Early Roman Cultures - Miss Burnett`s 6th grade Classroom
... • Rivals of Rome • Fought in Punic Wars against Rome ...
... • Rivals of Rome • Fought in Punic Wars against Rome ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... Western Mediterranean • The First Punic War (264241 BC) – Island of Sicily – Roman navy – Rome eventually prevailed • Terms of settlement ...
... Western Mediterranean • The First Punic War (264241 BC) – Island of Sicily – Roman navy – Rome eventually prevailed • Terms of settlement ...
The Republic - s3.amazonaws.com
... BUT, he was killed by senate Gaius Gracchus Same reforms, same fate ...
... BUT, he was killed by senate Gaius Gracchus Same reforms, same fate ...
Plebeian Council - CLIO History Journal
... was organized as an Assembly, and not as a Council even though only patricians were members. • Assembly of the Centuries – (comitia centuriata or "Army Assembly") of the Roman Republic was the democratic assembly of the Roman soldiers. The Century Assembly was organized as an Assembly, as every Roma ...
... was organized as an Assembly, and not as a Council even though only patricians were members. • Assembly of the Centuries – (comitia centuriata or "Army Assembly") of the Roman Republic was the democratic assembly of the Roman soldiers. The Century Assembly was organized as an Assembly, as every Roma ...
Patronas - WordPress.com
... Romulus in 753BCE. Monarchical rule in Rome grew steadily more tyrannical until Rome overthrew the seventh king, the spectacularly named Tarquinius Superbus in about 550BCE. This revolution in which plebian and patrician joined forces to establish a democracy was a hugely significant event and shape ...
... Romulus in 753BCE. Monarchical rule in Rome grew steadily more tyrannical until Rome overthrew the seventh king, the spectacularly named Tarquinius Superbus in about 550BCE. This revolution in which plebian and patrician joined forces to establish a democracy was a hugely significant event and shape ...
File
... Overhead # 3 Republic 509 BCE Republic- Citizens elect leaders to run government Consuls- Leaders elected by Assembly, advised by a senate, and replaced kings Early republic was not a democracy why?- citizens didn’t have same economic power, thus could not have same role in the government. ...
... Overhead # 3 Republic 509 BCE Republic- Citizens elect leaders to run government Consuls- Leaders elected by Assembly, advised by a senate, and replaced kings Early republic was not a democracy why?- citizens didn’t have same economic power, thus could not have same role in the government. ...
The Roman Republic and Empire
... Romans established a government called a republic (a government in which supreme power belongs to the citizens through their right to vote) Romans thought a republic (indirect democracy) would keep any individual from gaining too much power The 300 members of the republic’s senate were all patrician ...
... Romans established a government called a republic (a government in which supreme power belongs to the citizens through their right to vote) Romans thought a republic (indirect democracy) would keep any individual from gaining too much power The 300 members of the republic’s senate were all patrician ...
The Roman Republic
... 2) The accuser must prove their case, not the accused 3) Unreasonable or unfair laws would be set aside Justinian’s Code ...
... 2) The accuser must prove their case, not the accused 3) Unreasonable or unfair laws would be set aside Justinian’s Code ...
Founding the Roman Republic
... Republic- A form of government in which voters elect officials to run the state. Only adult male citizens were entitled to vote and take part in government Senate Most influential and powerful of the three governing bodies because it controlled public funds and decided foreign policy Somet ...
... Republic- A form of government in which voters elect officials to run the state. Only adult male citizens were entitled to vote and take part in government Senate Most influential and powerful of the three governing bodies because it controlled public funds and decided foreign policy Somet ...
How did the Rome Republic come to an end?
... B. Various laws had been put to limit the rights of the Plebians C. Series of civil wars broke out. At the same time, the Roman Army was winning over territories. D. Corruptions and competition within the government ...
... B. Various laws had been put to limit the rights of the Plebians C. Series of civil wars broke out. At the same time, the Roman Army was winning over territories. D. Corruptions and competition within the government ...
Roman Reformers
... General who became consul in 107 B.C. first lower class Roman to be elected to such a high office Set up professional army, everyone could join. Offered pay, land, pensions, and items Helped by providing jobs, hurt by making soldiers loyal to general rather than the government ...
... General who became consul in 107 B.C. first lower class Roman to be elected to such a high office Set up professional army, everyone could join. Offered pay, land, pensions, and items Helped by providing jobs, hurt by making soldiers loyal to general rather than the government ...
WHCH_51 - Teacherpage
... Republic • Romans defeated the Etruscans and drove them away in 509 B.C. • Republic – “res publica” that which belongs to the people • People chose some of the officials • Romans believed this would stop an individual from gaining to much power ...
... Republic • Romans defeated the Etruscans and drove them away in 509 B.C. • Republic – “res publica” that which belongs to the people • People chose some of the officials • Romans believed this would stop an individual from gaining to much power ...
Rome Republic TEST Study Guide
... government, checks and balances, and civic duty. We highlighted key phrases to help you on pg. 38 of your binder’s ISN section. o Your answer needs to be specific and descriptive. You cannot just “name” what we got from the Romans, nor can 2 Consuls you say “and we use it today” without further -Sen ...
... government, checks and balances, and civic duty. We highlighted key phrases to help you on pg. 38 of your binder’s ISN section. o Your answer needs to be specific and descriptive. You cannot just “name” what we got from the Romans, nor can 2 Consuls you say “and we use it today” without further -Sen ...
Early Peoples powerpoint
... • In 509 B.C. the Romans rebelled against the Republic Etruscans and formed a _______________. ...
... • In 509 B.C. the Romans rebelled against the Republic Etruscans and formed a _______________. ...
The Roman Empire (after 27 BC)
... former magistrates. It made local laws, and its members were appointed for life. In an emergency, the Council could appoint a Praefectus Iure Dicundo, who was in effect a dictator. He would run the city until the emergency was over. This was the case following the earthquake of 62 AD in Pompeii. ...
... former magistrates. It made local laws, and its members were appointed for life. In an emergency, the Council could appoint a Praefectus Iure Dicundo, who was in effect a dictator. He would run the city until the emergency was over. This was the case following the earthquake of 62 AD in Pompeii. ...
The Roman Republic
... The Assembly was composed of all the plebeian citizens of Rome, the common man. The Assembly did not have a building. It was the right of the common man to assemble in the Forum and vote. In the beginning, the Assembly had very limited power. They could vote for or suggest laws, but the Senate could ...
... The Assembly was composed of all the plebeian citizens of Rome, the common man. The Assembly did not have a building. It was the right of the common man to assemble in the Forum and vote. In the beginning, the Assembly had very limited power. They could vote for or suggest laws, but the Senate could ...
From the Roman Republic to the Roman Empire
... Consuls. Was the most powerful political position in Rome. • The consuls issued laws and led the army. In order to prevent one person from becoming too powerful, each consul could veto the decisions of the other. ...
... Consuls. Was the most powerful political position in Rome. • The consuls issued laws and led the army. In order to prevent one person from becoming too powerful, each consul could veto the decisions of the other. ...
From the Roman Republic to the Roman Empire
... Consuls. The most powerful political position in Rome. • The consuls issued laws • Led the army. • In order to prevent one person from becoming too powerful, each consul could veto the decisions of the other. ...
... Consuls. The most powerful political position in Rome. • The consuls issued laws • Led the army. • In order to prevent one person from becoming too powerful, each consul could veto the decisions of the other. ...
He was probably the greatest general of Roman history His soldiers
... In 50 BC Pompey’s allies in the senate ordered Caesar to give up his legions and return to Rome In 49 BC Caesar “crossed the Rubicon,” which led to civil war ...
... In 50 BC Pompey’s allies in the senate ordered Caesar to give up his legions and return to Rome In 49 BC Caesar “crossed the Rubicon,” which led to civil war ...
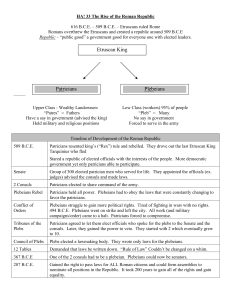
Patricians Plebeians Etruscan King
... 2 *consuls—chief magistrates who presided over the Senate and assemblies, administered legislation, served as generals in military campaigns, and represented Rome in foreign affairs. Consuls could appoint and/or serve as *dictator for up to 6 months in times of emergency. When their term of office w ...
... 2 *consuls—chief magistrates who presided over the Senate and assemblies, administered legislation, served as generals in military campaigns, and represented Rome in foreign affairs. Consuls could appoint and/or serve as *dictator for up to 6 months in times of emergency. When their term of office w ...
The Government of the Republic
... From Monarchy to Republic Rome began as an independent city state ...
... From Monarchy to Republic Rome began as an independent city state ...
Roman Senate

The Roman Senate was a political institution in ancient Rome. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being established in the first days of the city (traditionally founded in 753 BC). It survived the overthrow of the kings in 509 BC, the fall of the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC, the division of the Roman Empire in 395 AD, the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD, and the barbarian rule of Rome in the 5th, 6th, and 7th centuries.During the days of the kingdom, it was little more than an advisory council to the king. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Republic.During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the executive magistrates were quite powerful. Since the transition from monarchy to constitutional rule was probably gradual, it took several generations before the Senate was able to assert itself over the executive magistrates. By the middle Republic, the Senate had reached the apex of its republican power. The late Republic saw a decline in the Senate's power, which began following the reforms of the tribunes Tiberius and Gaius Gracchus.After the transition of the Republic into the Principate, the Senate lost much of its political power as well as its prestige. Following the constitutional reforms of the Emperor Diocletian, the Senate became politically irrelevant, and never regained the power that it had once held. When the seat of government was transferred out of Rome, the Senate was reduced to a municipal body. This decline in status was reinforced when the emperor Constantine the Great created an additional senate in Constantinople.After the Western Roman Empire fell in 476, the Senate in the west functioned for a time under barbarian rule before being restored after the reconquest of much of the Western Roman Empire's territories during the reign of Justinian I. The Senate in Rome ultimately disappeared at some point between 603 and 630. However, the Eastern Senate survived in Constantinople, until the ancient institution finally vanished there circa 14th century.