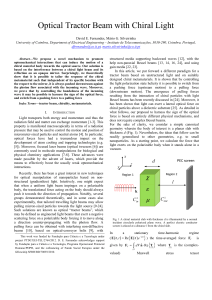
seCTion 2 - Comlibris
... 6. Refraction of the light through lenses 7. Refraction of the light through a prism/dispersion 8. Measurement of the focal length of a mirror and of a lens with spherometer 9. Images given by mirrors 10. Images given by lenses 11. Optical instruments ...
... 6. Refraction of the light through lenses 7. Refraction of the light through a prism/dispersion 8. Measurement of the focal length of a mirror and of a lens with spherometer 9. Images given by mirrors 10. Images given by lenses 11. Optical instruments ...
ENGINEERING OPTICS WITH
... the ray path is a straight line as the shortest OPL between the two end points is along a straight line which assumes the shortest time for the ray to travel. 1.2 Reflection and Refraction When a ray of light is incident on the interface separating two different optical media characterized by m and ...
... the ray path is a straight line as the shortest OPL between the two end points is along a straight line which assumes the shortest time for the ray to travel. 1.2 Reflection and Refraction When a ray of light is incident on the interface separating two different optical media characterized by m and ...
L1 WHAT IS LIGHT ? OBJECTIVES
... Speed of light and refractive index The speed of light in a transparent material is always less than the speed, c, in vacuum. The ratio of the speed in a vacuum to the speed in the medium is called the refractive index (n) of the medium. c n = v . ...
... Speed of light and refractive index The speed of light in a transparent material is always less than the speed, c, in vacuum. The ratio of the speed in a vacuum to the speed in the medium is called the refractive index (n) of the medium. c n = v . ...
lecture1430261805
... another Point on the line called centre of Oscillation is equivalent Length of pendulum . So,the distance between centre of suspension & centre of Oscillation is equivalent length of pendulum .If these two points are interchanged then “time period” will be constant. L.C CIRCUIT(NON MECHANICAL OSCIL ...
... another Point on the line called centre of Oscillation is equivalent Length of pendulum . So,the distance between centre of suspension & centre of Oscillation is equivalent length of pendulum .If these two points are interchanged then “time period” will be constant. L.C CIRCUIT(NON MECHANICAL OSCIL ...
Electromagnetic Radiation
... transverse waves radiating outward from a source. As you learned in Chapter 8, a wave is a transfer of energy in the form of a disturbance. The energy transfer usually occurs in, but is not limited to, a material medium like water. A water wave travels in a straight line, reflects from surfaces, and ...
... transverse waves radiating outward from a source. As you learned in Chapter 8, a wave is a transfer of energy in the form of a disturbance. The energy transfer usually occurs in, but is not limited to, a material medium like water. A water wave travels in a straight line, reflects from surfaces, and ...
Physics 202
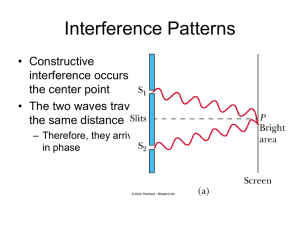
... oscillating in the same way. If they continue to oscillate in phase when they reach a given point, the interference is constructive ⇒ Brightest or most intense spot. The condition for this to be so is that their difference in path lengths should be a integral multiple of the wavelength. l2 − l1 = mλ ...
... oscillating in the same way. If they continue to oscillate in phase when they reach a given point, the interference is constructive ⇒ Brightest or most intense spot. The condition for this to be so is that their difference in path lengths should be a integral multiple of the wavelength. l2 − l1 = mλ ...
Chapter 13
... converge, or appear to diverge from, after being reflected centre of curvature (C) – the point on the principal axis that would represent the centre of the sphere from which the curved mirror was cut 3. In specular or regular reflection, parallel rays that are incident on a flat, smooth, reflecting ...
... converge, or appear to diverge from, after being reflected centre of curvature (C) – the point on the principal axis that would represent the centre of the sphere from which the curved mirror was cut 3. In specular or regular reflection, parallel rays that are incident on a flat, smooth, reflecting ...
PDF Version - Physics (APS)
... given set of electric and magnetic fields, and their associated Poynting vectors. Next, imagine that the coordinates are continuously distorted into a new system. Transformation optics was born of the realization that lines of force are effectively glued to the coordinate system [2]. As the system i ...
... given set of electric and magnetic fields, and their associated Poynting vectors. Next, imagine that the coordinates are continuously distorted into a new system. Transformation optics was born of the realization that lines of force are effectively glued to the coordinate system [2]. As the system i ...
Resource Doc File - Dayton Regional Stem Center
... one medium into another, and changes its speed. Light waves are refracted when crossing the boundary from one transparent medium into another because the speed of light is different in different media. he bending occurs because the wave fronts do not travel as far in one cycle in the glass as they d ...
... one medium into another, and changes its speed. Light waves are refracted when crossing the boundary from one transparent medium into another because the speed of light is different in different media. he bending occurs because the wave fronts do not travel as far in one cycle in the glass as they d ...
ELECTROMAGNETIC OPTICS
... Figure 5.0-2 Wave optics is the scalar approximation of electromagnetic the limit of wave optics when the wavelength is very short. ...
... Figure 5.0-2 Wave optics is the scalar approximation of electromagnetic the limit of wave optics when the wavelength is very short. ...
$doc.title
... Do plane wave satisfy Maxwell’s equations? EM waves are a consequence of Maxwell’s equations in the sense that we used the 4 Maxwell’s Equations to derive the wave equations for E and B: ...
... Do plane wave satisfy Maxwell’s equations? EM waves are a consequence of Maxwell’s equations in the sense that we used the 4 Maxwell’s Equations to derive the wave equations for E and B: ...
Electromagnetic Waves (option G)
... The origin of EM radiation If your physics teacher were to bring a charged object into class, it would make your hair stand on end, not because it is frightening but because your hairs would be repelling each other. The way we explain how this can happen, even though the object is not touching you, ...
... The origin of EM radiation If your physics teacher were to bring a charged object into class, it would make your hair stand on end, not because it is frightening but because your hairs would be repelling each other. The way we explain how this can happen, even though the object is not touching you, ...
Enhanced enantioselectivity in excitation of chiral molecules by
... energy density, and w is the angular frequency. The quantity gCPL is purely molecular, a function of molecular transition moments and energy levels. The quantity (cC/2wUe) is purely electrodynamic. The fact that these two quantities combine in a simple product implies that, if one can enhance the ra ...
... energy density, and w is the angular frequency. The quantity gCPL is purely molecular, a function of molecular transition moments and energy levels. The quantity (cC/2wUe) is purely electrodynamic. The fact that these two quantities combine in a simple product implies that, if one can enhance the ra ...
PHS 342 - The Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta
... that light is a form of electromagnetic wave. Of course, this hypothesis turned out to be correct. We can still appreciate that Maxwell’s achievement in identifying light as a form of electromagnetic wave was quite remarkable. After all, his equations were derived from the results of bench-top labor ...
... that light is a form of electromagnetic wave. Of course, this hypothesis turned out to be correct. We can still appreciate that Maxwell’s achievement in identifying light as a form of electromagnetic wave was quite remarkable. After all, his equations were derived from the results of bench-top labor ...
Principles of optics - Assets - Cambridge
... 15.2.2 Fresnel's formulae for the propagation of light in crystals 15.2.3 Geometrical constructions for determining the velocities of propagation and the directions of vibration (a) The ellipsoid of wave normals (b) The ray ellipsoid (c) The normal surface and the ray surface 15.3 Optical properties ...
... 15.2.2 Fresnel's formulae for the propagation of light in crystals 15.2.3 Geometrical constructions for determining the velocities of propagation and the directions of vibration (a) The ellipsoid of wave normals (b) The ray ellipsoid (c) The normal surface and the ray surface 15.3 Optical properties ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2013 Semester
... • Rotation of the plane of linear polarization (eg, propagation through a sugar solution) cos E − sin E B= sin E cos E ...
... • Rotation of the plane of linear polarization (eg, propagation through a sugar solution) cos E − sin E B= sin E cos E ...
electromagnetic waves 18
... waves exhibit the properties of relection, refraction, interference, difraction and polarisation. Furthermore, they travelled at the speed of light. Since these properties are also exhibited by light, Hertz’s experiment had shown that light is a form of a transverse electromagnetic wave. In 1905, Al ...
... waves exhibit the properties of relection, refraction, interference, difraction and polarisation. Furthermore, they travelled at the speed of light. Since these properties are also exhibited by light, Hertz’s experiment had shown that light is a form of a transverse electromagnetic wave. In 1905, Al ...
Metamaterials and the Control of Electromagnetic Fields
... performing noble metal in this respect, is far from ideal. The restrahlen bands of ionic materials such as silicon carbide perform far better in this respect, but their application is confined to the far infra red. Silicon carbide does however have the advantage that it can be deposited using conven ...
... performing noble metal in this respect, is far from ideal. The restrahlen bands of ionic materials such as silicon carbide perform far better in this respect, but their application is confined to the far infra red. Silicon carbide does however have the advantage that it can be deposited using conven ...
Young`s Experiment and Thin Film
... • The conditions are valid if the medium above the top surface is the same as the medium below the bottom surface • If the thin film is between two different media, one of lower index than the film and one of higher index, the conditions for constructive and destructive interference are reversed ...
... • The conditions are valid if the medium above the top surface is the same as the medium below the bottom surface • If the thin film is between two different media, one of lower index than the film and one of higher index, the conditions for constructive and destructive interference are reversed ...
OPTH100 Ophthalmic Materials I Lecture
... 1. The students will begin to develop a firm foundation in the language of ophthalmic optics (GE-NJ 1) 2. The students will develop an understanding of ophthalmic prescriptions and an appreciation for the intricacies of correcting human vision (GE-NJ ...
... 1. The students will begin to develop a firm foundation in the language of ophthalmic optics (GE-NJ 1) 2. The students will develop an understanding of ophthalmic prescriptions and an appreciation for the intricacies of correcting human vision (GE-NJ ...
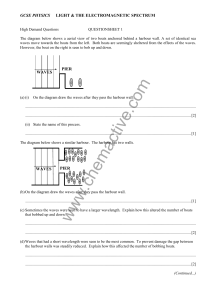
light electro questions
... The diagram below shows a prism used to split light from the sun into parts of the electromagnetic spectrum including the colours of the spectrum. The red end of the spectrum can be seen in the prism. The other colours have not been drawn on the diagram. ...
... The diagram below shows a prism used to split light from the sun into parts of the electromagnetic spectrum including the colours of the spectrum. The red end of the spectrum can be seen in the prism. The other colours have not been drawn on the diagram. ...
Light
... Wave-Particle Duality Can this strange wave-particle duality theory “predict” new things to look for? This wave-particle duality theory has been developed to become the Quantum Theory. It has predicted the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, it has led to an understanding of the Pauli Exclusion Princ ...
... Wave-Particle Duality Can this strange wave-particle duality theory “predict” new things to look for? This wave-particle duality theory has been developed to become the Quantum Theory. It has predicted the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, it has led to an understanding of the Pauli Exclusion Princ ...
What are some ways to produce light?
... What are some ways light can transfer information? • Infrared radiation is invisible electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than human eyes can detect. • Space-based telescopes, weather satellites, and some night vision goggles use infrared radiation to collect data and help people see i ...
... What are some ways light can transfer information? • Infrared radiation is invisible electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than human eyes can detect. • Space-based telescopes, weather satellites, and some night vision goggles use infrared radiation to collect data and help people see i ...
Optics

Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties.Most optical phenomena can be accounted for using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be accounted for in geometric optics. Historically, the ray-based model of light was developed first, followed by the wave model of light. Progress in electromagnetic theory in the 19th century led to the discovery that light waves were in fact electromagnetic radiation.Some phenomena depend on the fact that light has both wave-like and particle-like properties. Explanation of these effects requires quantum mechanics. When considering light's particle-like properties, the light is modelled as a collection of particles called ""photons"". Quantum optics deals with the application of quantum mechanics to optical systems.Optical science is relevant to and studied in many related disciplines including astronomy, various engineering fields, photography, and medicine (particularly ophthalmology and optometry). Practical applications of optics are found in a variety of technologies and everyday objects, including mirrors, lenses, telescopes, microscopes, lasers, and fibre optics.