A Light History of Electromagnetic Waves: Waves and Particles
... that Newton reported on as being different rays of light in themselves. Hooke compared it to sound (a comparison that was often made in the 17th and 18th centuries), and specifically, a noise coming from an instrument, “the ray is like the string, strained between the luminous object and the eye, an ...
... that Newton reported on as being different rays of light in themselves. Hooke compared it to sound (a comparison that was often made in the 17th and 18th centuries), and specifically, a noise coming from an instrument, “the ray is like the string, strained between the luminous object and the eye, an ...
SR 52(5) 14-21
... Polarisers are used in applications such as aeroplane windows, automobile headlights, visors, camera filters, laser windows, anti-glare sunglasses and stereoscopic (three-dimensional) viewing. Polariscope, which uses two polarisers in tandem, is used in viewing of colourless objects. Polarisation st ...
... Polarisers are used in applications such as aeroplane windows, automobile headlights, visors, camera filters, laser windows, anti-glare sunglasses and stereoscopic (three-dimensional) viewing. Polariscope, which uses two polarisers in tandem, is used in viewing of colourless objects. Polarisation st ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2015 Semester Lecture 31 – Electromagnetic Waves
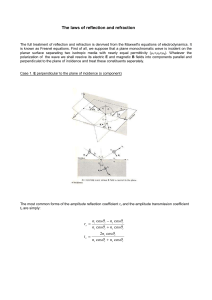
... • At normal incidence, cos j = 1 there really is no component parallel to the plane of incidence. • In this case >e h6 − h ...
... • At normal incidence, cos j = 1 there really is no component parallel to the plane of incidence. • In this case >e h6 − h ...
Notes follow and parts taken from Physics (6th Edition, Cutnell
... You might have noticed that it seems that the least damaging kinds of radiation are clustered at one end of the spectrum (radio) and the most damaging (UV, X-ray, etc.) are at the other end. That’s not a coincidence – we’ll see later that the energy of an individual piece of light (photon) is propor ...
... You might have noticed that it seems that the least damaging kinds of radiation are clustered at one end of the spectrum (radio) and the most damaging (UV, X-ray, etc.) are at the other end. That’s not a coincidence – we’ll see later that the energy of an individual piece of light (photon) is propor ...
File
... **Angles are always measured with respect to the normal** - this law is true for both particles and waves ...
... **Angles are always measured with respect to the normal** - this law is true for both particles and waves ...
Concave and Convex Mirrors and Lenses
... • Light waves travel from their source in all directions. • A ray can be used to show the path and direction of a light wave after it bounces or bends. ...
... • Light waves travel from their source in all directions. • A ray can be used to show the path and direction of a light wave after it bounces or bends. ...
Chapter 2 Optical Fibers: Structures, Waveguiding
... • In the context of classical optics, electromagentic radiation propagates in the form of two mutually coupled vector waves, an electric field-wave & magnetic field wave. It is possible to describe many optical phenomena such as diffraction, by scalar wave theory in which light is described by a si ...
... • In the context of classical optics, electromagentic radiation propagates in the form of two mutually coupled vector waves, an electric field-wave & magnetic field wave. It is possible to describe many optical phenomena such as diffraction, by scalar wave theory in which light is described by a si ...
Week 4
... • an asymmetry between right and left allows opposing circular polarizations to have differing refractive indices • optical activity rotates the polarization plane of linearly polarized light • may be observed in vapours, liquids and ...
... • an asymmetry between right and left allows opposing circular polarizations to have differing refractive indices • optical activity rotates the polarization plane of linearly polarized light • may be observed in vapours, liquids and ...
Reflection of Light
... 2) The purpose of this lab is to investigate the reflective property of light, so a mirror would be useful, and the mirror needs to be in one position throughout the experiment. To make sure of this, attach a plane mirror to a small block of wood. 3) Draw five lines from the midpoint, each with diff ...
... 2) The purpose of this lab is to investigate the reflective property of light, so a mirror would be useful, and the mirror needs to be in one position throughout the experiment. To make sure of this, attach a plane mirror to a small block of wood. 3) Draw five lines from the midpoint, each with diff ...
The laws of reflection and refraction θ θ θ θ θ θ θ
... transmission axis to an angle at which it is parallel to the plane of incidence or the plane of vibration for the “p” beam. Hence, the light sensor can only measure the intensity of “p” beam of reflected light. 4. Mount the metal lens holder on the Brewster’s angle base disk, as shown in Figure 2. T ...
... transmission axis to an angle at which it is parallel to the plane of incidence or the plane of vibration for the “p” beam. Hence, the light sensor can only measure the intensity of “p” beam of reflected light. 4. Mount the metal lens holder on the Brewster’s angle base disk, as shown in Figure 2. T ...
Module - EPS School Projects
... Ability to tackle problems relating fields to matter and vice-versa. Appreciation of the vector basis of electromagnetism. Understanding of the use of Maxwell’s equations as a unified electromagnetic description. Applications of plane wave equation solutions at boundaries. Understanding of basic opt ...
... Ability to tackle problems relating fields to matter and vice-versa. Appreciation of the vector basis of electromagnetism. Understanding of the use of Maxwell’s equations as a unified electromagnetic description. Applications of plane wave equation solutions at boundaries. Understanding of basic opt ...
Reflection and Transmission
... Light, the giver of life, has always fascinated human beings. It is therefore natural that people have been trying to find out what light actually is, for a very long time. We can see it, feel its warmth on our skin but we cannot touch it. The ancient Greek philosophers thought light was an extremel ...
... Light, the giver of life, has always fascinated human beings. It is therefore natural that people have been trying to find out what light actually is, for a very long time. We can see it, feel its warmth on our skin but we cannot touch it. The ancient Greek philosophers thought light was an extremel ...
3rd 9 weeks
... I can differentiate among the various categories of the electromagnetic spectrum. I can solve for frequency or wavelength of an electromagnetic wave given the other quantity. I can order the EM spectrum in terms of energy, wavelength, and frequency. ...
... I can differentiate among the various categories of the electromagnetic spectrum. I can solve for frequency or wavelength of an electromagnetic wave given the other quantity. I can order the EM spectrum in terms of energy, wavelength, and frequency. ...
Welcome to Physics 152!
... This course is an introduction to electromagnetism. The importance of electromagnetism cannot be overstated. Electromagnetic theory allows us to answer the following questions about common observations: Why do balloons stick to the wall after you rub them over your hair? What causes the heart to bea ...
... This course is an introduction to electromagnetism. The importance of electromagnetism cannot be overstated. Electromagnetic theory allows us to answer the following questions about common observations: Why do balloons stick to the wall after you rub them over your hair? What causes the heart to bea ...
Light Test Study Guide Answer Key Name: Date: Core: Directions
... 5. Which best explains the relationship between the electromagnetic spectrum and sight? Answer: Visible Light is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be seen with the eye. 6. What happens when thicker strings are added to a guitar? Answer: It changes the vibrations made by the guitar. 7 ...
... 5. Which best explains the relationship between the electromagnetic spectrum and sight? Answer: Visible Light is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be seen with the eye. 6. What happens when thicker strings are added to a guitar? Answer: It changes the vibrations made by the guitar. 7 ...
Principles of Nulling and Imaging Ellipsometry Imaging Ellipsometer Technical Release Note
... B. Polarization of Light Light is an electromagnetic wave. In order to describe light one considers the strength and direction of the electric field E, because this has a stronger interaction with matter than the magnetic field. Monochromatic light may, at a point in space E, be resolved into three ...
... B. Polarization of Light Light is an electromagnetic wave. In order to describe light one considers the strength and direction of the electric field E, because this has a stronger interaction with matter than the magnetic field. Monochromatic light may, at a point in space E, be resolved into three ...
Light
... If light moves, how fast is it? Galileo tried to measure the speed of light using signals from lanterns on two mountains. He was unsuccessful – light is too fast! The first measurement of the speed of light was astronomical, made by Roemer in 1676 using the eclipses of the moons of Jupiter (which h ...
... If light moves, how fast is it? Galileo tried to measure the speed of light using signals from lanterns on two mountains. He was unsuccessful – light is too fast! The first measurement of the speed of light was astronomical, made by Roemer in 1676 using the eclipses of the moons of Jupiter (which h ...
Chapter 7
... • For Incident angles greater than Critical, 100.000...% reflection. • Today's BIG use for TIR: Keeps light energy from leaking out the walls of FIBER OPTICS. {DRAW Fiber Construction }(see p.214) • Fiber Optics uses: • Medicine: First developed for Endoscopes to see inside body. ...
... • For Incident angles greater than Critical, 100.000...% reflection. • Today's BIG use for TIR: Keeps light energy from leaking out the walls of FIBER OPTICS. {DRAW Fiber Construction }(see p.214) • Fiber Optics uses: • Medicine: First developed for Endoscopes to see inside body. ...
Chapter 27: Light
... We know that light travels in transverse not longitudinal waves because of a phenomenon called polarization. Polarization refers to whether the wave is going up and down or side to side. An up and down wave is vertically polarized and a side to side wave is horizontally polarized. The polarization o ...
... We know that light travels in transverse not longitudinal waves because of a phenomenon called polarization. Polarization refers to whether the wave is going up and down or side to side. An up and down wave is vertically polarized and a side to side wave is horizontally polarized. The polarization o ...
Chapter 18 Notes
... • When light strikes a _______ medium, the light can be reflected, absorbed, or transmitted. When light is ___________, it can be refracted, polarized, or scattered. Reflection • When you look in a _____, you see a clear image of yourself. • An ________ is a copy of an object formed by reflected (or ...
... • When light strikes a _______ medium, the light can be reflected, absorbed, or transmitted. When light is ___________, it can be refracted, polarized, or scattered. Reflection • When you look in a _____, you see a clear image of yourself. • An ________ is a copy of an object formed by reflected (or ...
Light
... • Just like with mirrors, we will need to follow rules to draw ray diagrams to predict the location of an image. • Thin lenses also have focal points, these points are determined not only by the curve of the lens but the index of refraction of the lens as well. • A lens has two focal points, one on ...
... • Just like with mirrors, we will need to follow rules to draw ray diagrams to predict the location of an image. • Thin lenses also have focal points, these points are determined not only by the curve of the lens but the index of refraction of the lens as well. • A lens has two focal points, one on ...
Light
... In this application, the cable consists of two fiber-optic lines: one to transmit a beam of light into the stomach ...
... In this application, the cable consists of two fiber-optic lines: one to transmit a beam of light into the stomach ...
1700_Maxwell_2013aug
... • 1812 Fresnel develops wave theory of transverse polarized light • 1815 Brewster’s angle: at this angle of incidence the reflected light is entirely “s” polarized such that electric field is parallel to the interface surface ...
... • 1812 Fresnel develops wave theory of transverse polarized light • 1815 Brewster’s angle: at this angle of incidence the reflected light is entirely “s” polarized such that electric field is parallel to the interface surface ...
Optics

Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties.Most optical phenomena can be accounted for using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be accounted for in geometric optics. Historically, the ray-based model of light was developed first, followed by the wave model of light. Progress in electromagnetic theory in the 19th century led to the discovery that light waves were in fact electromagnetic radiation.Some phenomena depend on the fact that light has both wave-like and particle-like properties. Explanation of these effects requires quantum mechanics. When considering light's particle-like properties, the light is modelled as a collection of particles called ""photons"". Quantum optics deals with the application of quantum mechanics to optical systems.Optical science is relevant to and studied in many related disciplines including astronomy, various engineering fields, photography, and medicine (particularly ophthalmology and optometry). Practical applications of optics are found in a variety of technologies and everyday objects, including mirrors, lenses, telescopes, microscopes, lasers, and fibre optics.