Variations of Sciatic Nerve Its Exit in Relation to Piriformis Muscle in
... Several studies declared that there are numerous variations both in the course and distribution of the sciatic nerve. The main variations were the relationship of sciatic nerve to Piriformis muscle and its level of bifurcation. The relationships between the Piriformis muscle and sciatic nerve have b ...
... Several studies declared that there are numerous variations both in the course and distribution of the sciatic nerve. The main variations were the relationship of sciatic nerve to Piriformis muscle and its level of bifurcation. The relationships between the Piriformis muscle and sciatic nerve have b ...
Insulin action on skeletal muscle protein metabolism during
... the relationship between insulin and muscle protein synthesis, Millward and Rivers [56] reported that parallel changes in the two parameters were only observable in the low insulin range because additional provision of insulin to fed rats failed to further stimulate muscle protein synthesis [6]. The ...
... the relationship between insulin and muscle protein synthesis, Millward and Rivers [56] reported that parallel changes in the two parameters were only observable in the low insulin range because additional provision of insulin to fed rats failed to further stimulate muscle protein synthesis [6]. The ...
Insulin action on skeletal muscle protein metabolism during
... the relationship between insulin and muscle protein synthesis, Millward and Rivers [56] reported that parallel changes in the two parameters were only observable in the low insulin range because additional provision of insulin to fed rats failed to further stimulate muscle protein synthesis [6]. The ...
... the relationship between insulin and muscle protein synthesis, Millward and Rivers [56] reported that parallel changes in the two parameters were only observable in the low insulin range because additional provision of insulin to fed rats failed to further stimulate muscle protein synthesis [6]. The ...
Anatomy of the Head, Neck, Face, and Jaws.
... understand the relationships of structures. A good automotive mechanic knows where the parts of an engine are located and what they do. Without that knowledge, he cannot repair a malfunction. The language of anatomy must be understood before the general subject can be learned. Relationships and posi ...
... understand the relationships of structures. A good automotive mechanic knows where the parts of an engine are located and what they do. Without that knowledge, he cannot repair a malfunction. The language of anatomy must be understood before the general subject can be learned. Relationships and posi ...
Selective Neck Dissection - Vula
... retropharyngeal) or non-lymphatic structures (skin, muscle, nerve, blood vessels etc.) not usually included in a comprehensive neck dissection. It has been proposed that neck dissections be more logically and precisely described and classified by naming the structures and the nodal levels that have ...
... retropharyngeal) or non-lymphatic structures (skin, muscle, nerve, blood vessels etc.) not usually included in a comprehensive neck dissection. It has been proposed that neck dissections be more logically and precisely described and classified by naming the structures and the nodal levels that have ...
SURFACE EMG MADE EASY: A Beginner`s Guide for Rehabilitation
... 3. Explain to the patient what he or she can expect to feel and do during the session. Example Remarks to Patient “When you move, your brain sends off a series of commands that go down the spinal cord and out over nerves to muscles. Muscles do what the brain tells them to do. The brain sends these s ...
... 3. Explain to the patient what he or she can expect to feel and do during the session. Example Remarks to Patient “When you move, your brain sends off a series of commands that go down the spinal cord and out over nerves to muscles. Muscles do what the brain tells them to do. The brain sends these s ...
Anatomy Exam 2 Review Lecture 8-Thyroid and Adrenal Glands
... During development the thyroid gland descends into the neck and moves around and pulls with it a layer of fascia. Problems with this migration can result in a Thyroglossal duct, which connects the tongue to the thyroid. If migration doesn’t occur properly, thyroid tissues can be deposited at v ...
... During development the thyroid gland descends into the neck and moves around and pulls with it a layer of fascia. Problems with this migration can result in a Thyroglossal duct, which connects the tongue to the thyroid. If migration doesn’t occur properly, thyroid tissues can be deposited at v ...
MEF2 and HDAC Proteins Regulate Striated Muscle
... Mef2c differentiates and forms normal myofibers during embryogenesis, but myofibers rapidly deteriorate after birth due to disorganized sarcomeres and a loss of integrity of the M-line. We discovered that MEF2C directly regulates important structural genes required for the maintenance of sarcomere i ...
... Mef2c differentiates and forms normal myofibers during embryogenesis, but myofibers rapidly deteriorate after birth due to disorganized sarcomeres and a loss of integrity of the M-line. We discovered that MEF2C directly regulates important structural genes required for the maintenance of sarcomere i ...
Studies on the abdominal musculature of the subterranean mysid
... muscle has a main portion lying medial to the central muscle of the segment and presents a broad surface which is pressed against its fellow of the opposite side. It starts from above the central muscle and runs in a posteroventral direction to get inserted on to the posterior margin of the segment. ...
... muscle has a main portion lying medial to the central muscle of the segment and presents a broad surface which is pressed against its fellow of the opposite side. It starts from above the central muscle and runs in a posteroventral direction to get inserted on to the posterior margin of the segment. ...
II./2.3. Examination of cranial nerves II.2.3.1. Examination of the
... diseases of the retina (diabetes, hypertension), opalescence of the vitreous body, etc. Optic fundus The optic nerve head (optic disc, papilla) and its surrounding area is examined with the help of an ophthalmoscope. The optic nerve head is affected in inflammatory conditions of the optic nerve, in ...
... diseases of the retina (diabetes, hypertension), opalescence of the vitreous body, etc. Optic fundus The optic nerve head (optic disc, papilla) and its surrounding area is examined with the help of an ophthalmoscope. The optic nerve head is affected in inflammatory conditions of the optic nerve, in ...
The Larynx of the White
... and lateral surfaces. The oblique line is indistinct. The rostral cornu is thin, long and, straight. It is directed rostrodorsally. Its medial face shows on its tip a rounded, small and, flat hyoid articular surface. The rostral cornu forms with the rostral border of the lamina a relatively shallow ...
... and lateral surfaces. The oblique line is indistinct. The rostral cornu is thin, long and, straight. It is directed rostrodorsally. Its medial face shows on its tip a rounded, small and, flat hyoid articular surface. The rostral cornu forms with the rostral border of the lamina a relatively shallow ...
Distribution of Muscarinic Acetylcholine
... contraction (3, 38). Current evidence suggests that the slowing of the rate is mediated by a increase in the potassium conductance of the membrane (and a hyperpolarization), whereas the decreased force of contraction is the result of a decreased influx of calcium during the action potential (13, 15, ...
... contraction (3, 38). Current evidence suggests that the slowing of the rate is mediated by a increase in the potassium conductance of the membrane (and a hyperpolarization), whereas the decreased force of contraction is the result of a decreased influx of calcium during the action potential (13, 15, ...
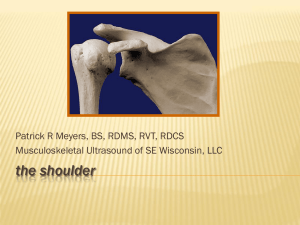
the shoulder
... • lies between the greater and lesser tuberosity of the humeral head • covered by transverse humeral ligament at tuberosities ...
... • lies between the greater and lesser tuberosity of the humeral head • covered by transverse humeral ligament at tuberosities ...
15 Resection of the Posterior Compartment of the Thigh
... ischium and the linea aspera. The lateral hamstrings insert onto the fibular head whereas the medial hamstrings insert onto the medial and posteromedial aspect of the tibia and joint capsule. The most significant anatomic structure of the posterior compartment is the sciatic nerve that runs from the ...
... ischium and the linea aspera. The lateral hamstrings insert onto the fibular head whereas the medial hamstrings insert onto the medial and posteromedial aspect of the tibia and joint capsule. The most significant anatomic structure of the posterior compartment is the sciatic nerve that runs from the ...
34 Scapulectomy
... tumors, or infected tumors; those in whom limbsparing resection has failed; and those with tumors invading the major nerves and vessels or chest wall. A classification system for resection of tumors of the scapula and shoulder girdle is described in Chapter 9. The most common resection for a high-gr ...
... tumors, or infected tumors; those in whom limbsparing resection has failed; and those with tumors invading the major nerves and vessels or chest wall. A classification system for resection of tumors of the scapula and shoulder girdle is described in Chapter 9. The most common resection for a high-gr ...
Microanatomy and Surgical Approaches to the
... of the temporal bone and greater wing of the sphenoid bone that is sitting deep to the ramus of the mandible. The principal structure to understanding its relationships is the lateral pterygoid muscle. Other important structures are the medial pterygoid muscle, the maxillary artery, the pterygoid ve ...
... of the temporal bone and greater wing of the sphenoid bone that is sitting deep to the ramus of the mandible. The principal structure to understanding its relationships is the lateral pterygoid muscle. Other important structures are the medial pterygoid muscle, the maxillary artery, the pterygoid ve ...
PPT
... with the numerically corresponding vertebral body and that of the vertebra immediately above 2- Neck: is a constricted portion situated between the head and the tubercle 3-Tubercle:is a prominence on the outer surface of the rib at the junction of the neck with the shaft. It has a facet for articula ...
... with the numerically corresponding vertebral body and that of the vertebra immediately above 2- Neck: is a constricted portion situated between the head and the tubercle 3-Tubercle:is a prominence on the outer surface of the rib at the junction of the neck with the shaft. It has a facet for articula ...
Brachial muscles in the chick embryo: the fate of
... band of connective tissue (Fig. 2). Unlike the pectoralis major, both regions have the same embryonic origins: somites 16, 17 and 18. Coracobrachialis posterior This muscle originates on the coracoid and inserts on the humerus. For much of its length it is situated between the coracoid bone and the ...
... band of connective tissue (Fig. 2). Unlike the pectoralis major, both regions have the same embryonic origins: somites 16, 17 and 18. Coracobrachialis posterior This muscle originates on the coracoid and inserts on the humerus. For much of its length it is situated between the coracoid bone and the ...
Salivary glands
... extremities. It reach to the base of hyoid bone rostrally, the duct is formed by union of small radicals and pass cranially along the medial surface of the body of the mandible and open at the level of the canine by flattened papillae called sublingual caruncle. In sheep and ox: It is larger then pa ...
... extremities. It reach to the base of hyoid bone rostrally, the duct is formed by union of small radicals and pass cranially along the medial surface of the body of the mandible and open at the level of the canine by flattened papillae called sublingual caruncle. In sheep and ox: It is larger then pa ...
An unusual variation of Pectoralis minor muscle and its clinical
... The anatomical knowledge of variations of origin and insertion of Pectoralis minor muscle is of great significance to minimise complications during surgical procedures. An unusual variation of Pectoralis minor muscle was encountered in an adult male cadaver on right side, during routine dissection. ...
... The anatomical knowledge of variations of origin and insertion of Pectoralis minor muscle is of great significance to minimise complications during surgical procedures. An unusual variation of Pectoralis minor muscle was encountered in an adult male cadaver on right side, during routine dissection. ...
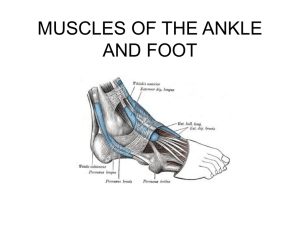
THE ANKLE AND FOOT
... • Origin: upper 2/3 of the posterior surfaces of the tibia and fibula • Insertion: posterior surface of the calcaneus via Achilles tendon • Action: – plantar flexion • Superficial posterior compartment ...
... • Origin: upper 2/3 of the posterior surfaces of the tibia and fibula • Insertion: posterior surface of the calcaneus via Achilles tendon • Action: – plantar flexion • Superficial posterior compartment ...
Surgical Technique
... be done with extreme care because the thin superficial layer of the cervical fascia is the only tissue now included in the specimen. We strongly recommend performing this, as well as most other parts of the operation, using knife dissection. The fascial planes of the neck are mainly avascular and ca ...
... be done with extreme care because the thin superficial layer of the cervical fascia is the only tissue now included in the specimen. We strongly recommend performing this, as well as most other parts of the operation, using knife dissection. The fascial planes of the neck are mainly avascular and ca ...
BACK AND UPPER LIMB
... Hand: leaves the forearm by winding laterally around the radius onto the dorsal aspect of the scaphoid; crosses the floor of the anatomical snuff box and passes through the heads of the 1st dorsal interosseous muscle to enter the palm Gives off: *Radial recurrent artery Location: passes laterally ...
... Hand: leaves the forearm by winding laterally around the radius onto the dorsal aspect of the scaphoid; crosses the floor of the anatomical snuff box and passes through the heads of the 1st dorsal interosseous muscle to enter the palm Gives off: *Radial recurrent artery Location: passes laterally ...
Robison, B.H., Raskoff, K.A., Sherlock, R.E. (2005) Ecological substrate in midwater: Doliolula equus , a new, mesopelagic tunicate. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom .
... gap. Muscle IV is complete and terminates the atrial cavity, bordering a short vestibule. Muscle V is the sphincter of the atrial siphon. The distance between muscles IV and V is much greater than that between muscles I and II. The pharyngeal cavity (chamber) is about twice the volume of the atrial ...
... gap. Muscle IV is complete and terminates the atrial cavity, bordering a short vestibule. Muscle V is the sphincter of the atrial siphon. The distance between muscles IV and V is much greater than that between muscles I and II. The pharyngeal cavity (chamber) is about twice the volume of the atrial ...
Rehab Of The Thrower`s Shoulder
... facilitate permanent changes in tissue length – Should begin to see some progress in a few weeks Progress with younger throwers often much faster due to pliability The more an athlete has thrown the longer it may take ...
... facilitate permanent changes in tissue length – Should begin to see some progress in a few weeks Progress with younger throwers often much faster due to pliability The more an athlete has thrown the longer it may take ...
Myocyte

A myocyte (also known as a muscle cell) is the type of cell found in muscle tissue. Myocytes are long, tubular cells that develop from myoblasts to form muscles in a process known as myogenesis. There are various specialized forms of myocytes: cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells, with various properties. The striated cells of cardiac and skeletal muscles are referred to as muscle fibers. Cardiomyocytes are the muscle fibres that form the chambers of the heart, and have a single central nucleus. Skeletal muscle fibers help support and move the body and tend to have peripheral nuclei. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the stomach.