electron
... mass 10.012 amu and a relative abundance of 19.91%. The isotope with mass 11.009 amu has a relative abundance of 80.09%. 1. Calculate the atomic mass of this element (show all work) and then name this element. ...
... mass 10.012 amu and a relative abundance of 19.91%. The isotope with mass 11.009 amu has a relative abundance of 80.09%. 1. Calculate the atomic mass of this element (show all work) and then name this element. ...
Matt Knorr 2/3/2014 Summary: This lesson will explore the smallest
... Objective 2: Relate the structure, behavior, and scale of an atom to the particles that compose it. d. Generalize the relationship of proton number to the element’s identity. Objective 3: Correlate atomic structure and the physical and chemical properties of an element to the position of the element ...
... Objective 2: Relate the structure, behavior, and scale of an atom to the particles that compose it. d. Generalize the relationship of proton number to the element’s identity. Objective 3: Correlate atomic structure and the physical and chemical properties of an element to the position of the element ...
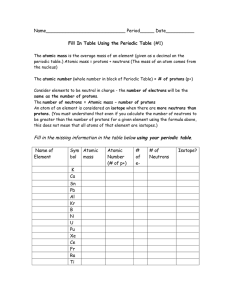
Periodic Table Fill in Table 1
... The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the number of electrons will be the same as the number of protons. The number of neutrons = Atomic mass – number of protons An atom of an element is considered an isotope when ...
... The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the number of electrons will be the same as the number of protons. The number of neutrons = Atomic mass – number of protons An atom of an element is considered an isotope when ...
Atomic Structure and Radioactivity
... - decay: the nucleus composition does not change. -decay occurs in large, unstable, nuclei. The heaviest stable isotope is 20983Bi. -decay transforms a neutron into a proton (n p+ + e ) Electron capture: p+ + e n and p+ n + e+ ...
... - decay: the nucleus composition does not change. -decay occurs in large, unstable, nuclei. The heaviest stable isotope is 20983Bi. -decay transforms a neutron into a proton (n p+ + e ) Electron capture: p+ + e n and p+ n + e+ ...
Unit #3 Atoms / Atomic Structure / Subatomic Particles
... What is a compound? Compoundchemical combination of elements. Each has its own unique and identifiable characteristics. Cannot be separated by physical means. Can be separated by chemical means. Example: Na is explosive when wet. Cl2 is a poisonous gas. When combined, they produce the compound know ...
... What is a compound? Compoundchemical combination of elements. Each has its own unique and identifiable characteristics. Cannot be separated by physical means. Can be separated by chemical means. Example: Na is explosive when wet. Cl2 is a poisonous gas. When combined, they produce the compound know ...
Unit 3 Power Point
... What is a compound? Compoundchemical combination of elements. Each has its own unique and identifiable characteristics. Cannot be separated by physical means. Can be separated by chemical means. Example: Na is explosive when wet. Cl2 is a poisonous gas. When combined, they produce the compound know ...
... What is a compound? Compoundchemical combination of elements. Each has its own unique and identifiable characteristics. Cannot be separated by physical means. Can be separated by chemical means. Example: Na is explosive when wet. Cl2 is a poisonous gas. When combined, they produce the compound know ...
the teeni tiny atoms - Supercomputing Challenge
... Buckminster fullerene. Diamond is the hardest natural material known to man, Graphite has a special crystalline structure with the carbon atom are on layers of each other, The Buckminster fullerene is made out of carbon and looks like a soccer ball, also it’s a molecule consisting sixty carbon atoms ...
... Buckminster fullerene. Diamond is the hardest natural material known to man, Graphite has a special crystalline structure with the carbon atom are on layers of each other, The Buckminster fullerene is made out of carbon and looks like a soccer ball, also it’s a molecule consisting sixty carbon atoms ...
Prentice hall Biology Worksheets
... 3. Different isotopes of the same element have different numbers of 4. Isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties because they have the same number of 5. In a(an) one atom to another. ...
... 3. Different isotopes of the same element have different numbers of 4. Isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties because they have the same number of 5. In a(an) one atom to another. ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... you will have time to ask questions about what you don’t understand. Do not forget to use your study guide from the first quarter exam to also help you review for your semester final. If you do not have your first quarter review packet you can get another (and the answers) at: http://www.ncusd203.or ...
... you will have time to ask questions about what you don’t understand. Do not forget to use your study guide from the first quarter exam to also help you review for your semester final. If you do not have your first quarter review packet you can get another (and the answers) at: http://www.ncusd203.or ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... you will have time to ask questions about what you don’t understand. Do not forget to use your study guide from the first quarter exam to also help you review for your semester final. If you do not have your first quarter review packet you can get another (and the answers) at: http://www.ncusd203.or ...
... you will have time to ask questions about what you don’t understand. Do not forget to use your study guide from the first quarter exam to also help you review for your semester final. If you do not have your first quarter review packet you can get another (and the answers) at: http://www.ncusd203.or ...
Chemical reaction
... distributed into another • Solute – the substance dissolved in the solution (Sugar) • Solvent – the substance in which the ...
... distributed into another • Solute – the substance dissolved in the solution (Sugar) • Solvent – the substance in which the ...
Central New Brunswick Academy
... Frederick Soddy, a colleague of Rutherford’s at McGill, was the first to propose that the number of neutrons can vary from atom to atom, even in atoms of the same element. An isotope is a form of an element in which the atoms have the same number of protons as all other form of that element, but a d ...
... Frederick Soddy, a colleague of Rutherford’s at McGill, was the first to propose that the number of neutrons can vary from atom to atom, even in atoms of the same element. An isotope is a form of an element in which the atoms have the same number of protons as all other form of that element, but a d ...
Practice Exam I
... store energy catalyze reactions contain hereditary information make up membranes ...
... store energy catalyze reactions contain hereditary information make up membranes ...
Isotopes - Wando High School
... What is an isotope? • Not every atom is exactly the same • We know that different elements have different number of protons. • However even atoms of the same element are not exactly the same. • Atoms of the same element can have different number of neutrons. These are called Isotopes. ...
... What is an isotope? • Not every atom is exactly the same • We know that different elements have different number of protons. • However even atoms of the same element are not exactly the same. • Atoms of the same element can have different number of neutrons. These are called Isotopes. ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions History
... Angstrom (A) - a convenient non-SI unit of length used to express atomic dimensions. • 1 Angstrom = 1 x 10-10 meters -10 m • most atoms have diameters between ...
... Angstrom (A) - a convenient non-SI unit of length used to express atomic dimensions. • 1 Angstrom = 1 x 10-10 meters -10 m • most atoms have diameters between ...
Section 6.2 Notes - oologah.k12.ok.us
... Isotopes Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Because isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons, they also have different mass numbers Hydrogen has three isotopes What are they? ...
... Isotopes Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Because isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons, they also have different mass numbers Hydrogen has three isotopes What are they? ...
Name: _key Date: ______ Period: Unit 3 – Atomic Structure Review
... 8. What do we call atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons? isotopes 9. What are atoms that have different numbers of protons? 10. How many protons, neutron, and electrons does U-234 have? P-92, E-92, N-142 11. How many electrons would it take to equal the mass of one proto ...
... 8. What do we call atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons? isotopes 9. What are atoms that have different numbers of protons? 10. How many protons, neutron, and electrons does U-234 have? P-92, E-92, N-142 11. How many electrons would it take to equal the mass of one proto ...
C C C H1 H H
... Copyright 2002-2004 by Jason Neil. All rights reserved. To make copies permission must be obtained from www.ChemistryInquiry.com ...
... Copyright 2002-2004 by Jason Neil. All rights reserved. To make copies permission must be obtained from www.ChemistryInquiry.com ...
C C C H1 H H
... Copyright 2002-2004 by Jason Neil. All rights reserved. To make copies permission must be obtained from www.ChemistryInquiry.com ...
... Copyright 2002-2004 by Jason Neil. All rights reserved. To make copies permission must be obtained from www.ChemistryInquiry.com ...
PrepGuide - Structure of the Atom
... Copyright 2002-2004 by Jason Neil. All rights reserved. To make copies permission must be obtained from www.ChemistryInquiry.com ...
... Copyright 2002-2004 by Jason Neil. All rights reserved. To make copies permission must be obtained from www.ChemistryInquiry.com ...
Name: Date: AP Chemistry/Chemistry 145 Summer Assignment
... and 25.98259 amu. The relative abundances of these three isotopes are 78.70%, 10.13 %, and 11.17% respectively. Calculate the average atomic mass. ...
... and 25.98259 amu. The relative abundances of these three isotopes are 78.70%, 10.13 %, and 11.17% respectively. Calculate the average atomic mass. ...
Structure of the Atom
... 3) Atoms combine in whole-number ratios to form compounds 4) In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged – but never changed into atoms of another element. ...
... 3) Atoms combine in whole-number ratios to form compounds 4) In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged – but never changed into atoms of another element. ...
The Structure of the Atom
... • The number of protons in an atom. • The atomic number can never be changed in an element. • The Periodic Table organizes all known elements by increasing atomic number. (figure 1) the image to the left shows liquid nitrogen rapid evaporating. Pencil lead is just one product made from carbon atoms ...
... • The number of protons in an atom. • The atomic number can never be changed in an element. • The Periodic Table organizes all known elements by increasing atomic number. (figure 1) the image to the left shows liquid nitrogen rapid evaporating. Pencil lead is just one product made from carbon atoms ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.