* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download New Atomic Model and Properties of Light
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Thermal radiation wikipedia , lookup
Variable speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
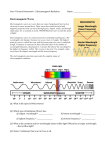
Chemistry ‘S’ – Chapter 4 I Development of a New Atomic Model The Rutherford model of the atom was an improvement over previous models. However, the model could not answer the question _______________________________________________________? After all, it was known that oppositely charged particles attract each other. In the early twentieth century, a new atomic model evolved as investigations into the _________________ and _______________ of light by matter. The studies revealed a relationship between light and an atom’s __________. II Properties of Light Before 1900, scientists thought light behaved solely as a ________. Later, it was discovered that light also had _________ - like properties. Wave Description of Light Visible light is a form of __________ _________, which is a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space. Other kinds of Electromagnetic Radiation – X Rays, Microwaves, Radio Waves, UV, IR, etc. Together, all forms of electromagnetic radiation form the __________ __________ All forms of electromagnetic radiation travel at a constant speed of ______________, which is known as the __________ of _________. Wave motion is repetitive, and characterized by the measurable properties of ____________ and ____________. Wavelength is the distance between ____________ points on ___________ waves. Wavelength is symbolized as ( ), which is the Greek symbol ________. The unit for wavelength is a distance unit, and can be measured in a number using many different units. *See Figures 1 and 2 in text, Page 98* Know these Equalities!! 1 m = 1 x 109 nm 1 cm = 1 x 108 A nm – nanometers A = Angstroms Visible Light Spectrum - 400 to 700 nm Frequency is the number of _________ that pass a given point in a specific time, usually ____________. Frequency is symbolized as ( ), which is the Greek symbol ___________. One unit for frequency is waves/second or hertz (Hz.), named after Heinrich Hertz. Mathematically, wavelength and frequency are related as follows: Speed of Light = Wavelength x Frequency -or- _______ = _________ x _________ Relationship Between Wavelength and Frequency