The Foundations of Rome
... b. In what ways do you think the rule of the Etruscans might have been good for Rome? c. How did plebeian life change after 494 BC? Why? d. What were the duties of the magistrates? e. How could the tribunes influence the magistrates? f. How could the Senate control the magistrates? g. What happened ...
... b. In what ways do you think the rule of the Etruscans might have been good for Rome? c. How did plebeian life change after 494 BC? Why? d. What were the duties of the magistrates? e. How could the tribunes influence the magistrates? f. How could the Senate control the magistrates? g. What happened ...
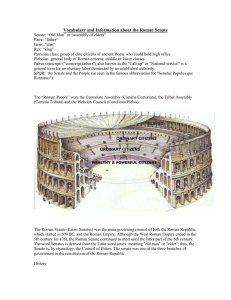
Vocabulary and Information about the Roman Senate
... The Senate held considerable authority (auctoritas) in Roman politics. It was the official body that sent and received ambassadors, and it appointed officials to manage public lands, including the provincial governors. It conducted wars and it also appropriated all public funds and issued money. It ...
... The Senate held considerable authority (auctoritas) in Roman politics. It was the official body that sent and received ambassadors, and it appointed officials to manage public lands, including the provincial governors. It conducted wars and it also appropriated all public funds and issued money. It ...
The Senate - wbphillipskhs
... – Became a republic – “a thing of the people” – where all officials were elected – Kept any one person from gaining too much power – SPQR = Senatus Populus que Romanus (The Senate and People of Rome) ...
... – Became a republic – “a thing of the people” – where all officials were elected – Kept any one person from gaining too much power – SPQR = Senatus Populus que Romanus (The Senate and People of Rome) ...
The Roman Republic Political Structure
... modern political system. Since the Romans did not want one man to make all of the laws, they decided to balance the power: ...
... modern political system. Since the Romans did not want one man to make all of the laws, they decided to balance the power: ...
The Roman Republic (510-44 BC) The Roman Republic (Latin: Res
... embodiment of Rome, it was the official body that sent and received ambassadors on behalf of the city, that appointed officials to manage the public lands – including provincial (an official in ...
... embodiment of Rome, it was the official body that sent and received ambassadors on behalf of the city, that appointed officials to manage the public lands – including provincial (an official in ...
Rome -- The Kings, Tarquins and Early Republic
... Another story is The Aeneid, by Virgil,featuring Aeneas, (a-KNEE-us) a survivor of Troy in the myth, The Illiad, Aeneas built the city and his sons were Romulus and Remus The historical truth: seven villages of Latins which were separated by swamp, were attacked by the Sabines and the Etruscans, the ...
... Another story is The Aeneid, by Virgil,featuring Aeneas, (a-KNEE-us) a survivor of Troy in the myth, The Illiad, Aeneas built the city and his sons were Romulus and Remus The historical truth: seven villages of Latins which were separated by swamp, were attacked by the Sabines and the Etruscans, the ...
Ancient Rome Powerpoint
... The assembly gathered into a public place called “The Forum” where they would make votes. Tasks of the assembly: • vote on new laws suggested by ...
... The assembly gathered into a public place called “The Forum” where they would make votes. Tasks of the assembly: • vote on new laws suggested by ...
JUICY DETALS
... • In theory, the position of emperor was not hereditary – It was not passed down automatically from father to son – According to law, when an emperor dies, his power reverted back to the people of Rome and they could then give this power to whomever they ...
... • In theory, the position of emperor was not hereditary – It was not passed down automatically from father to son – According to law, when an emperor dies, his power reverted back to the people of Rome and they could then give this power to whomever they ...
Greek and Roman Government - Mr. Hudec and His Latin Stuff
... Two elected men at least 40 years old; executive power ...
... Two elected men at least 40 years old; executive power ...
Growing Unrest in Rome
... –Recruited his armies by ______________________ the _________________poor that he would give them land if they swore an __________________ to __________________, not to Rome. •Result: This type of army was __________________ in government control. –More power in the hands of the generals Sulla •Was ...
... –Recruited his armies by ______________________ the _________________poor that he would give them land if they swore an __________________ to __________________, not to Rome. •Result: This type of army was __________________ in government control. –More power in the hands of the generals Sulla •Was ...
The Roman Republic
... could be elected to office, so they held all political power. Magistrates Elected government officials who enforce the law The top officials in the Roman Republic Consuls ...
... could be elected to office, so they held all political power. Magistrates Elected government officials who enforce the law The top officials in the Roman Republic Consuls ...
Roman Emperors Through the First Century
... f.A revolt of legions in Spain and Gaul led to his suicide. 8. Year of the Four Emperors, A.D. 69. a.Marked the end of the Julio-Claudian Emperors, so called because all those from Augustus to Nero wore the family name of Julius or Claudius. b.Galba, Otho, and Vitellius in turn managed to get contro ...
... f.A revolt of legions in Spain and Gaul led to his suicide. 8. Year of the Four Emperors, A.D. 69. a.Marked the end of the Julio-Claudian Emperors, so called because all those from Augustus to Nero wore the family name of Julius or Claudius. b.Galba, Otho, and Vitellius in turn managed to get contro ...
Slide 1
... peace, stability and order. 180 magistrates (judges) would oversee the court cases. They were broken into 4 court rooms, so there were 45 judges at each trial. The accused were allowed to have lawyers and the public was allowed to watch the trials. Oftentimes lawyers would hire crowds of spectators ...
... peace, stability and order. 180 magistrates (judges) would oversee the court cases. They were broken into 4 court rooms, so there were 45 judges at each trial. The accused were allowed to have lawyers and the public was allowed to watch the trials. Oftentimes lawyers would hire crowds of spectators ...
Fall of the Roman Republic
... • RESULT: Senators were furious • They later killed both brothers ...
... • RESULT: Senators were furious • They later killed both brothers ...
The Roman Republic - `er` and `est` (1)
... society were the 600 men in the Senate who were called Senators. • It was made up of men who had served as magistrates and could then became members of the Senate for life. • They discussed and debated issues. • They made the laws. ...
... society were the 600 men in the Senate who were called Senators. • It was made up of men who had served as magistrates and could then became members of the Senate for life. • They discussed and debated issues. • They made the laws. ...
Social Studies Study Guide
... o Republic – a country where citizens elect their government officials. o Empire – areas that are ruled by one country. o Dictator – during the Roman Republic, dictators were appointed in times of crisis to serve for 6 months. o Twelve Tables – written laws that were engraved in stone and placed in ...
... o Republic – a country where citizens elect their government officials. o Empire – areas that are ruled by one country. o Dictator – during the Roman Republic, dictators were appointed in times of crisis to serve for 6 months. o Twelve Tables – written laws that were engraved in stone and placed in ...
Chp 8, Sec 1 The Beginning of Rome Powerpoint
... Plebeians felt the Senate was unfair to them and refused to continue to serve in the army until changes were made • Senate created the The Twelve Tables, a list of laws that applied to all citizens, Patrician or ...
... Plebeians felt the Senate was unfair to them and refused to continue to serve in the army until changes were made • Senate created the The Twelve Tables, a list of laws that applied to all citizens, Patrician or ...
Chapter 10 “The Roman Republic” Cornell Notes I. A
... Vocabulary to know a. Republic: government where citizens have the right to vote and elect officials b. Patricians: (Aristocracy), nobles and wealthy families of ancient Rome c. Plebeians: citizens of Rome, common man, lower class i. Nickname was ‘Plebs’- Latin for “to fill up” d. Orator: person who ...
... Vocabulary to know a. Republic: government where citizens have the right to vote and elect officials b. Patricians: (Aristocracy), nobles and wealthy families of ancient Rome c. Plebeians: citizens of Rome, common man, lower class i. Nickname was ‘Plebs’- Latin for “to fill up” d. Orator: person who ...
the roman republic
... Patricians: these were the wealthy Latin aristocrats who pushed the Etruscans out and established a government where only they could hold office. This government was really for nobles (aristocracy) Plebeians These were the commoners of wealth and poverty. From merchant to the street worker, ...
... Patricians: these were the wealthy Latin aristocrats who pushed the Etruscans out and established a government where only they could hold office. This government was really for nobles (aristocracy) Plebeians These were the commoners of wealth and poverty. From merchant to the street worker, ...
The Roman Republic
... Tripartite – government was divided into 3 parts which limited power of each part Consul – replaced the king Senate – group of 300 leaders who advised the consuls Dictator – leader who had complete power during his time in office, which was limited to 6 months Patrician – wealthy landowners from ear ...
... Tripartite – government was divided into 3 parts which limited power of each part Consul – replaced the king Senate – group of 300 leaders who advised the consuls Dictator – leader who had complete power during his time in office, which was limited to 6 months Patrician – wealthy landowners from ear ...
The Kings, Tarquins and Early Republic - ancient-rome
... who had been doing the right things and even entertained him as a guest Lucretia told her husband and then killed her self to right the matter, led to a rebellion against the Tarquins led by Brutus, who had acted liked an idiot to avoid being killed Brutus became one of 1st consuls, killed his own s ...
... who had been doing the right things and even entertained him as a guest Lucretia told her husband and then killed her self to right the matter, led to a rebellion against the Tarquins led by Brutus, who had acted liked an idiot to avoid being killed Brutus became one of 1st consuls, killed his own s ...
Lat-CULTURE_HISTORY-Littletown-Pt3-2016
... i. G______________M________, a general, reformed the army and made it professional; was consul several times and held a lot of political power; supported the common people and belonged to the P_____________ party ii. Later, another general, S_______, took control of the Roman government with the sup ...
... i. G______________M________, a general, reformed the army and made it professional; was consul several times and held a lot of political power; supported the common people and belonged to the P_____________ party ii. Later, another general, S_______, took control of the Roman government with the sup ...
Early Roman Republic Lecture (complete Roman Republic Flowchart)
... • A system of government where a group of leaders is elected to govern as representatives of the people. ...
... • A system of government where a group of leaders is elected to govern as representatives of the people. ...
Roman Senate

The Roman Senate was a political institution in ancient Rome. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being established in the first days of the city (traditionally founded in 753 BC). It survived the overthrow of the kings in 509 BC, the fall of the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC, the division of the Roman Empire in 395 AD, the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD, and the barbarian rule of Rome in the 5th, 6th, and 7th centuries.During the days of the kingdom, it was little more than an advisory council to the king. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Republic.During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the executive magistrates were quite powerful. Since the transition from monarchy to constitutional rule was probably gradual, it took several generations before the Senate was able to assert itself over the executive magistrates. By the middle Republic, the Senate had reached the apex of its republican power. The late Republic saw a decline in the Senate's power, which began following the reforms of the tribunes Tiberius and Gaius Gracchus.After the transition of the Republic into the Principate, the Senate lost much of its political power as well as its prestige. Following the constitutional reforms of the Emperor Diocletian, the Senate became politically irrelevant, and never regained the power that it had once held. When the seat of government was transferred out of Rome, the Senate was reduced to a municipal body. This decline in status was reinforced when the emperor Constantine the Great created an additional senate in Constantinople.After the Western Roman Empire fell in 476, the Senate in the west functioned for a time under barbarian rule before being restored after the reconquest of much of the Western Roman Empire's territories during the reign of Justinian I. The Senate in Rome ultimately disappeared at some point between 603 and 630. However, the Eastern Senate survived in Constantinople, until the ancient institution finally vanished there circa 14th century.