Molecular size scales in biology
... 3. Lac repressor complex with DNA 4. Hemoglobin 5. Myoglobin 6. Green fluorescent protein (GFP) 7. RNA polymerase • Download a program that allows structure viewing such as RasMol (U. Massachusettes). • Use the measurement tools in these programs to measure the maximal length of these molecules (max ...
... 3. Lac repressor complex with DNA 4. Hemoglobin 5. Myoglobin 6. Green fluorescent protein (GFP) 7. RNA polymerase • Download a program that allows structure viewing such as RasMol (U. Massachusettes). • Use the measurement tools in these programs to measure the maximal length of these molecules (max ...
Describe the relationship between genes, nucleic acids, amino
... Describe the relationship between genes, nucleic acids, amino acids, and proteins. DNA is a specific nucleic acid that directs protein making in all living things Proteins function in a variety of critical ways in living things not the least of which is to serve as enzymes that catalyze numerous and ...
... Describe the relationship between genes, nucleic acids, amino acids, and proteins. DNA is a specific nucleic acid that directs protein making in all living things Proteins function in a variety of critical ways in living things not the least of which is to serve as enzymes that catalyze numerous and ...
Chapter 8: Polarization • Introduction – Light is a transverse
... E = E0 [îcos(kz − ωt) − ĵsin(kz − ωt)], that is E rotates counter-clockwise: left circuularly polarized. • Elliptical Polarization: E vector rotates and changes its magnitude and thus traces out an ellipse. • State of Polarization: Linearly or Plane Polarize: P state, Right or Left circular polari ...
... E = E0 [îcos(kz − ωt) − ĵsin(kz − ωt)], that is E rotates counter-clockwise: left circuularly polarized. • Elliptical Polarization: E vector rotates and changes its magnitude and thus traces out an ellipse. • State of Polarization: Linearly or Plane Polarize: P state, Right or Left circular polari ...
HonBio Chapter 3 notes
... Lipids are water insoluble (hydrophobic – “water fearing”) compounds that are made from glycerol and fatty acids. They contain twice as much energy as a polysaccharide, so their main function is ...
... Lipids are water insoluble (hydrophobic – “water fearing”) compounds that are made from glycerol and fatty acids. They contain twice as much energy as a polysaccharide, so their main function is ...
Lecture 1
... hydrogen bonds with Ala residues located in an ahelix? A. Residues in a neighbouring a-helix. ...
... hydrogen bonds with Ala residues located in an ahelix? A. Residues in a neighbouring a-helix. ...
Life’s molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon 8/25/2011 1
... • Signal proteins: Such as hormones that coordinate body activity ...
... • Signal proteins: Such as hormones that coordinate body activity ...
Protein?
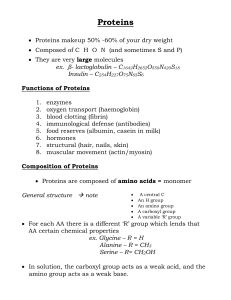
... catalyzing chemical reactions to building the structures of all living things. Despite this wide range of functions all proteins are made out of the same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino acids are arranged dictates the folding of the protein into its uni ...
... catalyzing chemical reactions to building the structures of all living things. Despite this wide range of functions all proteins are made out of the same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino acids are arranged dictates the folding of the protein into its uni ...
Proteins - Boardworks
... Proteins are a diverse group of large and complex polymer molecules, made up of long chains of amino acids. They have a wide range of biological roles, including: ...
... Proteins are a diverse group of large and complex polymer molecules, made up of long chains of amino acids. They have a wide range of biological roles, including: ...
Biomolecules Review Game
... What are the names of these functional Groups found at either end of every Amino acid molecule? ...
... What are the names of these functional Groups found at either end of every Amino acid molecule? ...
Cell Building Blocks
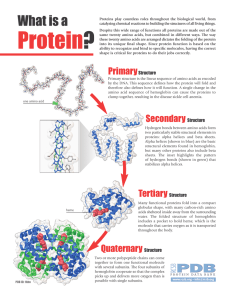
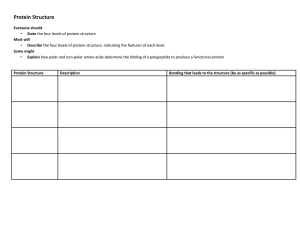
... The secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between amino acids. The polypeptide can coil into a helix or form a pleated sheet. The tertiary structure refers to the three-dimensional folding of the helix or pleated sheet. Quaternary The quaternary structure refers to the spatial relationship ...
... The secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between amino acids. The polypeptide can coil into a helix or form a pleated sheet. The tertiary structure refers to the three-dimensional folding of the helix or pleated sheet. Quaternary The quaternary structure refers to the spatial relationship ...
PDF
... Proteins are heteropolymers • hetero – (from Greek) other, another different • polymer – a molecule consis=ng of repea=ng units ...
... Proteins are heteropolymers • hetero – (from Greek) other, another different • polymer – a molecule consis=ng of repea=ng units ...
Abstract
... residue correlations for a large number of protein domains. Information uncovered by mfDCA allows us to reconstruct the structure of contact maps for many protein domains. Inferred contacts by mfDCA can be utilized as a reliable guide in high accuracy computational predictions of domain structure. O ...
... residue correlations for a large number of protein domains. Information uncovered by mfDCA allows us to reconstruct the structure of contact maps for many protein domains. Inferred contacts by mfDCA can be utilized as a reliable guide in high accuracy computational predictions of domain structure. O ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.