* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Using Technology To See Beyond The Visible
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
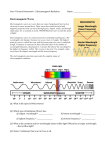
Using Technology to see beyond the visible Not all information from stars can be seen. Optical telescopes give us information 20 based on visible light. However, objects in space, such as stars and galaxies, also 34 emit radio waves, infrared (heat) waves, and x-rays. These are all forms of 47 electromagnetic energy. This energy travels at the speed of light, 300 000 km/s, 59 but has different wavelengths and frequencies from those of light. Wavelength is a measurement of the distance from one point on a wave (such as the crest) to the 72 88 same point on the next wave. Frequency is the number of waves that pass a single 104 point in one second. 108 Energy with a high frequency has a short wavelength. Gamma rays, for instance, 121 have a high frequency and a very short wavelength (less than a millionth of a 136 centimeter). Radio waves have a low frequency, but wavelengths that can be 148 several kilometers long. 151 The visible light we see all around us occupies a small section of the entire 166 electromagnetic spectrum, which covers the whole range of electromagnetic 175 energy. Visible light has a wavelength measured in micrometer. One micrometer 186 is 1 millionth of a metre. 193 Science in action 9 Grade 9 page 440