Carbon - 12. Atomic Weight - is the average weight of all the atoms of all the isotop ...
The Periodic Table of Elements
... • The atomic mass of an element is often listed as the average atomic mass as found in nature. • This is a weighted average of the isotopes for that particular element. The more commonly found isotopes have a greater effect on the averages mass than the more rare isotopes. Ex: Cl 24% Cl-37 and 76% C ...
... • The atomic mass of an element is often listed as the average atomic mass as found in nature. • This is a weighted average of the isotopes for that particular element. The more commonly found isotopes have a greater effect on the averages mass than the more rare isotopes. Ex: Cl 24% Cl-37 and 76% C ...
Chemistry Standard 2A-Nucleus Section 20.1
... 4. The stability of an isotope nucleus depends on the ____. Page answer is found ____________ a. valence electrons c. number of neutrons b. atomic number d. neutron-to-proton ratio 5. What is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus emits charged particles or energy or both? Page answer is fo ...
... 4. The stability of an isotope nucleus depends on the ____. Page answer is found ____________ a. valence electrons c. number of neutrons b. atomic number d. neutron-to-proton ratio 5. What is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus emits charged particles or energy or both? Page answer is fo ...
Chapter 03
... 1. All matter is composed of atoms. 2. The atoms of a given element differ from the atoms of all other elements. 3. Chemical compounds consist of atoms combined in specific ratios. 4. Chemical reactions change only the way the atoms are combined in compounds; the atoms themselves are unchanged. Copy ...
... 1. All matter is composed of atoms. 2. The atoms of a given element differ from the atoms of all other elements. 3. Chemical compounds consist of atoms combined in specific ratios. 4. Chemical reactions change only the way the atoms are combined in compounds; the atoms themselves are unchanged. Copy ...
File - 7th Grade Science
... • Many buildings are made of just a few basic building materials, such as wood, nails, and glass. You can combine those materials in many different ways to make buildings of various shapes and sizes. How many things can you make from ...
... • Many buildings are made of just a few basic building materials, such as wood, nails, and glass. You can combine those materials in many different ways to make buildings of various shapes and sizes. How many things can you make from ...
Page | 1 MATS1101 Chemistry notes semester 2 2012 TOPIC 1
... Using this theory we can explain three fundamental laws of chemical behaviour: 1. Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy: Matter is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Energy is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, but it may be transformed from one form to another. ...
... Using this theory we can explain three fundamental laws of chemical behaviour: 1. Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy: Matter is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Energy is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, but it may be transformed from one form to another. ...
7th Science - Carterville CUSD #5
... 13. Atoms of the SAME ELEMENT always have the SAME NUMBER OF ________________. The two ways that atoms of the SAME ELEMENT can be different are if the number of _______________________ changes (then it is called an ___________________) or the number of _________________________ changes (this is call ...
... 13. Atoms of the SAME ELEMENT always have the SAME NUMBER OF ________________. The two ways that atoms of the SAME ELEMENT can be different are if the number of _______________________ changes (then it is called an ___________________) or the number of _________________________ changes (this is call ...
vibrations and waves
... ____________________ 3. Both Democritus and Dalton suggested that matter is made up of atoms. ____________________ 4. Dalton’s atomic theory stated that atoms separate, combine, or rearrange in chemical reactions. ____________________ 5. Dalton’s atomic theory stated that matter is mostly empty spac ...
... ____________________ 3. Both Democritus and Dalton suggested that matter is made up of atoms. ____________________ 4. Dalton’s atomic theory stated that atoms separate, combine, or rearrange in chemical reactions. ____________________ 5. Dalton’s atomic theory stated that matter is mostly empty spac ...
atom - BSCSChemistryA
... • Ionic compounds are compounds resulting from a reaction between ions e.g Sodium Chloride (Salt) ...
... • Ionic compounds are compounds resulting from a reaction between ions e.g Sodium Chloride (Salt) ...
Chapter 2 Notes - Duplin County Schools
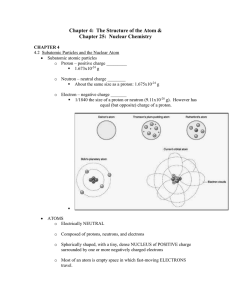
... nucleus in energy levels First energy level -- 2e Second energy level -- 8e Third energy level -- 18e ...
... nucleus in energy levels First energy level -- 2e Second energy level -- 8e Third energy level -- 18e ...
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom &
... o Gamma radiation is made of GAMMA RAYS (high energy radiation) No mass or charge Symbol is _______________ ...
... o Gamma radiation is made of GAMMA RAYS (high energy radiation) No mass or charge Symbol is _______________ ...
energy
... • Single sugar molecules are called monosaccharides • The large macromolecules formed from monosaccharides are known as polysaccharides ...
... • Single sugar molecules are called monosaccharides • The large macromolecules formed from monosaccharides are known as polysaccharides ...
Review Sheet for Chemistry* First Semester Final
... What happens when an “excited” electron falls back to its ground state? What does an emission spectrum allow one to do? ...
... What happens when an “excited” electron falls back to its ground state? What does an emission spectrum allow one to do? ...
Biology: Ch. 2
... Macromolecules are made from thousands of smaller molecules. Monomers-small unit that can join with other small units to form polymers. Polymers-large compound formed from combinations of many monomers. Four groups of organic compounds found in living things are carbohydrates, lipids, nuclei ...
... Macromolecules are made from thousands of smaller molecules. Monomers-small unit that can join with other small units to form polymers. Polymers-large compound formed from combinations of many monomers. Four groups of organic compounds found in living things are carbohydrates, lipids, nuclei ...
Biochemistry
... What is a molecule? A molecule is a very small piece of something. It is made up of different kinds of atoms. Example – a Water molecule (H2O) is made of 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen. A water molecule looks like this: ...
... What is a molecule? A molecule is a very small piece of something. It is made up of different kinds of atoms. Example – a Water molecule (H2O) is made of 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen. A water molecule looks like this: ...
Stoichiometry 1 amu = 1.6606 x 10-24 g The amu mass of an atom
... Stoichiometry 1 amu = 1.6606 x 10-24 g The amu mass of an atom of carbon-12 is 12 amu 1 mole = count multiplier = 6.022 x 1023 items subscript to the right of an element symbol = atom count multiplier = the number of atoms of the element in a chemical formula number before chemical formula in a chem ...
... Stoichiometry 1 amu = 1.6606 x 10-24 g The amu mass of an atom of carbon-12 is 12 amu 1 mole = count multiplier = 6.022 x 1023 items subscript to the right of an element symbol = atom count multiplier = the number of atoms of the element in a chemical formula number before chemical formula in a chem ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.