Grade 9 Science EXAM REVIEW – ASTRONOMY
... Earth and burns up. Meteorite = a small body of matter from outer space that hits the Earth’s surface Revolution = movement around the Sun Rotation = spinning about its axis Galaxy = A collection of stars, gas, and dust bound together by gravity. The smallest galaxies may contain only a few hundred ...
... Earth and burns up. Meteorite = a small body of matter from outer space that hits the Earth’s surface Revolution = movement around the Sun Rotation = spinning about its axis Galaxy = A collection of stars, gas, and dust bound together by gravity. The smallest galaxies may contain only a few hundred ...
Introduction to the EarthESci 100Dr. Albanese, Tuesdays and
... 9. The sun's energy results from the conversion of hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei. 10. The length of daylight on the moon is about one month. 11. Most of the moon’s craters are volcanic in origin. 12. Galileo built the first known telescope. 13. Although current technology will allow the constru ...
... 9. The sun's energy results from the conversion of hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei. 10. The length of daylight on the moon is about one month. 11. Most of the moon’s craters are volcanic in origin. 12. Galileo built the first known telescope. 13. Although current technology will allow the constru ...
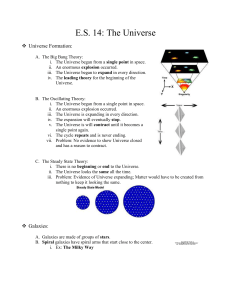
E.S. 14: The Universe Universe Formation: The Big Bang Theory
... B. Spiral galaxies have spiral arms that start close to the center. i. Ex: The Milky Way ...
... B. Spiral galaxies have spiral arms that start close to the center. i. Ex: The Milky Way ...
sc_examII_spring_2002 - University of Maryland Astronomy
... A. continuous B. absorption C. emission D. blue shifted E. red shifted 2. The smaller the parallax angle for a star, A. the less massive the star. B. the more massive the star. C. the smaller the distance to the star. D. the greater the distance to the star. E. both A and C 3. By combining informati ...
... A. continuous B. absorption C. emission D. blue shifted E. red shifted 2. The smaller the parallax angle for a star, A. the less massive the star. B. the more massive the star. C. the smaller the distance to the star. D. the greater the distance to the star. E. both A and C 3. By combining informati ...
Stellar Astronomy Unit 3 Key Terms and Matching Definitions _____
... 7. A flattened galaxy reminiscent of a pinwheel. 8. An oval galaxy with no distinguishing spiral arms. 9. A collection of galaxies held together by their mutual gravitational attraction. 10. The collection of approximately 40 galaxies that includes the Milky Way Galaxy. 11. When two similarly-sized ...
... 7. A flattened galaxy reminiscent of a pinwheel. 8. An oval galaxy with no distinguishing spiral arms. 9. A collection of galaxies held together by their mutual gravitational attraction. 10. The collection of approximately 40 galaxies that includes the Milky Way Galaxy. 11. When two similarly-sized ...
galaxy phenomenology
... SDSS images of spiral galaxies, selected according to classifications in NED to be Sa–Sd (including barred types). The images are sorted by absolute magnitude in the horizontal direction, ranging between Mr − 5 log10 h ∼ −18.5 and −22 from left to right, and g − r color in the vertical direction, ra ...
... SDSS images of spiral galaxies, selected according to classifications in NED to be Sa–Sd (including barred types). The images are sorted by absolute magnitude in the horizontal direction, ranging between Mr − 5 log10 h ∼ −18.5 and −22 from left to right, and g − r color in the vertical direction, ra ...
Big Bang Theory
... • Hubble found that most galaxies had redshifted (meaning…) • They are moving away from the observer • This means that the universe is expanding • In honour of this discovery: the first large space telescope was named after Hubble ...
... • Hubble found that most galaxies had redshifted (meaning…) • They are moving away from the observer • This means that the universe is expanding • In honour of this discovery: the first large space telescope was named after Hubble ...
Origin and Formation of the Universe – PowerPoint notes
... 1. Considered to be a ____________________ Big Bang Theory. 2. The universe ____________________ and ___________________ until about _______________ second after the big bang when it became so cool that the forces of nature caused the universe to _____________________________________. 3. This initia ...
... 1. Considered to be a ____________________ Big Bang Theory. 2. The universe ____________________ and ___________________ until about _______________ second after the big bang when it became so cool that the forces of nature caused the universe to _____________________________________. 3. This initia ...
Origin and Formation of the Universe – PowerPoint notes I
... 1. Considered to be a ____________________ Big Bang Theory. 2. The universe ____________________ and ___________________ until about _______________ second after the big bang when it became so cool that the forces of nature caused the universe to _____________________________________. 3. This initia ...
... 1. Considered to be a ____________________ Big Bang Theory. 2. The universe ____________________ and ___________________ until about _______________ second after the big bang when it became so cool that the forces of nature caused the universe to _____________________________________. 3. This initia ...
Class notes 2 - University of Texas Astronomy
... Sagittarius, is visible in the infrared and radio). Bright stars and gas are concentrated in spiral arms. The gas is clumped in clouds, though there is also a diffuse background of gas. ...
... Sagittarius, is visible in the infrared and radio). Bright stars and gas are concentrated in spiral arms. The gas is clumped in clouds, though there is also a diffuse background of gas. ...
The Milky Way at Different Wavelengths
... Owing to the strong obscuration by interstellar dust the light is primarily from stars within a few thousand light-years of the Sun, nearby on the scale of the Milky Way, which has a diameter on the order of 100,000 light years. Nebulosity from hot, low-density gas is widespread in the image. Dark p ...
... Owing to the strong obscuration by interstellar dust the light is primarily from stars within a few thousand light-years of the Sun, nearby on the scale of the Milky Way, which has a diameter on the order of 100,000 light years. Nebulosity from hot, low-density gas is widespread in the image. Dark p ...
Star Composition: Flame Testing Lab S-2
... chemical has its own pattern of lines like a fingerprint. You will use a spectrograph to analyze chemical flames. 8th grade science standards: b. Students know that the Sun is one of many stars in the Milky Way galaxy and that stars may differ in size, temperature, and color. d. Students know that s ...
... chemical has its own pattern of lines like a fingerprint. You will use a spectrograph to analyze chemical flames. 8th grade science standards: b. Students know that the Sun is one of many stars in the Milky Way galaxy and that stars may differ in size, temperature, and color. d. Students know that s ...
Life2
... Radiation seen today as microwave background radiation Most of early universe made of about ¾ hydrogen, ¼ helium and trace (.000,000,001) of lithium. No elements produced with an atomic number higher than lithium !!!!!! Heterogeneous universe from a homogenous one ? Quantum fluctuations in early uni ...
... Radiation seen today as microwave background radiation Most of early universe made of about ¾ hydrogen, ¼ helium and trace (.000,000,001) of lithium. No elements produced with an atomic number higher than lithium !!!!!! Heterogeneous universe from a homogenous one ? Quantum fluctuations in early uni ...
What is a Scientist? - Cockeysville Middle School
... Objective: To describe the characteristics of galaxies in order to classify different galaxies. Astronomy Note: Are all galaxies the same? ...
... Objective: To describe the characteristics of galaxies in order to classify different galaxies. Astronomy Note: Are all galaxies the same? ...
lung volumes and capacities
... Small fragments of matter moving in space that sometimes enter Earth’s atmosphere. METEOROIDS When they strike the Earth, they are called Meteorites. A system of stars, gases and dust appearing as a bright white path across the sky. Our MILKY WAY solar system is in part of this galaxy. GALAXY The pa ...
... Small fragments of matter moving in space that sometimes enter Earth’s atmosphere. METEOROIDS When they strike the Earth, they are called Meteorites. A system of stars, gases and dust appearing as a bright white path across the sky. Our MILKY WAY solar system is in part of this galaxy. GALAXY The pa ...
Another exAmple: expository mode
... stars. Young stars convert hydrogen to helium through a process known as nuclear fusion to produce light. As stars use up this hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redg ...
... stars. Young stars convert hydrogen to helium through a process known as nuclear fusion to produce light. As stars use up this hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redg ...
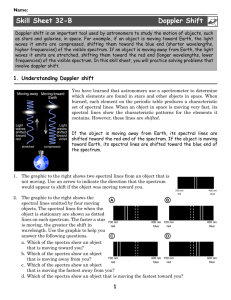
Skill Sheet 32-B Doppler Shift
... not moving. Use an arrow to indicate the direction that the spectrum would appear to shift if the object was moving toward you. 2. The graphic to the right shows the spectral lines emitted by four moving objects. The spectral lines for when the object is stationary are shown as dotted lines on each ...
... not moving. Use an arrow to indicate the direction that the spectrum would appear to shift if the object was moving toward you. 2. The graphic to the right shows the spectral lines emitted by four moving objects. The spectral lines for when the object is stationary are shown as dotted lines on each ...
8th Grade - Astronomy
... within the umbra experience a total eclipse. The penumbra casts a larger shadow that is less dark. People in the penumbra experience a partial eclipse. (p. 481) A huge group of stars, star clusters, star systems, dust and gas bound together by Galaxy gravity. There are billions of galaxies in the un ...
... within the umbra experience a total eclipse. The penumbra casts a larger shadow that is less dark. People in the penumbra experience a partial eclipse. (p. 481) A huge group of stars, star clusters, star systems, dust and gas bound together by Galaxy gravity. There are billions of galaxies in the un ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Welcome to Modern Astronomy Fall 2003
... Welcome to Modern Astronomy Fall 2007 • Initial pleasantries, who I am, who you are • This should be the most interesting course you take in college • National Solar Observatory ...
... Welcome to Modern Astronomy Fall 2007 • Initial pleasantries, who I am, who you are • This should be the most interesting course you take in college • National Solar Observatory ...
Our Universe (ES1-E) I know that our Sun is one of hundreds of
... around 30 galaxies called the _________ _________ galaxy cluster. • The largest galaxies in the Local Group are the Milky Way and the ____________ galaxy • The Andromeda galaxy is one of the __________ spiral galaxies known. It is 2.4 million light years away. ...
... around 30 galaxies called the _________ _________ galaxy cluster. • The largest galaxies in the Local Group are the Milky Way and the ____________ galaxy • The Andromeda galaxy is one of the __________ spiral galaxies known. It is 2.4 million light years away. ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.