Slide 1
... When you see a sinusoidal curve that is supposed to represent light, what is the displacement of the points on the curve from the “x axis” supposed to represent? a) The component of the electric field in a particular direction. b) The component of the magnetic field in a particular direction. c) Ei ...
... When you see a sinusoidal curve that is supposed to represent light, what is the displacement of the points on the curve from the “x axis” supposed to represent? a) The component of the electric field in a particular direction. b) The component of the magnetic field in a particular direction. c) Ei ...
Using Technology To See Beyond The Visible
... but has different wavelengths and frequencies from those of light. Wavelength is a measurement of the distance from one point on a wave (such as the crest) to the ...
... but has different wavelengths and frequencies from those of light. Wavelength is a measurement of the distance from one point on a wave (such as the crest) to the ...
Supplementary Material
... The secondary structure definitions of amino acids were generated with DSSP [1] considering only three groups: helical (H), extended (E) and coil (C). Based on this 7 types of protein interfaces can be defined taking into consideration the amount of each of the three basic secondary structural eleme ...
... The secondary structure definitions of amino acids were generated with DSSP [1] considering only three groups: helical (H), extended (E) and coil (C). Based on this 7 types of protein interfaces can be defined taking into consideration the amount of each of the three basic secondary structural eleme ...
Quiz Next Tuesday (09/18) - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... The Coplanar Nature of the Peptide Bond Six atoms of the peptide group lie in a plane! ...
... The Coplanar Nature of the Peptide Bond Six atoms of the peptide group lie in a plane! ...
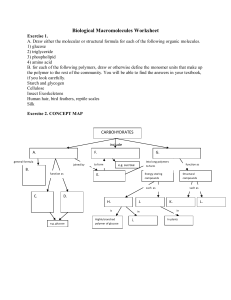
Biological Macromolecules Worksheet
... Exercise 3. 1. A triglyceride contains ______ and _______. 2. A fatty acid is unsaturated if it contains ____________. 3. Saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids differ in ___________. 4. Explain why phospholipids form a bilayer membrane. Exercise 4. Define what a protein is and/or of wha ...
... Exercise 3. 1. A triglyceride contains ______ and _______. 2. A fatty acid is unsaturated if it contains ____________. 3. Saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids differ in ___________. 4. Explain why phospholipids form a bilayer membrane. Exercise 4. Define what a protein is and/or of wha ...
Ch 4 Reading Guide
... Reading Guide, Stryer Short Course, Chapter 4 1. Draw the tripeptide Gly-Phe-Leu at pH 7.4. Indicate the backbone, one peptide bond, and one sidechain. 2. Give three reasons it is important to know the primary sequence of a protein. 3. Give a chemical explanation of why a peptide bond is planar. 4. ...
... Reading Guide, Stryer Short Course, Chapter 4 1. Draw the tripeptide Gly-Phe-Leu at pH 7.4. Indicate the backbone, one peptide bond, and one sidechain. 2. Give three reasons it is important to know the primary sequence of a protein. 3. Give a chemical explanation of why a peptide bond is planar. 4. ...
Midterm Exam No. 02 (Fall 2014) PHYS 520A: Electromagnetic Theory I
... Find the effective charge density by calculating −∇ · P. In particular, you should obtain two terms, one containing θ(R − r) that is interpreted as a volume charge density, and another containing δ(R − r) that can be interpreted as a surface charge density. 4. (25 points.) A particle of mass m and c ...
... Find the effective charge density by calculating −∇ · P. In particular, you should obtain two terms, one containing θ(R − r) that is interpreted as a volume charge density, and another containing δ(R − r) that can be interpreted as a surface charge density. 4. (25 points.) A particle of mass m and c ...
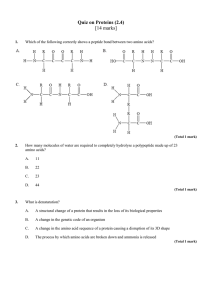
Quiz-2
... 7. Ramchandran’s plot for poly-glycine shows four big squares of allowed conformations which is very different from any polypeptide. Explain why? 8. Find out the primary structure of the peptide based on the information provided ...
... 7. Ramchandran’s plot for poly-glycine shows four big squares of allowed conformations which is very different from any polypeptide. Explain why? 8. Find out the primary structure of the peptide based on the information provided ...
hw08_assingnment
... 3. If the magnetic field in a traveling EM wave has a peak magnitude of 17.5 nT at a given point, what is the peak magnitude of the electric field? ...
... 3. If the magnetic field in a traveling EM wave has a peak magnitude of 17.5 nT at a given point, what is the peak magnitude of the electric field? ...
Amino acids
... • peptides (2 - 100 units of A. A.) • oligopeptides (2 – 10 A. A.) • polypeptides (10 – 100 A. A.) ...
... • peptides (2 - 100 units of A. A.) • oligopeptides (2 – 10 A. A.) • polypeptides (10 – 100 A. A.) ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.