Electric Potential
... AM = Amplitude Modulation where information is imbedded into the wave by changing its amplitude or power. ...
... AM = Amplitude Modulation where information is imbedded into the wave by changing its amplitude or power. ...
Organic Molecules
... b. Frequently formed with covalent bonds. c. Found in living organisms. d. Usually larger than inorganic molecules (eg: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, ATP). e. Many organic molecules are formed by dehydration synthesis (ie: remove H+ from one molecule and OH- from another ...
... b. Frequently formed with covalent bonds. c. Found in living organisms. d. Usually larger than inorganic molecules (eg: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, ATP). e. Many organic molecules are formed by dehydration synthesis (ie: remove H+ from one molecule and OH- from another ...
PHY801: Survey of Atomic and Condensed Matter Physics
... 4.1. Consider an atom with the 3 S1 ground state. What is the value of the Landé g-factor? Find the magnetization M as a function of magnetic field B (oriented along the z axis), the temperature T , and the concentration n = N/V . Show that in the limit of very high temperatures, where µB B << kB T ...
... 4.1. Consider an atom with the 3 S1 ground state. What is the value of the Landé g-factor? Find the magnetization M as a function of magnetic field B (oriented along the z axis), the temperature T , and the concentration n = N/V . Show that in the limit of very high temperatures, where µB B << kB T ...
Lecture notes, part 5
... anti-Stokes scattering in which light causes a vibrational de-excitation. To observe the Stokes and anti-Stokes signals we need ...
... anti-Stokes scattering in which light causes a vibrational de-excitation. To observe the Stokes and anti-Stokes signals we need ...
Introduction to Proteins
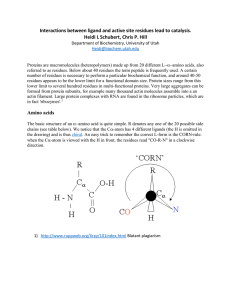
... (Notice that in the lower drawing, the molecule has been flopped over 90 degrees to the right for illustration purposes.) Cysteine has an R group that is similar but includes a sulfur atom. Other amino acids have R groups that range from a single hydrogen atom up to a double ring of carbon and nitro ...
... (Notice that in the lower drawing, the molecule has been flopped over 90 degrees to the right for illustration purposes.) Cysteine has an R group that is similar but includes a sulfur atom. Other amino acids have R groups that range from a single hydrogen atom up to a double ring of carbon and nitro ...
ppt
... ‘Perhaps the most remarkable features of the [protein] molecule are its complexity and its lack of symmetry. The arrangement seems to be almost totally lacking in the kind of regularities which one instinctively anticipates, and it is more complicated than has been predicted by any theory of protein ...
... ‘Perhaps the most remarkable features of the [protein] molecule are its complexity and its lack of symmetry. The arrangement seems to be almost totally lacking in the kind of regularities which one instinctively anticipates, and it is more complicated than has been predicted by any theory of protein ...
Chapter 2 Section 3: The Chemistry of Life
... • Each completed chain of amino acids is called a peptide. This is actually a synonym for a complete protein. The amino acids are linked together, to form a complete peptide chain, which is a protein. ...
... • Each completed chain of amino acids is called a peptide. This is actually a synonym for a complete protein. The amino acids are linked together, to form a complete peptide chain, which is a protein. ...
Proteins 1 - Dr Rob's A
... 2 aa’s can join (condensation) to form dipeptide Further reactions can occur making polypeptides ...
... 2 aa’s can join (condensation) to form dipeptide Further reactions can occur making polypeptides ...
A Brief History of Planetary Science
... Wave Equations We can generalize the waves as: E = Em sin (kx -wt) B = Bm sin (kx -wt) Nothing is actually moving ...
... Wave Equations We can generalize the waves as: E = Em sin (kx -wt) B = Bm sin (kx -wt) Nothing is actually moving ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.