THE BACK
... THE BACK MUSCLES • SUPERFICIAL EXTRINSIC BACK MUSCLES • INTERMEDIATE EXTRINSIC BACK MUSCLES • DEEP INTRINSIC BACK MUSCLES ...
... THE BACK MUSCLES • SUPERFICIAL EXTRINSIC BACK MUSCLES • INTERMEDIATE EXTRINSIC BACK MUSCLES • DEEP INTRINSIC BACK MUSCLES ...
1 - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... B. Infraspinatus C. Supraspinatus D. Subscapularis ...
... B. Infraspinatus C. Supraspinatus D. Subscapularis ...
9cd41c0f1293979
... It passes through the infraorbital groove and canal in the floor of the orbit, continues as the infraorbital nerve which it appears in the face through the infraorbital foramen. Branches: I- In the cranial cavity: meningeal branch to the dura matter of middle meningeal fossa II- In the pterygopalati ...
... It passes through the infraorbital groove and canal in the floor of the orbit, continues as the infraorbital nerve which it appears in the face through the infraorbital foramen. Branches: I- In the cranial cavity: meningeal branch to the dura matter of middle meningeal fossa II- In the pterygopalati ...
Soft-tissue anatomy of the Plesiosaur pectoral girdle inferred from
... 2002). Comparisons with placodonts are difficult because they evolved their own locomotion patterns that depart from those seen in Eosauropterygia (Mazin and Pinna, 1993). Therefore, until new discoveries are made, the other hypotheses appear to be more compelling. Similarly, not only are the baupla ...
... 2002). Comparisons with placodonts are difficult because they evolved their own locomotion patterns that depart from those seen in Eosauropterygia (Mazin and Pinna, 1993). Therefore, until new discoveries are made, the other hypotheses appear to be more compelling. Similarly, not only are the baupla ...
ANTEROLATERAL THIGH FLAP
... In clinical practice, it is best to trace the perforator in a retrograde manner from distal (skin side) to proximal (main pedicle), dividing the overlying muscle fibres in the manner of a facial nerve dissection during a superficial parotidectomy. Figure 5 For the purposes of this course, if you run ...
... In clinical practice, it is best to trace the perforator in a retrograde manner from distal (skin side) to proximal (main pedicle), dividing the overlying muscle fibres in the manner of a facial nerve dissection during a superficial parotidectomy. Figure 5 For the purposes of this course, if you run ...
1. Exoskeletons and endoskeletons differ in that
... A. Answer a is incorrect. The action potential must occur before the other events. The correct answer is d— B. Answer b is incorrect. Ca2+ must bind to troponin before myosin binds to actin. The correct answer is d— C. Answer c is incorrect. Ca2+ must bind to troponin before myosin binds to actin. T ...
... A. Answer a is incorrect. The action potential must occur before the other events. The correct answer is d— B. Answer b is incorrect. Ca2+ must bind to troponin before myosin binds to actin. The correct answer is d— C. Answer c is incorrect. Ca2+ must bind to troponin before myosin binds to actin. T ...
PART II - LWW.com
... their own referral patterns. Mostly, however, both refer pain to the face and the head, not the neck. The referrals often mimic the symptoms of atypical facial neuralgia or tension headaches. Often dentists recognize these referrals as a component of facial pain complaints. From the sternal portion ...
... their own referral patterns. Mostly, however, both refer pain to the face and the head, not the neck. The referrals often mimic the symptoms of atypical facial neuralgia or tension headaches. Often dentists recognize these referrals as a component of facial pain complaints. From the sternal portion ...
1. All of the statement are true except: a. The main action of the
... 58. Find the wrong sentences related to the torus tubarius: a. Is an elevation on pharyngeal wall b. Borders anteriorly pharyngeal recess c. Is caused by lateral direction of the pharyngotympanic tube d. Is due to posterolateral direction of the pharyngotympanic tube e. Lies in the oropharynx ...
... 58. Find the wrong sentences related to the torus tubarius: a. Is an elevation on pharyngeal wall b. Borders anteriorly pharyngeal recess c. Is caused by lateral direction of the pharyngotympanic tube d. Is due to posterolateral direction of the pharyngotympanic tube e. Lies in the oropharynx ...
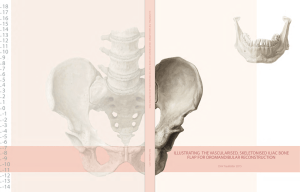
illustrating the vascularised, skeletonised iliac
... fascia lata are connected to the outer lip of the iliac crest, while the internal oblique attaches to its intermediate zone. Moreover, the transverse abdominis muscle, the quadratus lumborum muscle, the iliolumbar ligament and the iliac muscle, as well as the iliacus fascia and the transversalis fas ...
... fascia lata are connected to the outer lip of the iliac crest, while the internal oblique attaches to its intermediate zone. Moreover, the transverse abdominis muscle, the quadratus lumborum muscle, the iliolumbar ligament and the iliac muscle, as well as the iliacus fascia and the transversalis fas ...
Lecture 19: Female External Genitalia and Breast Intro to
... The lymphatic flow of the breast is of clinical significance because metastatic dissemination occurs primarily by lymphatic routes Axillary Nodes The axillary nodes—generally the first to be affected by metastasis—are divided into three levels (I-III) The (5-year) survival rate in breast can ...
... The lymphatic flow of the breast is of clinical significance because metastatic dissemination occurs primarily by lymphatic routes Axillary Nodes The axillary nodes—generally the first to be affected by metastasis—are divided into three levels (I-III) The (5-year) survival rate in breast can ...
INTRODUCTION - Austin Community College
... Describe the cytological structure of skeletal muscle cells and its relationship to muscle cell contraction Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle at the organ level List and describe the connective tissue components of skeletal muscle Name and describe the functional unit of the muscular syste ...
... Describe the cytological structure of skeletal muscle cells and its relationship to muscle cell contraction Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle at the organ level List and describe the connective tissue components of skeletal muscle Name and describe the functional unit of the muscular syste ...
ORIGIN AND DISTRIBUTION OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS IN WILD
... ABSTRACT: The origin and distribution of the brachial plexus in wild boar (Sus scrofa), a mammal belonging to the Suidae family were studied. Twelve specimens of wild boar, which were fixed in 10% formalin solution through different points of subcutaneous, intravenous, intramuscular, and intracavita ...
... ABSTRACT: The origin and distribution of the brachial plexus in wild boar (Sus scrofa), a mammal belonging to the Suidae family were studied. Twelve specimens of wild boar, which were fixed in 10% formalin solution through different points of subcutaneous, intravenous, intramuscular, and intracavita ...
Internal Anatomy of the Central Nervous System
... A discussion of the events related to the crossing of sensory fibers is important for an orientation to the course of the dorsal column fibers and their level of crossing (Fig. 3-8). The fasciculi of gracilis and cuneatus are the first-order sensory fibers; their sensory neurons are in the spinal do ...
... A discussion of the events related to the crossing of sensory fibers is important for an orientation to the course of the dorsal column fibers and their level of crossing (Fig. 3-8). The fasciculi of gracilis and cuneatus are the first-order sensory fibers; their sensory neurons are in the spinal do ...
Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial
... foramen. The superior and inferior sensory ganglia are located on the nerve as it passes through the foramen. The glossopharyngeal nerve then descends through the upper part of the neck to the back of the tongue . Important Branches of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve ■■ Tympanic branch passes to the tymp ...
... foramen. The superior and inferior sensory ganglia are located on the nerve as it passes through the foramen. The glossopharyngeal nerve then descends through the upper part of the neck to the back of the tongue . Important Branches of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve ■■ Tympanic branch passes to the tymp ...
Chapter 7 Body Systems
... • Efferent autonomic regulation ultimately depends on feedback from sensory receptors ...
... • Efferent autonomic regulation ultimately depends on feedback from sensory receptors ...
Subscapularis
... • The lateral lip of the bicipital groove. – The bicipital groove is also referred to as the intertubercular sulcis. This landmark is where the tendon for the long head of the biceps brachii lies. It is between the lesser tubercle and greater tubercle of the humerus. ...
... • The lateral lip of the bicipital groove. – The bicipital groove is also referred to as the intertubercular sulcis. This landmark is where the tendon for the long head of the biceps brachii lies. It is between the lesser tubercle and greater tubercle of the humerus. ...
The Calpain-Calpastatin System and the Calcium Paradox in the
... contraction bands), which in turn, is succeeded by sarcolemmal ruptures, Ca2+ overload and eventually, cell death [16-20]. Calpain activation, resulting from the massive Ca2+ influx, could be accounted for at least some of these observations. First, Ca2+ overload has been correlated with Z lines dis ...
... contraction bands), which in turn, is succeeded by sarcolemmal ruptures, Ca2+ overload and eventually, cell death [16-20]. Calpain activation, resulting from the massive Ca2+ influx, could be accounted for at least some of these observations. First, Ca2+ overload has been correlated with Z lines dis ...
RECENT ADVANCES IN COTTON FIBER DEVELOPMENT
... al., 2003). Plants with lower Sus protein in the seed coat compared to wild-type cotton produced fewer fibers that appeared shrunken and collapsed when viewed by scanning electron microscopy. The transgenic fibers had lower Sus activity, which correlated with decreased levels of hexoses and starch, ...
... al., 2003). Plants with lower Sus protein in the seed coat compared to wild-type cotton produced fewer fibers that appeared shrunken and collapsed when viewed by scanning electron microscopy. The transgenic fibers had lower Sus activity, which correlated with decreased levels of hexoses and starch, ...
19 O A and V Patterns C H A P T E R
... rectus muscles. If this were true, one would invariably find an A-pattern esotropia in patients with bilateral abducens paresis. This is clearly not the case. Indeed, we have occasionally observed a Vpattern esotropia in this condition, which contradicts the mechanism championed by Urist. Urist advo ...
... rectus muscles. If this were true, one would invariably find an A-pattern esotropia in patients with bilateral abducens paresis. This is clearly not the case. Indeed, we have occasionally observed a Vpattern esotropia in this condition, which contradicts the mechanism championed by Urist. Urist advo ...
Actin Dynamics in Muscle Cells
... In every cell, actin is a key component involved in migration, cytokinesis, endocytosis and generation of contraction. In non-muscle cells, actin filaments are very dynamic and regulated by an array of proteins that interact with actin filaments and/or monomeric actin. Interestingly, in non-muscle cel ...
... In every cell, actin is a key component involved in migration, cytokinesis, endocytosis and generation of contraction. In non-muscle cells, actin filaments are very dynamic and regulated by an array of proteins that interact with actin filaments and/or monomeric actin. Interestingly, in non-muscle cel ...
Pathogenesis of the Cleft Lip Nasal
... related to the technique of the primary surgery. This will be discussed later in the chapter. An understanding of the mechanisms that produce the malpositioning of the maxillary segments is helpful in developing further ideas that explain the cleft nose deformity. Scott9 originally proposed that the ...
... related to the technique of the primary surgery. This will be discussed later in the chapter. An understanding of the mechanisms that produce the malpositioning of the maxillary segments is helpful in developing further ideas that explain the cleft nose deformity. Scott9 originally proposed that the ...
Where is the external carotid artery located?
... to any names, marks, products, or services of third parties or hypertext links to thirdparty sites or information are provided solely as a convenience to you and do not in any way constitute or imply ECR's endorsement, sponsorship or recommendation of the third party, information, product or service ...
... to any names, marks, products, or services of third parties or hypertext links to thirdparty sites or information are provided solely as a convenience to you and do not in any way constitute or imply ECR's endorsement, sponsorship or recommendation of the third party, information, product or service ...
The Head and Neck
... The two nasal bones form the bridge of the nose, their lower borders, with the maxillae, make the anterior nasal aperture. The nasal cavity is divide into two by the bony nasal septum, which is largely formed by the vomer. The superior and the middle conchae are shelves of bone that project into the ...
... The two nasal bones form the bridge of the nose, their lower borders, with the maxillae, make the anterior nasal aperture. The nasal cavity is divide into two by the bony nasal septum, which is largely formed by the vomer. The superior and the middle conchae are shelves of bone that project into the ...
Hao Shi1*, Florian Gatzke2, Julia M. Molle
... and quantitative PCR (Figure 1A) for the expression of Mkp-1 and Mkp-5 and are referred to herein as MKP1/5-DKO mice. Male MKP1/5-DKO mice showed comparable body weights and muscle weights as compared with wild type mice (Figure 1B-C). Histologically, skeletal muscle from undamaged MKP ...
... and quantitative PCR (Figure 1A) for the expression of Mkp-1 and Mkp-5 and are referred to herein as MKP1/5-DKO mice. Male MKP1/5-DKO mice showed comparable body weights and muscle weights as compared with wild type mice (Figure 1B-C). Histologically, skeletal muscle from undamaged MKP ...
Myocyte

A myocyte (also known as a muscle cell) is the type of cell found in muscle tissue. Myocytes are long, tubular cells that develop from myoblasts to form muscles in a process known as myogenesis. There are various specialized forms of myocytes: cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells, with various properties. The striated cells of cardiac and skeletal muscles are referred to as muscle fibers. Cardiomyocytes are the muscle fibres that form the chambers of the heart, and have a single central nucleus. Skeletal muscle fibers help support and move the body and tend to have peripheral nuclei. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the stomach.