Module 11: The vector nature of electromagnetic radiation
... the same frequency and wavelength and the z component is lagging with a phase π/3. (Ans: Left elliptically polarized and the major axis is making an angle π/4 with the y axis.) 3. Find the state of polarization of a light which is moving in the positive x direction and having amplitudes of electric ...
... the same frequency and wavelength and the z component is lagging with a phase π/3. (Ans: Left elliptically polarized and the major axis is making an angle π/4 with the y axis.) 3. Find the state of polarization of a light which is moving in the positive x direction and having amplitudes of electric ...
Essential amino acids and nutrition
... 1. Consider why protein is needed and what amino acids and proteins are used for in the body. Describe the symptoms you would expect a person with protein deficiency to have. ...
... 1. Consider why protein is needed and what amino acids and proteins are used for in the body. Describe the symptoms you would expect a person with protein deficiency to have. ...
PROTEIN STRUCTURE CLASSIFICATION
... The Protein Data Bank (PDB) archive is the single worldwide repository of information about the 3D structures of large biological molecules, including proteins and nucleic acids. ...
... The Protein Data Bank (PDB) archive is the single worldwide repository of information about the 3D structures of large biological molecules, including proteins and nucleic acids. ...
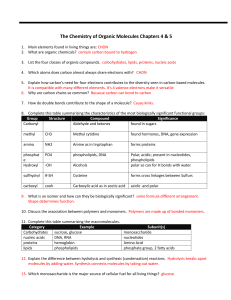
Macromolecule Study Guide 2016
... A. __________________________________ C. _________________________________ B. __________________________________ D. _________________________________ 2. Describe a function for each of the above compounds: a. _________________________ c._______________________________ b. _________________________ d. ...
... A. __________________________________ C. _________________________________ B. __________________________________ D. _________________________________ 2. Describe a function for each of the above compounds: a. _________________________ c._______________________________ b. _________________________ d. ...
Exam3Sol
... Solution: Polarizer 1 passes the y-component of the circularly polarized light. The ycomponent has magnitude Eo, since when the!rotating electric field!of the circularly polarized light points along the y-axis, there is no x-component, only y. The ycomponent oscillates up and down, and has a maximum ...
... Solution: Polarizer 1 passes the y-component of the circularly polarized light. The ycomponent has magnitude Eo, since when the!rotating electric field!of the circularly polarized light points along the y-axis, there is no x-component, only y. The ycomponent oscillates up and down, and has a maximum ...
Symmetry
... remaining the same. Their mirror reflection is different. Thus, many of these arrangements are actually precluded. In fact, proteins may only adopt 65 of the 230 possible 3D space groups. Many of these are observed when we crystallize proteins. In the case of naturally occurring multimers of protein ...
... remaining the same. Their mirror reflection is different. Thus, many of these arrangements are actually precluded. In fact, proteins may only adopt 65 of the 230 possible 3D space groups. Many of these are observed when we crystallize proteins. In the case of naturally occurring multimers of protein ...
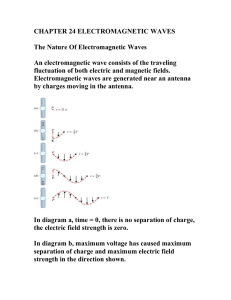
Electromagnetic Waves - Galileo and Einstein
... • Since light carries momentum, anything absorbing or reflecting light feels a pressure, a force equal to the rate of change of momentum, from Newton’s laws. • How can the perpendicular E and B fields push something forwards? • The electric field causes charged particles (electrons) to oscillate per ...
... • Since light carries momentum, anything absorbing or reflecting light feels a pressure, a force equal to the rate of change of momentum, from Newton’s laws. • How can the perpendicular E and B fields push something forwards? • The electric field causes charged particles (electrons) to oscillate per ...
Interaction Site Evolution
... COMPUTER SCIENCE - Interaction Site Evolution DNA is the blueprint for generating strings of amino acids which fold into proteins. The interactions these proteins form with each other are primary components of organismal physiology. Proteins assume very specific shapes, and the amino acids on their ...
... COMPUTER SCIENCE - Interaction Site Evolution DNA is the blueprint for generating strings of amino acids which fold into proteins. The interactions these proteins form with each other are primary components of organismal physiology. Proteins assume very specific shapes, and the amino acids on their ...
Chemistry and My Body - Mrs. Jones Mrs. Jones
... There are 20 different types of amino acids 8 are essential (humans have to obtain them from food) ...
... There are 20 different types of amino acids 8 are essential (humans have to obtain them from food) ...
Lecture 34
... Jones matrix for a linear polarizer Consider a linear polarizer with transmission axis along the vertical (y). Let a 2X2 matrix represent the polarizer operating on vertically polarized light. The transmitted light must also be vertically polarized. Thus, ...
... Jones matrix for a linear polarizer Consider a linear polarizer with transmission axis along the vertical (y). Let a 2X2 matrix represent the polarizer operating on vertically polarized light. The transmitted light must also be vertically polarized. Thus, ...
Spectroscopy - Jefferson Lab
... fulfill the requirements of the TAPS program at Jefferson Labs in Newport News, VA summer 2006. • This presentation was also designed to accompany and expound upon the topic of Light and the Electromagnetic Spectrum as required by the state of Virginia Physical Science SOL’s (PS.9c). ...
... fulfill the requirements of the TAPS program at Jefferson Labs in Newport News, VA summer 2006. • This presentation was also designed to accompany and expound upon the topic of Light and the Electromagnetic Spectrum as required by the state of Virginia Physical Science SOL’s (PS.9c). ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.