1
... Motor (efferent only) – carry impulses from CNS Mixed – sensory and motor fibers carry impulses to and from CNS, most common type of nerve These prefixes will be used through out the semester so remember them. Epi – (upon, on top of) always representing the outer most layer of the part being ...
... Motor (efferent only) – carry impulses from CNS Mixed – sensory and motor fibers carry impulses to and from CNS, most common type of nerve These prefixes will be used through out the semester so remember them. Epi – (upon, on top of) always representing the outer most layer of the part being ...
Nervous system: Detects information from the environment
... Protects the body's internal living tissues and organs against: invasion by infectious organisms dehydration abrupt changes in temperature Disposes of waste materials Contains receptors for touch, pressure, pain, heat, and cold. Stores water and fat. Provides shape and support Allows you to move Pro ...
... Protects the body's internal living tissues and organs against: invasion by infectious organisms dehydration abrupt changes in temperature Disposes of waste materials Contains receptors for touch, pressure, pain, heat, and cold. Stores water and fat. Provides shape and support Allows you to move Pro ...
ch. 48 Nervous System notes
... Receives information about position from joints and length of muscles, as well as auditory and visual systems Plays role in learning and remembering motor responses (hand-eye coordination) ...
... Receives information about position from joints and length of muscles, as well as auditory and visual systems Plays role in learning and remembering motor responses (hand-eye coordination) ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... Ependymal line the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord Astrocytes maintain the blood brain barrier (BBB), structural support, regulate ion content, and repair ...
... Ependymal line the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord Astrocytes maintain the blood brain barrier (BBB), structural support, regulate ion content, and repair ...
2nd Grade Tableau
... PO 101. Evaluate the playing space and setting used for a variety of dramatic works, classroom scenes, and informal or formal productions. PO 103. Evaluate how line, shape, texture, color, space, balance, and/or pattern Teacher Name: help illustrate the environment of a story. ...
... PO 101. Evaluate the playing space and setting used for a variety of dramatic works, classroom scenes, and informal or formal productions. PO 103. Evaluate how line, shape, texture, color, space, balance, and/or pattern Teacher Name: help illustrate the environment of a story. ...
Vertebrate and Invertebrate Notes
... enable them to find food and shelter How do animals and humans use their senses? • Animals and humans have sensory organs that allow them to detect changes in the environment • When change is detected organisms respond with certain behaviors • Senses tell animals what they need to know about their e ...
... enable them to find food and shelter How do animals and humans use their senses? • Animals and humans have sensory organs that allow them to detect changes in the environment • When change is detected organisms respond with certain behaviors • Senses tell animals what they need to know about their e ...
Introduction to Dissection
... together to maintain homeostasis. Understand the importance of maintaining a stable internal environment in the human body. ...
... together to maintain homeostasis. Understand the importance of maintaining a stable internal environment in the human body. ...
Nerves Ganglia Spinal nerves Cranial nerves Afferent neurons
... Division of the ANS that regulates resting and nutrition-related functions such as digestion, defecation, and urination ...
... Division of the ANS that regulates resting and nutrition-related functions such as digestion, defecation, and urination ...
Body Systems REVIEW
... 1. The process by which organ systems maintain relatively constant internal conditions is called ___________________. 2. Which system coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environment? __________________ 3. What provides support for the body, attachment sites for mu ...
... 1. The process by which organ systems maintain relatively constant internal conditions is called ___________________. 2. Which system coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environment? __________________ 3. What provides support for the body, attachment sites for mu ...
Slide 1
... appropriately. Motor activity, behavioral changes, coordination, sensory/motor reflex responses and body temperature should be evaluated. For example, a functional observation battery (FOB) (3), modified Irwin’s (4), or other appropriate test (5) can be used.” ...
... appropriately. Motor activity, behavioral changes, coordination, sensory/motor reflex responses and body temperature should be evaluated. For example, a functional observation battery (FOB) (3), modified Irwin’s (4), or other appropriate test (5) can be used.” ...
BODY SYSTEMS
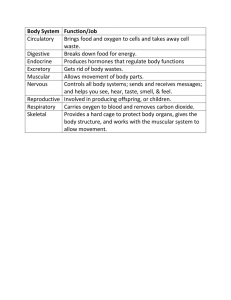
... Eleven Systems of the Human Body 1. Circulatory System - transports blood, nutrients, gases, and wastes 2. Digestive System - takes in food, breaks it down, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates solid waste 3. Respiratory System - Controls breathing, and exchanges gases in the lungs and tissues 4. Excr ...
... Eleven Systems of the Human Body 1. Circulatory System - transports blood, nutrients, gases, and wastes 2. Digestive System - takes in food, breaks it down, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates solid waste 3. Respiratory System - Controls breathing, and exchanges gases in the lungs and tissues 4. Excr ...
The body has 11 organ systems
... learning, and conscious thought are a few aspects of the functions of the _______________ system. Maintaining automatic functions such as heartbeat, breathing, control of involuntary muscle actions are performed by some of the parts of the __________________system. The ________________ system works ...
... learning, and conscious thought are a few aspects of the functions of the _______________ system. Maintaining automatic functions such as heartbeat, breathing, control of involuntary muscle actions are performed by some of the parts of the __________________system. The ________________ system works ...
Human Body Systems
... Stomach: breaks down food by physical and chemical means Brain: controls thinking and voluntary actions Human body systems and their functions: Skeletal: supports body, protects internal organs Muscular: moves organs and body parts Nervous: controls body activities; carries and interprets messages ...
... Stomach: breaks down food by physical and chemical means Brain: controls thinking and voluntary actions Human body systems and their functions: Skeletal: supports body, protects internal organs Muscular: moves organs and body parts Nervous: controls body activities; carries and interprets messages ...
Human Biology Human Body Systems Nervous System
... Relay information from sensory neurons to motor neurons . Motor Neuron Stimulate muscles or glands in effector organs to cause a response. ...
... Relay information from sensory neurons to motor neurons . Motor Neuron Stimulate muscles or glands in effector organs to cause a response. ...
Human Body Systems
... • break down food into molecules the body can use; • allow materials to be absorbed into bloodstream; • Eliminate wastes ...
... • break down food into molecules the body can use; • allow materials to be absorbed into bloodstream; • Eliminate wastes ...
Ch 2 Biology and Behavior
... Sensory nerves – bring input from skin, muscles and organs. Motor nerves – carry output to muscles, glands and organs ...
... Sensory nerves – bring input from skin, muscles and organs. Motor nerves – carry output to muscles, glands and organs ...
Review Senses and Nervous System Test
... Review Senses and Nervous System Test *(This is only an outline there is much more you should look over) CH 8 SENSES 1. What are the functions of the parts of eye? 2. What is blind spot, photoreceptors, rods, cones? 3. Read p 258, 262 4. What is colorblindness, cataracts, pink eye, glaucoma 5. What ...
... Review Senses and Nervous System Test *(This is only an outline there is much more you should look over) CH 8 SENSES 1. What are the functions of the parts of eye? 2. What is blind spot, photoreceptors, rods, cones? 3. Read p 258, 262 4. What is colorblindness, cataracts, pink eye, glaucoma 5. What ...
Chapter 7 Nervous System Every conscious action is governed by
... Special senses (sight, hearing, smell, taste) o General sensory receptors (touch, light, external heat, pain) o Visceral receptors (monitoring internal organ function) Information moves from PNS to CNS Information is processed by the CNS and the appropriate response is determined Motor respons ...
... Special senses (sight, hearing, smell, taste) o General sensory receptors (touch, light, external heat, pain) o Visceral receptors (monitoring internal organ function) Information moves from PNS to CNS Information is processed by the CNS and the appropriate response is determined Motor respons ...
Ch. 35.3
... between the brain stem and cerebrum Thalamus receives messages from the sense organs Hypothalamus controls recognition of hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and body temp ...
... between the brain stem and cerebrum Thalamus receives messages from the sense organs Hypothalamus controls recognition of hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and body temp ...
The Nervous System
... Example: Poison blocks muscle movement Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, learning, and memory **Brains of those suffering from Alzheimer’s have deteriorating Achproducing neurons Endorphins – natural neurotransmitters linked to pain control and pleasure **”Runner’s High” is an example of ...
... Example: Poison blocks muscle movement Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, learning, and memory **Brains of those suffering from Alzheimer’s have deteriorating Achproducing neurons Endorphins – natural neurotransmitters linked to pain control and pleasure **”Runner’s High” is an example of ...
Neurons
... Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS)- brain and spinal chord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)- all nerves extending from and going to the CNS Composed of over 100 billion neurons ...
... Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS)- brain and spinal chord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)- all nerves extending from and going to the CNS Composed of over 100 billion neurons ...
Neuroscience in space

Space neuroscience is the scientific study of the central nervous system (CNS) functions during spaceflight. Living systems can integrate the inputs from the senses to navigate in their environment and to coordinate posture, locomotion, and eye movements. Gravity has a fundamental role in controlling these functions. In weightlessness during spaceflight, integrating the sensory inputs and coordinating motor responses is harder to do because gravity is no longer sensed during free-fall. For example, the otolith organs of the vestibular system no longer signal head tilt relative to gravity when standing. However, they can still sense head translation during body motion. Ambiguities and changes in how the gravitational input is processed can lead to potential errors in perception, which affects spatial orientation and mental representation. Dysfunctions of the vestibular system are common during and immediately after spaceflight, such as space motion sickness in orbit and balance disorders after return to Earth.Adaptation to weightlessness involves not just the Sensory-motor coupling functions, but some autonomic nervous system functions as well. Sleep disorders and orthostatic intolerance are also common during and after spaceflight. There is no hydrostatic pressure in a weightless environment. As a result, the redistribution of body fluids toward the upper body causes a decrease in leg volume, which may affect muscle viscosity and compliance. An increase in intracranial pressure may also be responsible for a decrease in near visual acuity. In addition, muscle mass and strength both decrease as a result of the reduced loading in weightlessness. Moreover, approximately 70% of astronauts experience space motion sickness to some degree during the first days. The drugs commonly used to combat motion sickness, such as scopolamine and promethazine, have soporific effects. These factors can lead to chronic fatigue. The challenge of integrative space medicine and physiology is to investigate the adaptation of the human body to spaceflight as a whole, and not just as the sum of body parts because all body functions are connected and interact with each other.