Stars and Galaxies PP 2013
... times the sun) will undergo a supernova and will contract into a black hole. It is not really a hole. It has so much gravity that not even light can escape it. They can not be seen directly. ...
... times the sun) will undergo a supernova and will contract into a black hole. It is not really a hole. It has so much gravity that not even light can escape it. They can not be seen directly. ...
Review Quiz No. 17
... The radius in the interior of a star where fusion processes can no longer take place. The point in time of a star’s life when nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium ceases. The point in time of a star’s life when nuclear fusion processes cease alltogether. The point in a rotating star cluster beyond ...
... The radius in the interior of a star where fusion processes can no longer take place. The point in time of a star’s life when nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium ceases. The point in time of a star’s life when nuclear fusion processes cease alltogether. The point in a rotating star cluster beyond ...
Whirlpool Galaxy - astronomydennis
... At the center of the Whirlpool galaxy is its noted cross. The cross has been thought to have been caused by a jet of high speed plasma which confines radiation from the accretion disk to a pair of oppositely directed cones of light that ionize gas caught in their beams. In simple terms, it is the ab ...
... At the center of the Whirlpool galaxy is its noted cross. The cross has been thought to have been caused by a jet of high speed plasma which confines radiation from the accretion disk to a pair of oppositely directed cones of light that ionize gas caught in their beams. In simple terms, it is the ab ...
PASS Content Standard 5.1
... The stars differ from each other in size, temperature, and age, but they appear to be made up of the same elements that are found on the earth. ...
... The stars differ from each other in size, temperature, and age, but they appear to be made up of the same elements that are found on the earth. ...
Science Astronomy Name
... 16. Stars are glowing balls of gas that exists throughout space. 17. Our sun is a star that is the source of Earth’s light energy and heat energy. 18. A force that causes objects to attract each other is called gravity. (OVER) 19. Gravity keeps the planets orbiting the sun. It also keeps the moons o ...
... 16. Stars are glowing balls of gas that exists throughout space. 17. Our sun is a star that is the source of Earth’s light energy and heat energy. 18. A force that causes objects to attract each other is called gravity. (OVER) 19. Gravity keeps the planets orbiting the sun. It also keeps the moons o ...
Open clusters
... Some special stars change their luminosity with a regular pattern. For example, Cepheid Variable stars have a relationship between their luminosity and the period of variation. this can be used to determine the distance to the star. ...
... Some special stars change their luminosity with a regular pattern. For example, Cepheid Variable stars have a relationship between their luminosity and the period of variation. this can be used to determine the distance to the star. ...
Glossary File - Griffith Observatory
... extraterrestrial life. atom – a basic unit of matter. The simplest building block of the universe, an atom has a nucleus containing protons and neutrons and a cloud of electrons that surrounds the nucleus. comet – a small, icy object from the outer part of the solar system. Comets form tails as they ...
... extraterrestrial life. atom – a basic unit of matter. The simplest building block of the universe, an atom has a nucleus containing protons and neutrons and a cloud of electrons that surrounds the nucleus. comet – a small, icy object from the outer part of the solar system. Comets form tails as they ...
Chapter 10- Stars, Galaxies and the Universe
... b. high-mass star. c. protostar. d. low-mass star. ____ 11. From the cosmic background radiation, scientists can infer that, just after the big bang, the universe must have been a. very small. b. hot. c. the same average temperature as it is today. d. cooler than it is today. ____ 12. More than half ...
... b. high-mass star. c. protostar. d. low-mass star. ____ 11. From the cosmic background radiation, scientists can infer that, just after the big bang, the universe must have been a. very small. b. hot. c. the same average temperature as it is today. d. cooler than it is today. ____ 12. More than half ...
Science Astronomy Name
... 16. Stars are glowing balls of gas that exists throughout space. 17. Our sun is a star that is the source of Earth’s light energy and heat energy. 18. A force that causes objects to attract each other is called gravity. (OVER) ...
... 16. Stars are glowing balls of gas that exists throughout space. 17. Our sun is a star that is the source of Earth’s light energy and heat energy. 18. A force that causes objects to attract each other is called gravity. (OVER) ...
Lab 7: Emission Spectra
... This is a hydrogen absorption spectrum. It looks like a continuous spectrum with a few specific colors missing, and that's exactly what it is. Those missing colors are light with a specific wavelength that has been absorbed by a hydrogen atom. What causes absorption lines? The electrons in atoms h ...
... This is a hydrogen absorption spectrum. It looks like a continuous spectrum with a few specific colors missing, and that's exactly what it is. Those missing colors are light with a specific wavelength that has been absorbed by a hydrogen atom. What causes absorption lines? The electrons in atoms h ...
Lecture1
... Is used to calibrate other, more indirect distance indicators. Ultimately even our estimates of distances to the most remote galaxies rests on a reliable measure of parallax to the nearest stars ...
... Is used to calibrate other, more indirect distance indicators. Ultimately even our estimates of distances to the most remote galaxies rests on a reliable measure of parallax to the nearest stars ...
The Star–Gas–Star Cycle
... Twelve million miles a minute, and that's the fastest speed there is. ...
... Twelve million miles a minute, and that's the fastest speed there is. ...
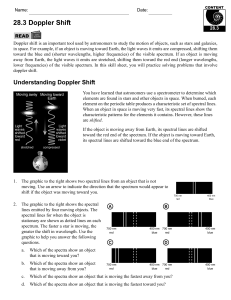
28.3 Doppler Shift
... star moving away from or toward Earth? One of the spectral lines for a star has shifted from 560 nm to 544 nm. What is the speed of the star? Is it moving away from or toward Earth? An astronomer has determined that two galaxies are moving away from Earth. A spectral line for galaxy A is red shifted ...
... star moving away from or toward Earth? One of the spectral lines for a star has shifted from 560 nm to 544 nm. What is the speed of the star? Is it moving away from or toward Earth? An astronomer has determined that two galaxies are moving away from Earth. A spectral line for galaxy A is red shifted ...
stars
... Be stars are non-supergiant B-type stars whose spectra have, or had at some time, one or more Balmer lines in emission. The mystery of the "Be phenomenon" is that the emission, which is well understood to originate from a flattened circumstellar disk (e.g. Struve, 1931), can come and go episodically ...
... Be stars are non-supergiant B-type stars whose spectra have, or had at some time, one or more Balmer lines in emission. The mystery of the "Be phenomenon" is that the emission, which is well understood to originate from a flattened circumstellar disk (e.g. Struve, 1931), can come and go episodically ...
Stellar Kinematics
... Galaxies are rotating as if they contain much more mass than we can see Due to? Faint stars – Dust or gas – Compact objects and planets – Strange particles – should show up in very sensitive detectors ...
... Galaxies are rotating as if they contain much more mass than we can see Due to? Faint stars – Dust or gas – Compact objects and planets – Strange particles – should show up in very sensitive detectors ...
The “Tuning Fork” Diagram Galaxy Properties 1 “Early”
... Ratio Gaussian fit: • Convolution turns into multiplication in F.T. space. • F.T. of a Gaussian is a Gaussian. ...
... Ratio Gaussian fit: • Convolution turns into multiplication in F.T. space. • F.T. of a Gaussian is a Gaussian. ...
Astronomy Study Guide
... B. The Outer Planets 1. They are much (smaller, larger) than the earth 2. They are made of _________________ and ______________ 3. ___________ is now classified as a dwarf planet 4. Planets don’t go flying out into space because of _______________ 5. __________ is the most massive planet 6. Neptune ...
... B. The Outer Planets 1. They are much (smaller, larger) than the earth 2. They are made of _________________ and ______________ 3. ___________ is now classified as a dwarf planet 4. Planets don’t go flying out into space because of _______________ 5. __________ is the most massive planet 6. Neptune ...
Cosmology Fact Sheet
... However, if you measure the distance to a certain type of star using parallax and see how bright it is, then you have the beginning of a “standard candle”. If you can recognize this same type of star, only much further away (using chemical composition found by spectral lines, or some other method), ...
... However, if you measure the distance to a certain type of star using parallax and see how bright it is, then you have the beginning of a “standard candle”. If you can recognize this same type of star, only much further away (using chemical composition found by spectral lines, or some other method), ...
Lecture 12: Age, Metalicity, and Observations Abundance
... Star spectra: absorption lines Gas spectra: emission lines Galaxy spectra: both Metal-rich/poor stars: stronger/weaker metal lines relative to H. ...
... Star spectra: absorption lines Gas spectra: emission lines Galaxy spectra: both Metal-rich/poor stars: stronger/weaker metal lines relative to H. ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.